What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus . Infections of hepatitis C occur when the virus is able to enter the blood stream and reach the liver.
There are other kinds of viral hepatitis such as hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis D, and hepatitis E. These diseases and the viruses that cause them are not related to hepatitis C even though they also affect the liver. They may have other, different symptoms and different modes of transmission, which means that there are different ways of spreading the disease and different means for preventing and controlling these diseases.
If I Get Tested For Hepatitis C And The Result Is Positive Do I Need Any Other Tests To Be Sure
When your provider wants to test you for hepatitis C, the first test you will have is the hepatitis C antibody . If this test is positive, it means you were infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in the past. But this test alone is not enough. You will still need another test to confirm if you still have the hepatitis C virus in your system. About 1 out of 5 people who get infected with hepatitis C will be able get the rid of the virus on their own, without treatment, very early after their infection. So some people will have a positive antibody test, but a negative HCV RNA .
So, the second test that your provider should request is called hepatitis C virus RNA or HCV RNA test. There are several different tests available to check the HCV RNA. What matters is that if the RNA test is positive, then you do have chronic hepatitis C virus infection. If the RNA test is negative, then you may need to have this test again to be sure. If these RNA tests are all negative, then you no longer have hepatitis C infection and do not have chronic hepatitis C.
If your hepatitis C antibody test is positive, be sure that you get tested for hepatitis C RNA to find out whether the infection has become chronic or whether it has cleared. If the infection has become chronic, there are treatments your provider can prescribe to fight off the hepatitis C virus and keep your liver healthy.
Its Different Than Hepatitis A And B
Each form of hepatitis has its own specific virus that spreads and is treated differently. Hepatitis simply means inflammation of the liver, or that the virus has an affinity for hurting the liver, Reau says.
- Hepatitis A is an acute, short-term infection that often does not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B hides deep in the body and, like hepatitis C, is treated in a variety of ways, from antiviral medications to liver transplants.
The viruses are different, but all of them should be taken very seriously since they can lead to significant liver disease and even death, she adds.
Read Also: Herbal Cure For Hepatitis B
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Where Can You Get More Information
Your doctor, nurse, or health care clinic listed in the telephone directory can provide you with more information.
Persons who inject drugs can substantially reduce their risk of getting and transmitting HIV, viral hepatitis and other blood borne infections by using a sterile needle and syringe for every injection. The Massachusetts Department of Public Health supports programs where persons who inject drugs can access sterile needles and syringes through syringe services programs . Through these programs you can get sterile needles and syringes free of cost, dispose of used needles and syringes, and get connected to other services such as testing for hepatitis C, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, overdose education, and narcan . To find an MDPH-supported SSP program near you, please click here.
Hepatitis C and Related Resources in Massachusetts This provides information about MDPH-supported programs including testing for hepatitis C, linkage to treatment for individuals with hepatitis C infection, and other resources such as overdose prevention programs.
Additional information about substance use disorder treatment programs may be obtained from the MDPH.
Viral Hepatitis Information from the CDC. The CDC provides resources on a variety of topics, including general information regarding transmission and prevention, statistics about HCV, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C.
