Hepatitis C Management In Primary Care
- A new direct-acting antiviral oral regimen for the treatment of hepatitis C, glecaprevir + pibrentasvir will be subsidised without restriction from 1 February, 2019.
- Treatment with glecaprevir + pibrentasvir is simpler than with Viekira Pak regimens and patients with hepatitis C should now predominantly receive treatment in primary care.
- Glecaprevir + pibrentasvir can be prescribed to patients with hepatitis C virus infection due to any of the HCV genotypes.
- Glecaprevir + pibrentasvir is taken as a once daily regimen of three tablets, for eight weeks, regardless of HCV genotype.
- Glecaprevir + pibrentasvir can be prescribed to patients infected with any HCV genotype, therefore genotype testing prior to initiating treatment is no longer required.
- Ribavirin is not required for patients with genotype 1a infection receiving glecaprevir + pibrentasvir treatment.
- Patients should present prescriptions for glecaprevir + pibrentasvir to an enrolled pharmacy.
- Viekira Pak regimens will be delisted.
- Ledipasvir + sofosbuvir continues to be subsidised for patients with advanced disease.
Our Testimonials
The Need For A Therapeutic Hcv Vaccine
Current gold-standard therapy for HCV infection is weekly subcutaneous injections of pegylated interferon combined with daily oral ribavirin for a period of 24 weeks for genotypes 2 and 3, and 48 weeks for genotypes 1 and 4. Therapy is fraught with significant side effects and leads to a sustained virological response in approximately 40-50% of patients with genotype 1 infection, 65-70% with genotype 3 and 80% of those with genotype 2. PEG-IFN and ribavirin treatment is also expensive and, at an average cost of approximately GB£7000 in the UK for a treatment course, is unaffordable in developing countries .
Two viral protease inhibitors are currently in Phase III clinical trials for HCV and more are in development. These drugs will need concomitant PEG-IFN/ribavirin therapy to avoid the rapid emergence of viral mutants and are currently only effective against genotype 1 infection. It is expected they will increase SVR rates following treatment to 70% . Because these drugs will be used together with PEG-IFN/ribavirin, the cost of treatment will rise further and additional side effects, in particular skin rashes, can be anticipated. The cost of a 3-month course of protease inhibitor in the UK is currently predicted to be GB£18,000-22,000 . Many other direct antiviral therapies are in development but these are unlikely to reach clinical application in the next few years.
What Do Hepatitis B And C Have In Common
Hepatitis is a family of viruses that infect the liver. While hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C can all cause short-term infections, hepatitis B and C can also lead to chronic, long-term infections that severely damage the liver over time. This can cause cirrhosis or scarring of the liver, liver-related cancer, or complete liver failure, especially if you have hepatitis B.
Vaccines exist, but only for hepatitis A and B infections. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Both the hepatitis B and C viruses can lead to mild infections that your immune system can fight off. But, in over half of all cases, the infection doesnt go away, and the virus remains in your body for a much longer period.
You might not experience any symptoms during a chronic hepatitis B or C infection. But because hepatitis is contagious, you may inadvertently transmit it to others. That’s why its very important to get tested if you think that you might have been exposed.
If you’ve had a long-term infection, the effects of hepatitis B or C may not surface until many years sometimes decades later. One of the first effects you might feel involve damage to your liver. Generally speaking, the younger you are at the time of a viral hepatitis infection, the more likely that it’ll become chronic.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
How And When Should You Receive The Hepatitis A Vaccine
You receive the injection of the hepatitis A vaccine in the muscle of your upper arm. Start the vaccine series when you are at risk of infection and at least one month before traveling. You need two doses six to twelve months apart.
There are also combination vaccines for adults that protect against both hepatitis A and hepatitis B. However, these have a different dosing schedule. Ask your doctor for details. You might prefer this option if, for example, you are traveling to countries with high rates of both diseases.
Vbi Vaccines Receives Positive Chmp Opinion For 3
- Following positive CHMP recommendation, final EMA regulatory decision expected in coming months
- European Union brand name to be PreHevbri
- If approved, PreHevbri will be the only approved 3-antigen hepatitis B vaccine for adults in the E.U.
VBI Vaccines Inc. , a biopharmaceutical company driven by immunology in the pursuit of powerful prevention and treatment of disease, today announced that the European Medicines Agencys Committee for Medicinal Products for Human use has adopted a positive opinion for VBIs 3-antigen hepatitis B vaccine, under the brand name PreHevbri . The CHMP recommends PreHevbri for active immunization against infection caused by all known subtypes of the hepatitis B virus in adults.
The positive CHMP opinion for PreHevbri underscores its potential to be a meaningful option for healthcare providers as they help protect their patients against hepatitis B, said Jeff Baxter, VBIs President & CEO. Hepatitis B remains a persistent public health problem in Europe and this milestone is a meaningful advancement in our efforts to be part of the solution.
The CHMPs positive opinion was supported by data from the two pivotal, randomized, double-blind, controlled Phase 3 studies PROTECT and CONSTANT as well as other relevant data.
