Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Ethical Approval And Informed Consent
The China Kadoorie Biobank complies with all the required ethical standards for medical research on human subjects. Ethical approvals were granted and have been maintained by the relevant institutional ethical research committees in the UK and China: UK Kadoorie Study of Chronic disease in China – Baseline, Oxford Tropical Research Ethics Committee OxTREC Ref: 25-04 China Kadoorie Study of Chronic disease in China Baseline, Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Ethical Review Committee Approval Notice 005/2004. Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis A
Blood Test Panel To Diagnose Hepatitis B:
The only way to tell someones hepatitis B status is through a panel of blood tests the tests are all done at one time, and only one small tube of blood is needed. These tests are not included in routine testing, so it is important to ask your doctor to test you for hepatitis B or try to find a free screening event near you . The panel consists of the following tests to determine your hepatitis B status:
To learn more about interpreting your test results, click here.
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
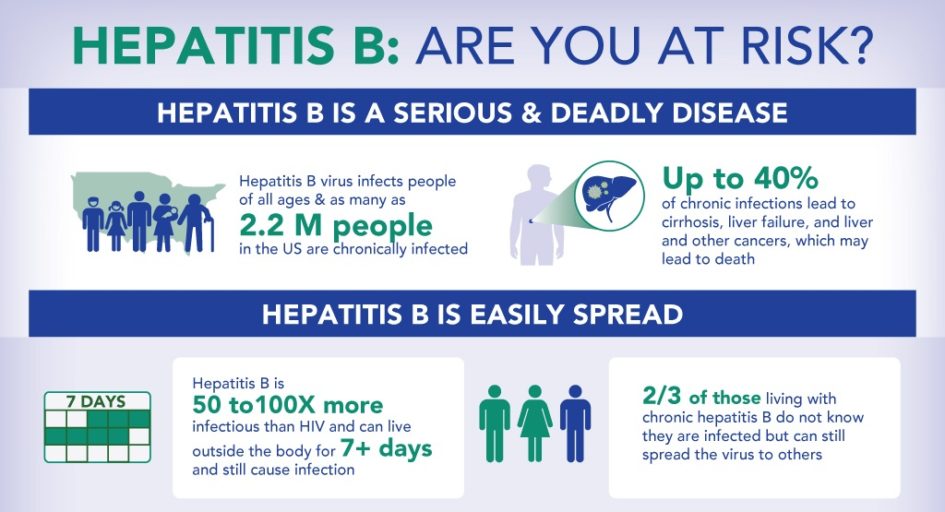
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Vaccine San Diego Free
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
Acute Hepatitis B Symptoms
There are three phases of acute hepatitis B infection, and symptoms may differ depending on the stage. Early in the disease, called the prodromal phase, symptoms may include:
- Dark urine and light stool color
During the icteric phase:
- Anorexia, nausea and vomiting may worsen
- Irritated skin lesions may develop
- Other symptoms may subside
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis B Curable Or Treatable
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Getting the hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually administered in two, three, or four doses. In many countries, infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth and finish all doses at 6 to 18 months old.
The CDC also recommends all children under the age of 19 years old be vaccinated if they havent already received the vaccination.
Adults can also get the hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine is generally recommended if you have an increased risk of contracting the virus. Some of these risk factors include:
- traveling to or living in a region where hepatitis B is common
- being sexually active with more than one partner or with a partner who has hepatitis B
- working in a medical setting or other workplaces where youre exposed to bodily fluids
- using intravenous drugs and sharing drug equipment
- having chronic liver disease, a human immunodeficiency virus infection, a hepatitis C infection, diabetes, or kidney disease on dialysis
If youve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and havent been vaccinated, try to see a doctor right away. They can administer the first dose of the vaccine, though youll need to follow up to receive the remaining doses over the next few months.