You May Like: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
If You Notice Symptoms See A Doctor Right Away
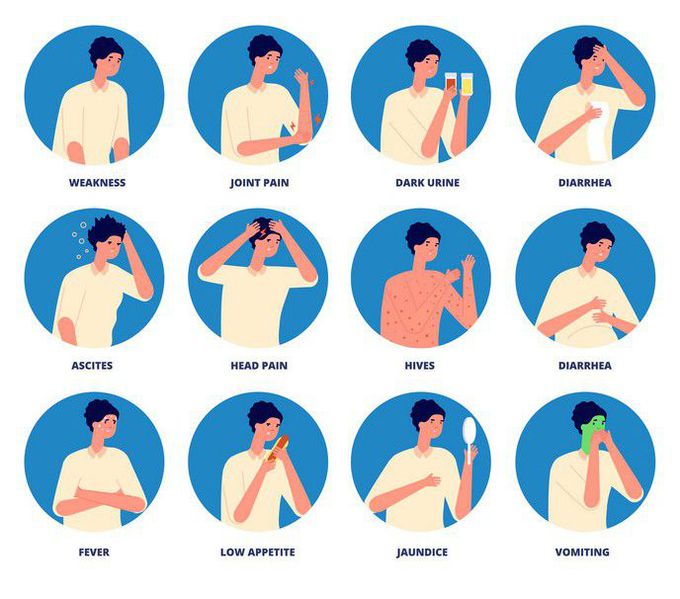
Symptoms of hepatitis C include the following:
- Jaundice a yellowish tone to the eyes and skin
- Mild, chronic right belly pain
- Loss of appetite
If you believe you have been exposed to hepatitis C or notice any symptoms, visit your primary care doctor as soon as possible. If you test positive for the virus, your doctor can refer you to a hepatologist to discuss your options.
“I strongly encourage all baby boomers and others who are at high risk to get tested, even if you don’t look or feel sick,” Reau says. “If you do have hepatitis C, the earlier we discover it, the more likely we can prevent it from progressing and causing more serious damage.”
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Adults
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Talk to your doctor about getting tested for Hepatitis C if you:
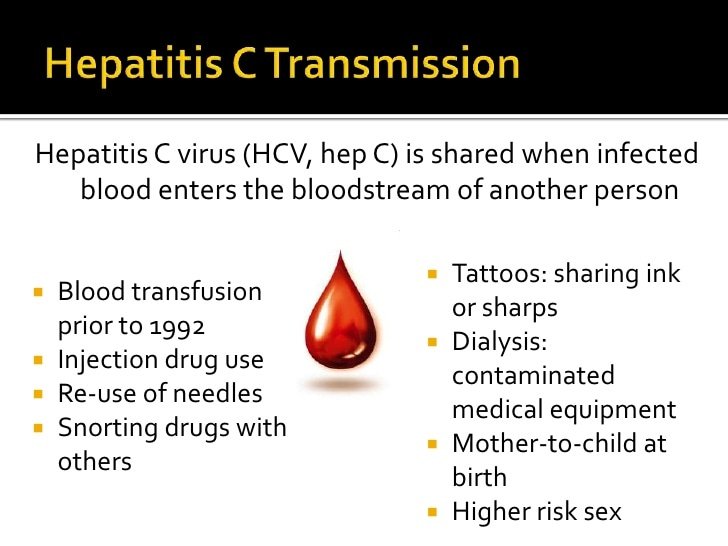
- Are a current or former drug user who used needles to inject, even if you only did this one time or did it many years ago
- Have a sex partner who has chronic Hepatitis C or have had many sex partners
- Had your blood filtered by a machine for a long period of time because your kidneys werent working
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant from a donor before July 1992
- Received a blood clotting factor to treat a bleeding disorder before 1987
- Are a healthcare worker and were exposed to blood through a needle stick or had other contact with blood or bodily fluids
- Have evidence of liver disease, such as abnormal liver tests
- Were born between 1945 and 1965. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a one-time screening for all baby boomers.
Learn more, use the Centers for Disease Controls Hepatitis Risk Assessment tool.
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
- All people born between 1945 and 1965
- Anyone who has ever injected drugs, even if once or many years ago
- People with HIV infection
- People who had a blood transfusion organ transplantation before 1992
- People who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or other injury
- People receiving hemodialysis
- People who have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv
Rashes Associated With Chronic Hcv
Many skin conditions are associated with chronic hepatitis C, some common and others uncommon. They include pruritus , a common condition affecting up to 40% of those with chronic HCV infection.
Four skin conditions directly linked to HCV can cause rashes during the chronic stage of infection:
- Lichen planus: This is an inflammatory condition caused by an abnormal immune response that affects the skin and mucous membranes. Symptoms include flat, purplish, itchy bumps on the skin, swollen gums, and painful erosive patches on the tongue.