About Hepatitis B
About PreHevbri
U.S. Indication and Use
U.S. Important Safety Information
Immunocompromised persons, including those on immunosuppressant therapy, may have a diminished immune response to PreHevbrio.
Read Also: Blood Donation Hepatitis B Antibodies
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
Are Alternative Medicines Available
Some people believe certain forms of alternative medicine help cure hepatitis C.
However, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health reports that there are no effective, research-proven forms of alternative treatment or complementary medicine for hepatitis C.
Silymarin, also known as milk thistle, is an herb commonly suggested to help cure hepatitis C liver disease. But a rigorous did not find any beneficial effects from this supplement.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
Who Should Receive Hepatitis B Vaccination
- All newborns before hospital discharge. Infants born to hepatitis B-positive women need hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth.
- All children and adolescents not previously vaccinated.
- Children born in the U.S. to individuals born in a country with high hepatitis B endemicity.
- All individuals at risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Sex partners of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually-transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Persons who inject drugs
- Household contacts of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Persons born in countries where hepatitis B infection is endemic should be tested and vaccinated if susceptible
- International travelers to regions with high or intermediate rates of endemic hepatitis B infection
- Health care and public safety workers that may be exposed to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons, corrections facilities, and other facilities that serve adults at risk for hepatitis B infection
- Persons with end-stage renal disease, including pre-dialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients
- Persons with chronic liver disease
- Persons to age 60 years with diabetes
- Persons with HIV infection
- All other persons seeking protection from hepatitis B infection.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hcv Infection
Hepatitis C can be a “silent but deadly” infection. Most people with HCV have no symptoms. But even without symptoms, they can develop health problems decades later and can still pass the disease to others.
When symptoms do happen , they can be similar to those of hepatitis A and hepatitis B and include:
- jaundice
- fever
- nausea, vomiting, and lack of appetite
- belly pain
- joint pain
Read Also: Hepatitis B Liver Cancer Symptoms
Is There A Hepatitis C Vaccine
Currently, no vaccine protects you against hepatitis C. But research is ongoing. A promising study is currently researching a possible vaccine for both hepatitis C and HIV.
However, there are vaccines for other hepatitis viruses, including hepatitis A and hepatitis B. If you have hepatitis C, your doctor may suggest that you get these vaccines. Thats because hepatitis A or B infection can lead to further complications when treating hepatitis C.
Preventing other forms of hepatitis is especially important if your liver has already been damaged.
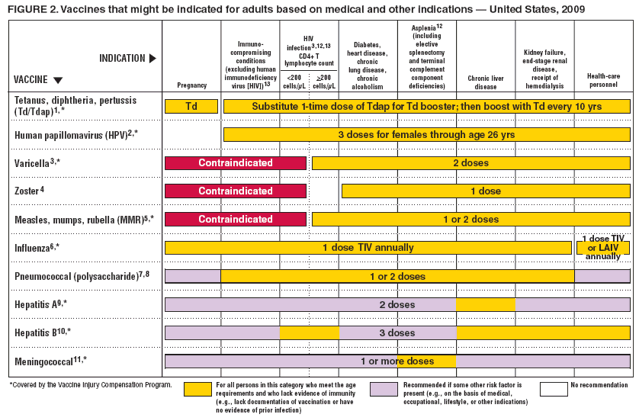
Measles Mumps And Rubella Vaccination
Routine vaccination
- No evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 1 dose
- Evidence of immunity: Born before 1957 , documentation of receipt of MMR vaccine, laboratory evidence of immunity or disease
Special situations
- Pregnancy with no evidence of immunity to rubella: MMR contraindicated during pregnancy after pregnancy , 1 dose
- Nonpregnant women of childbearing age with no evidence of immunity to rubella: 1 dose
- HIV infection with CD4 count 200 cells/mm3 for at least 6 months and no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart MMR contraindicated for HIV infection with CD4 count < 200 cells/mm3
- Severe immunocompromising conditions: MMR contraindicated
- Students in postsecondary educational institutions, international travelers, and household or close, personal contacts of immunocompromised persons with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart if previously did not receive any doses of MMR or 1 dose if previously received 1 dose MMR
- Health care personnel:
- Born in 1957 or later with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart for measles or mumps or at least 1 dose for rubella
- Born before 1957 with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella: Consider 2-dose series at least 4 weeks apart for measles or mumps or 1 dose for rubella
Read Also: Hepatitis C How Is It Transmitted
Haemophilus Influenzae Type B Vaccination
Special situations
- Anatomical or functional asplenia : 1 dose if previously did not receive Hib if elective splenectomy, 1 dose, preferably at least 14 days before splenectomy
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplant : 3-dose series 4 weeks apart starting 612 months after successful transplant, regardless of Hib vaccination history
Routine vaccination
- Not at risk but want protection from hepatitis A: 2-dose series HepA or 3-dose series HepA-HepB
Special situations
- At risk for hepatitis A virus infection: 2-dose series HepA or 3-dose series HepA-HepB as above
- Chronic liver disease
- HIV infection
Routine vaccination
- Not at risk but want protection from hepatitis B: 2- or 3-dose series or 3-dose series HepA-HepB
Special situations
- At risk for hepatitis B virus infection: 2-dose or 3-dose series or 3-dose series HepA-HepB as above
- Chronic liver disease
- HIV infection
- Sexual exposure risk
- Current or recent injection drug use
- Percutaneous or mucosal risk for exposure to blood
- Incarcerated persons
- Travel in countries with high or intermediate endemic hepatitis B
- Pregnancy if at risk for infection or severe outcome from infection during pregnancy. Heplisav-B not currently recommended due to lack of safety data in pregnant women
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
The only way to know if you have ever had hepatitis C is to get a blood test, called a hepatitis C antibody test. This test looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus. If you get infected, antibodies are released into your bloodstream. Antibodies stay in your bloodstream, even if you get rid of the virus.