They may also prescribe a medication called
Important Things To Know About Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Someone who has markers of past infection, particularly hepatitis B core antibody, can be at risk for hepatitis B reactivation. Reactivation can be triggered by immunosuppressive therapies and cause significant life-threatening challenges. If you test HBcAb+, please talk to your doctor about what that means, and make sure you notify all future health care providers.
Also Check: Most Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Serum Viral Load And Hbeag Status
Because sera from the patients with AHB did not suffice for all assays, serum viral load from only one-third of the samples was tested by quantitative PCR. The viral loads varied dramatically. Constant serum viral load was determined in 107 of the 113 ASCs. Serum viral load log10 copies/ml) in ASCs with HBV B2 was significantly higher than the viral load log10 copies/ml) in ASCs with HBV C2 .
In the 68 AHB patients with HBV genotyped, no difference in seropositivity of HBeAg was determined between the patients with HBV B2 and those with HBV C2 . In the 25 patients who progressed to chronic infection, seropositivity of HBeAg was 45% and 80% in those with HBV C2 and HBV B2, respectively. No statistical differences in seropositivities of HBeAg were determined between AHB patients and those who progressed to chronic infection, neither in those with HBV B2 nor in those with HBV C2. However, seropositivity of HBeAg in the neighbourhood ASC with HBV B2 was significantly higher than that in those with HBV C2 .
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Do You Catch It
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Strengths Of The Study

This study was the first of its kind to be done within western Kenya covering a range of high-risk populations. Female sex workers, MSM and substance users have not been previously screened for HBV infection in Kenya. Overall, many persons were screened for Hepatitis B although some groups were smaller than others depending on the available numbers from these groups. The persons selected into the risk group were all screened, this represented 100% of all persons presenting to primary care or otherwise. This project was important in showing feasibility of screening.
You May Like: How To Cure Hepatitis C At Home
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis and other drug use.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
From an infected pregnant person to their newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna
How The Hepatitis B Virus Works
In the case of the hepatitis B virus, the host is the liver cell. As the virus makes more copies of itself, the liver may become damaged, and sometimes it is unable to carry out its essential tasks to regulate metabolism, nutrients, and digestion. It is best to prevent hepatitis B infections when we can and since antibodies are the best defense against the virus, the hepatitis B vaccine can be used to signals the body to make antibodies to fight the virus. The hepatitis B vaccine provides lifelong protection from the virus. However, this is only possible before infection with the virus. If somebody is already infected with the virus, antiviral therapy is used to control the virus and prevent liver damage antiviral medications disrupt the life cycle of the virus by disabling viral receptors from binding to liver cells.
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
Don’t Miss: What Are The Causes Of Hepatitis D
Hepatitis B Prevention And Vaccination
Hepatitis B infection is vaccine-preventable. An effective and safe vaccine is used to protect children and adults from the disease. In addition, the implementation of safe injection procedures, blood safety strategies and safer sex practices can protect against HBV transmission. There are simple and effective ways to prevent the spread of Hepatitis B:
- Practice safe sex using protective measures
- Avoid direct contact with bodily fluids and blood
- Wash your hands carefully after any potential exposure
- Clean up blood spills with a disinfecting solution
- Avoid sharing sharp personal items such as nail clippers, razors or toothbrushes
- Cover all wounds and cuts carefully
- Avoid street drugs
- Make sure sterile needles are used for tattoos, piercing, and acupuncture
- Moreover, all blood and blood components used for blood transfusions should undergo quality-assured screening to reduce the chance of getting HBV.
Hepatitis B virus vaccine
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B Sexually Transmitted
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of The Hepatitis
Causes And Risk Factors
Hepatitis B is caused by a viral infection. The virus can survive outside of the body for at least seven days. During this time, it can infect a person if it enters his or her body. It can be detected within 30 to 60 days after infection. It can persist and develop into chronic hepatitis B, especially if someone is infected at a young age.
It can be transmitted or spread in several ways, including :
Anyone can get this virus. But some people are at a greater risk of exposure to the virus. This includes people who:
- Have multiple sexual partners
- Travel to countries with a high hepatitis B rate