- Mixed cryoglobulinemia: This is an inflammatory condition caused by an abnormal immune response that affects blood vessels. Symptoms include a raised, purplish skin rash , typically on the lower legs. Itchiness is also common.
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: This is a rare condition that causespainful lesions on sun-exposed areas of skin. Hyperpigmentation , hypopigmentation , and waxy, hardened skin plaques can also occur.
- Necrolytic acral erythema: This is another rare condition that starts with an outbreak of blistering rash that soon evolves into darkened areas of hardened, cracked skin. The feet are most commonly affected.
These skin conditions can occur for reasons other than hepatitis C. Even so, HCV testing is recommended due to their strong association with HCV.
Prurigo nodularis, a chronic itchy skin condition with a symmetrical rash, is also more common in people with hepatitis C.
How Long Does Hepatitis C Appear Symptom
Patients with hepatitis C virus infection will have recurrent urticaria skin symptoms, which means that the virus in vivo, human replication, disease instability, or HCV infection.
If the anti HCV antibody is positive, the skin symptoms of patients infected with HCV are pruritus, which means that the disease is stubborn and the treatment is difficult.
The skin symptoms of patients infected with hepatitis C virus were flat polygon papules, dark red or purplish red, glossy surface, or large papules scattered on the tip of the needle, linear or reticular arrangement, most likely lichen planus. About 37% of hepatitis C patients were in the unstable stage, and the improvement of hepatitis C subsided, and the aggravation of hepatitis C worsened.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Symptoms
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
If you are at risk of hepatitis C infection, or think you may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the past, see your doctor for an assessment of your liver health. This will include blood tests and possibly a non-invasive test for liver damage .
There are 2 blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. Usually these can be done at the same time but sometimes they will be done separately.
The first test known as a hepatitis C antibody test can tell you whether you have ever been exposed to hepatitis C.
It may take 2 to 3 months from the time of infection until a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis C, so there is a window period during which you cannot tell if you are or have been infected. In this time, take precautions to prevent the potential spread of the virus.
The second test is called hepatitis C PCR, which will be done if the antibody test is positive. This determines if the virus is still present in your blood or liver or if you have already cleared the infection.
If you have cleared the virus or had successful treatment to cure it, the PCR test will be negative.
A liver ultrasound or Fibroscan can also be performed to assess if you have any liver damage.
If your doctor is inexperienced in diagnosing hepatitis C you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Testing For Hepatitis C
To diagnose a hepatitis C infection, doctors use a hepatitis C antibody test, which is a blood test. The test must have the approval of the Food and Drug Administration .
The hepatitis C antibody can show if a persons body has made any antibodies to HCV. If they have, this indicates that they have had the infection at some point in their lives.
Some people have the infection at some time, but their immune system eliminates the virus after a few months. In others, the body is unable to fight off the virus, leading to chronic hepatitis C infection. Many people will not experience any symptoms until the disease has progressed significantly.
A non-reactive or negative test result will generally indicate that a person does not have HCV. However, if the person has the test during the window period, they could receive inaccurate results.
If the person knows when exposure occurred, a doctor may recommend waiting a few weeks before repeating the test.
A reactive or positive result tells a doctor that the person has had an HCV infection at some point in their lives. The result indicates that their body has created antibodies to fight the virus.
However, this does not mean that a person still has active HCV. Even if their immune system has eliminated the virus, they will still have the antibodies.
Read Also: How To Tell If You Have Hepatitis C
The Acute Phase Of Hepatitis C
The term Acute Phase can be confusing. This is because it only refers to the 6 month period of time after the virus has first entered your body. It bears no relation to the acuteness of the symptoms or the severity of the disease.Antibodies to the virus are produced by your immune system when it reacts to the presence of the virus and are detectable in the blood from between 3 to 12 weeks after initial infection. Depending on how long it takes for the virus to take hold in the body, different immune systems will take different amounts of time to create antibodies. This is called the window period. Because it can take up to 3 months for the antibodies to show up in a blood test, if you suspect you have recently been infected, it is important to wait this long before having a test. If the antibody test is positive you will be offered a PCR or RNA test.