- A positive or reactive hepatitis C antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some time.
- A positive antibody test does not always mean you still have hepatitis C.
- Another blood test called an RNA test or PCR is needed to determine if you are currently infected with hepatitis C.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C For Good
Hepatitis C And Blood Spills
When cleaning and removing blood spills, use standard infection control precautions at all times:
- Cover any cuts or wounds with a waterproof dressing.
- Wear single-use gloves and use paper towel to mop up blood spills.
- Clean the area with warm water and detergent, then rinse and dry.
- Place used gloves and paper towels into a plastic bag, then seal and dispose of them in a rubbish bin.
- Wash your hands in warm, soapy water then dry them thoroughly.
- Put bloodstained tissues, sanitary towels or dressings in a plastic bag before throwing them away.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The first version of the hepatitis B vaccine was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1981. Since the early 1990s, the World Health Organization has recommended that all countries add the vaccine to their public immunization plans.
Several types of approved hepatitis B vaccines are available, including one suitable for people of all ages, from infants to adults. The Center for Disease Control recommends that everyone under age 19 get the vaccine, with infants receiving the first dose at birth. The agency also recommends that most adults get the vaccine, especially those who:
- have sexual or common household contact with someone with hepatitis B
- have more than one sexual partner
- have experienced sexual abuse
- are likely to be in contact with blood and bodily fluids at work
- have other liver conditions, including hepatitis C
- are being treated for sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV
The most common version of the vaccine requires three separate doses. There’s also a version that the FDA approved for adults that only requires two doses.
You can get the hepatitis B vaccine at the same time as other vaccines. You’ll never catch hepatitis B from the vaccine.
Combination vaccines also exist that protect against both hepatitis A and B. Once you’re vaccinated against hepatitis B, you should be immune for the rest of your life and won’t need a booster.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis C Do To You
Vaccines For People Who Could Become Pregnant
Vaccination is important for everyone of reproductive age, whether planning a pregnancy or not.
During pregnancy, your immune system changes and this can put you at risk for a number of serious infectious diseases and complications. Your baby can also be affected by these infections, which can result in:
- birth defects
- miscarriage
- death
Since an unplanned pregnancy can happen, it’s important to keep your vaccinations up to date at all times. This will help protect you and your baby from certain infections that could cause serious complications. Talk to your health care provider about your vaccination status.
Learn more about vaccination and pregnancy.
Hcv Diversity: Implications For Vaccine Development
Studies based on the molecular evolution of African and Asian HCVs suggest that HCV first appeared over 1000 years ago . Subsequently, HCV evolved in discrete geographical regions giving rise to six distinct genotypes . These genotypes share a genetic homology of approximately 80% and are further subdivided into more than 100 subtypes . In recent decades there has been a global epidemic of a few subtypes associated with intravenous drug use and modern medical practice. The HCV genotype not only has relevance in relation to geographic distribution but more importantly in determining response to current medical therapy .
HCV is a particularly fastidious virus and has only been demonstrated reproducibly to replicate in the hepatocytes of humans and chimpanzees. It is a ssRNA virus with an enveloped virion belonging to the family Flaviviridae . The positive-sense RNA genome is 9600 nucleotides in length. A single HCV polyprotein comprised of 3011 amino acids is translated from the genome and subsequently cleaved by cellular and viral proteases into three structural proteins and seven nonstructural proteins . The envelope proteins mediate viral cell entry by binding to a number of cell surface receptors .
You May Like: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A Vaccine: Canadian Immunization Guide
For health professionals
Last partial chapter update
: The immunoglobulin dosage for Hepatitis A pre-exposure and post-exposure prophylaxis was increased based on the Product Monograph update for GamaSTAN®, which is available on Health Canada’s Drug Product Database.
Last complete chapter revision: March 2018
Hepatitis Vaccine: What You Need To Know
Hepatitis is an inflammatory liver condition. There are five types of viral hepatitis: A, B, C,D, and E. Most cases are caused by a hepatitis virus. The condition can also be a result of excessive alcohol or drug use or a faulty inflammatory immune response that occurs when the immune system mistakes the liver as a threat to the body and begins to attack it.
There are two hepatitis vaccines that can help prevent hepatitis A and B infections. A third vaccine, developed for hepatitis E, is only permitted for use in China. This article discusses the types of hepatitis that can be prevented with a vaccine and what you need to know before getting one.
Read Also: Causes Of Hepatitis C Virus
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.