What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A Virus
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
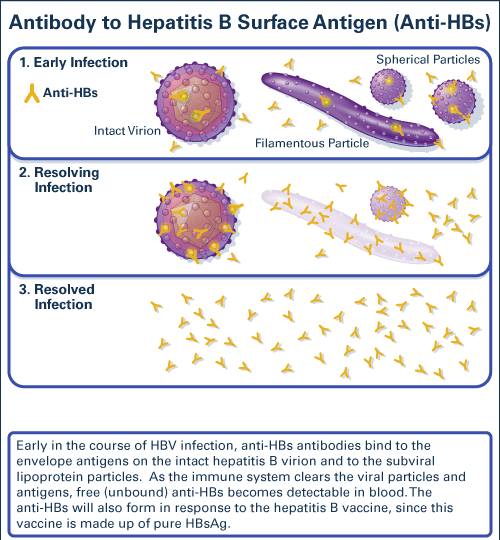
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Also Check: Early Signs Of Hepatitis B
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune â talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCPâs advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
Read Also: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C
Kinetics And Risk Of De Novo Hepatitis B Infection In Hbsagnegative Patients Undergoing Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
- CheeKin HuiCorrespondenceAddress requests for reprints to: CheeKin Hui, MD, University of Hong Kong, Queen Mary Hospital, Department of Medicine, 102 Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong SAR, China. fax: 2281 84030.Centre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- HaiYing ZhangAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- YuiHung YuengAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- John M. LukAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaDepartment of Surgery, Queen Mary Hospital, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
- George K.K. LauAffiliationsCentre For The Study of Liver Diseases, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaResearch Centre For Infection and Immunity, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Background & Aims:Methods:Results:
Abbreviations used in this paper:
Lancet.J Hepatol.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Ab
Membranous Nephropathy And Hepatitis B
Children with HBV-related MN show positivity of HbsAg and usually hepatitis B surface antibody is not detected. The hepatitis B early antigen can be detected in serum of 90% of patients.27 Hypocomplementemia is observed at the onset of disease , but titers of C3, C4 return to normal in the later part of disease.27 Circulatory immune complexes are detected in 80% of patients. Serum levels of transaminases may be raised on presentation.20,24 Liver biopsy shows evidence of chronic persistent hepatitis mainly in children, but chronic active hepatitis is seen in adults.
David O. Freedman, … Elaine C. Jong, in, 2008
High Titers Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus
Sung-Nan Pei, Ming-Chung Wang, Ming-Chung Ma, Ching-Yuan Kuo, Chien-Hung Chen, Po-Nan Wang High Titers of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatitis in Lymphoma Patients Treated with Rituximab-Based Chemotherapy. Blood 2015 126 : 3869. doi:
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Sexually
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Hepatitis C Medications
What Tests Will You Have To Do
Hepatitis B
You can be tested for hepatitis B at your VA medical center. This test is done by taking a sample of your blood.
Your provider may recommend the following tests:
Hepatitis B surface antibody If this test is positive, it means that:
- you have antibodies against hepatitis B and are safe from getting the disease
- you were either vaccinated against hepatitis B or exposed to it at some point in your lifetime
Hepatitis B core antibody If the test is positive, it means that:
- you have been exposed to hepatitis B and have developed an antibody to only part of the virus
- they will do more tests to find out if you currently have the disease
Hepatitis B surface antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you currently have hepatitis B infection
- you can spread the virus to others
Hepatitis B e antigen If the test is positive, it means that:
- you may have active hepatitis B and should be followed closely by your provider and possibly take hepatitis B medications
- you may be very contagious to others
Dont Miss: What Are The Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
Whats The Hepatitis B Titer Test Used For
A hepatitis B titer test measures antibodies in your blood to see if youre immune either due to vaccination or previous infection.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that targets your liver. It can be transmitted by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person. A person with the virus can also infect their child during birth.
Hepatitis B can develop into a chronic infection. Chronic infection occurs when your body cant fight off the virus within six months. Chronic hepatitis B infections most commonly develop less than six years old, especially in infants.
Hepatitis B titer tests can be used to evaluate:
- whether a high-risk person is immune to hepatitis B
- whether hepatitis B immunoglobulin is needed after a needle prick
- men who have sex with men
- people born in countries with a hepatitis B prevalence greater than 2 percent
- people born in the United States not vaccinated as children and with parents born in regions with more than 8 percent hepatitis B prevalence
You may need your titer test results as proof of hepatitis B immunity in order to get into healthcare programs at many schools for example, the nursing program at Lone Star College. In the United States, employers are not allowed to withdraw a job offer if they learn you have hepatitis B.
You May Like: Different Types Of Hepatitis Chart
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis Transmitted Sexually
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
Read Also: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Blood Test Results
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C An Std
Why Is This Analysis Important
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus that can lead to an acute or chronic liver infection that can severely damage the liver. It is transmitted by contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. Vaccination against hepatitis B is recommended for adults and children that are at high risk of infection which may be due to occupational exposure, or travel to certain areas of the world.
Read Also: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Last
Measures Of Immune Response And Duration Of Immunity/protection
In high-risk individuals who have had titers checked after primary HB immunization, a small percentage of apparently healthy recipients do not mount a detectable response to the vaccine. This failure to respond is related to factors such as age , male gender, smoking, obesity, HIV infection, or chronic disease. Persons > 40 years of age have an immune response < 90%, whereas only 65%75% of persons > 65 years of age develop protective anti-HBs antibody levels.29 For persons with these risk factors and who are at high risk of HB exposure, a postvaccination serology 16 months after the last dose should be done. Patients without detectable anti-HBs titers after primary series should begin a standard three-dose series and have serology 1 month after each dose for up to three doses until they seroconvert, or may wait until the three additional doses are administered before being tested. A similar approach can be taken for health care providers who have received a complete HB series but have undetectable anti-HBsAg titers.
Kyong-Mi Chang, in, 2012
Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
Recommended Reading: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?