Symptoms during the Acute Phase
During the acute phase most people do not seem to experience any noticeable symptoms. For the 25-35% of people who do, the symptoms are normally vague and non-specific. They can include low-grade fever, fatigue, appetite loss, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. About 20% of the people who develop symptoms contract jaundice. This can be seen in the yellowing of the skin and eyes. This is a sign of the livers functions being affected as bilirubin begins to build up in the body. Jaundice is a recognised sign of liver problems and may lead to a test for hepatitis C being suggested.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive Espaol
But Even If You’ve Been Cured It Can Have Lifelong Health Implications
“Hepatitis C is a lot more than just a liver disease,” Reau says. “It has been associated with many medical conditions, such as an increased risk of developing diabetes, kidney disease and cancer.”
While curing hepatitis C significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, like liver failure, liver cancer and the need for transplantation, it doesn’t completely eliminate the health risks associated with the disease.
“Hep C is linked to scarring of the liver or cirrhosis and the more scar tissue that develops, the greater the likelihood of complications,” Reau says. “If there is a lot of scarring, you will need lifelong monitoring.”
Reau also recommends leading a healthy lifestyle to help prevent re-infection and further liver damage: Limit alcohol consumption, control your weight, avoid high-risk activities and manage diabetes if you have it.
Gay Men Chemsex And Hep C
Group sex and chemsex parties provide the perfect storm for hepatitis C transmission.
The iBase guide Safer HCV sex for gay men is a useful reminder of what to avoid and what steps to take to protect yourself.
The Hepatitis C Trust has some useful information about transmission. They also provide an advocacy service for men who have sex with men who have been re-infected with hepatitis C after previously being successfully treated.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Virus Is Spread Through The Contact Of
Who Is At Risk
Your risk of infection with HCV is increased if you:
- Had tattoos or body piercings in an unclean environment using unsterile equipment
- Worked in a place where you came in contact with infected blood or needles, for example, healthcare workers
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Received a blood product for clotting problems made before 1987
- Needed to have your blood filtered by a machine for a long period of time because your kidneys werent working
- Were born to a mother with HCV
- Had unprotected sex with multiple partners
- Have or had a sexually transmitted disease
Why Should I Get Treated
Hepatitis C can be fatal when left untreated.
Untreated hepatitis C can lead to scarring of the liver known as cirrhosis.
A small number of people with cirrhosis will go on to get liver failure, the only treatment for which is a liver transplant. A small proportion of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer.
Read Also: How Long Is Hepatitis B Treatment
Once You Receive A Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C You Can Begin Treatment But Many People Dont Have Symptoms Of Infection Making Diagnosis Difficult Here Are The Signs To Look For
Sarah Bradley is a freelancer writer from Connecticut, where she lives with her husband and three sons. Her reported features and personal essays on parenting and womens health have appeared at On Parenting from The Washington Post, Real Simple, Womens Health, Parents, and O the Oprah Magazine, among others. She is a regular parenting content contributor at Verywell Family and Healthline Parenthood. In her so-called free time, Sarah is an amateur baker, homeschooler, and aspiring novelist.
Hepatitis C, a viral infection spread through blood, causes inflammation in the liver and, in some cases, serious liver disease, per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .¹ About 2.4 million people in the U.S. are infected with hepatitis C, the CDC notes, athough the true number is likely higher.
Unlike many other viral infections, hepatitis C can occur without symptoms, with around 50 percent of infected people being unaware that they have the virus.¹
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases , hepatitis C is the most common blood-borne virus in the U.S., and its infection rate has been rising steadily since 2006.² When you combine the widespread nature of hepatitis C with the seriousness of the illness, it becomes even more important to recognize any potential signs and symptoms of infection.