How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will look at your health history and give you a physical exam.
Some lab blood tests used to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis include:
- Liver function tests. These check for inflammation or damage to your liver.
- Complete blood count or CBC. Looks at the number and types of cells in your blood.
- Coagulation panel. This test looks at how well the clotting proteins are working.
- Electrolyte panel. Checks to see if you have an electrolyte imbalance.
- Autoimmune antibodies. These are used to see if you have autoimmune hepatitis or another liver disease with similar symptoms.
- Other liver tests. These are done to check for other possible types of liver disease.
You may also have imaging tests such as:
What Drugs Can Trigger Autoimmune Hepatitis
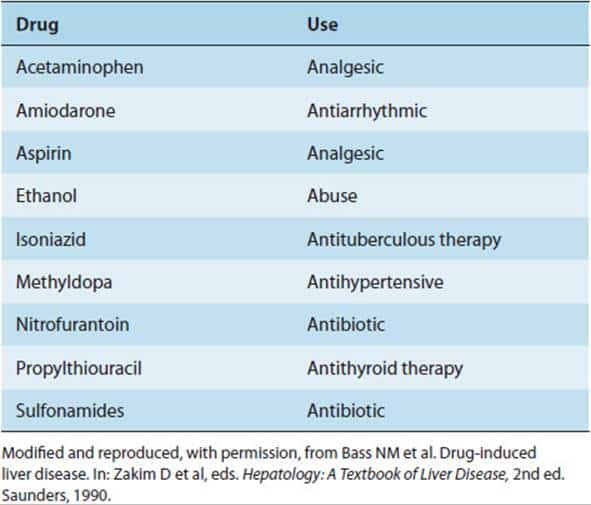
The root cause of autoimmune hepatitis is undetermined but it is a condition that can be triggered in high risk patients by certain external factors like herbs, viruses, or prescription medications. Drug-induced autoimmune liver disease is a variant of Autoimmune Hepatitis which has not been defined in detail in the literatures. A percentage of patients with drug induced autoimmune hepatitis can have symptoms quite similar to that of autoimmune hepatitis. There are many medications which have been known to cause autoimmune hepatitis even after stopping the medication which indicates that such medications activate dormant autoimmunity.
Autoimmune Hepatitis With Jama Darling Md
This is Episode Six of Autoimmune Disease: Pieces of the Picture. Dr. Jama Darling talks about autoimmune hepatitis, the importance of liver biopsy, how it is different from other types of hepatitis, and treatments of the disease. Dr. Darling is an Assistant Professor of Medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
When we have diagnosed a patient with autoimmune hepatitis, one of the most common questions I get is, Ive never done drugs or had a blood transfusion. I dont drink alcoholwhy on earth do I have hepatitis?I explain to the patient that they dont have a virus, they dont have a blood-blood transmission virus like hepatitis C, it isnt due to a behavior such as excess alcohol intake.. Their immune system is recognizing something in the liver as unwanted and trying to get rid of it, and this is of no fault of their own.
Jama Darling, MD
Ron Falk, MD: Hello, and welcome to the Chairs Corner from the Department of Medicine at the University of North Carolina.
Welcome to our series where we are exploring topics related to autoimmune diseases, to help patients and their loved ones understand and manage their condition. Today were going to focus on autoimmune hepatitis. We welcome Dr. Jama Darling who is an Assistant Professor of Medicine in our Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Dr. Darling specializes in the treatment of hepatitis and other chronic liver diseases. Welcome, Jama.
Jama Darling, MD: Thank you.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B Virus
Risk Factors For Drug
The risk factors for drug-induced autoimmune-like hepatitis are unpredictable. The factors that may affect drug-taking behavior as well as host-specific genetic and metabolic disturbances may affect drug handling. Socio-economic, psychological, and cultural issues can influence the type, frequency, and duration of treatment, and certain diseases with propensities for a particular gender or age group may skew the perception of risk. The major risk factors implicated in idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury are old age, gender, dose, drug interactions, cross-sensitization, genetic factors, and hepatic metabolism of the compound.
Types Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Doctors have identified two main forms of autoimmune hepatitis.
- Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. This is the most common type of the disease. It can occur at any age. About half the people with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis have other autoimmune disorders, such as celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis or ulcerative colitis.
- Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis. Although adults can develop type 2 autoimmune hepatitis, it’s most common in children and young people. Other autoimmune diseases may accompany this type of autoimmune hepatitis.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted Through Saliva
Alf And Acute On Chronic Liver Failure
AS-AIH with encephalopathy is defined as ALF caused by AIH . With regard to noninvasive diagnoses, heterogenous hypo-attenuated regions within the liver as visualized by unenhanced computed tomography is useful to differentiate patients with AS/ALF-AIH from those with viral-associated ALF . The volumetric measurement of the liver on CT is also valuable, because the size of the liver was reported to be significantly reduced in non-acetaminophen cases of acute liver injury/ALF compared to the acetaminophen-induced cases . A direct evaluation of indications for LT is recommended in ALF-AIH, because glucocorticoid therapy has not been associated with improved overall survival and is even harmful to patients with a model for end-stage liver disease score > 40 .
Noninvasive Assessment Of Fibrosis
The long-term outcome of AIH is associated with the stage of fibrosis. Since the evaluation of liver fibrosis by biopsy during the course of disease management is not feasible, noninvasive assessments have been conducted in clinical hepatology by using serum biomarkers, including the serum AST/platelet ratio index and the fibrosis-4 index . However, a recent systemic review of the diagnostic accuracy of APRI and FIB-4 demonstrated their poor performance for detecting advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in AIH .
Noninvasive assessment by liver stiffness has been shown to identify advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in AIH with reasonable accuracy. The performance levels of vibration-controlled transient elastography and magnetic resonance elastography were indicated to be superior to those of the APRI and FIB-4, and VCTE was validated in a systemic review as providing good performance . Considering that liver inflammation affects liver stiffness, the stiffness value at the initial diagnosis before the initiation of treatment with immunosuppressive agents is confounded by disease activity. In fact, the value of VCTE within 3 months after the start of treatment was significantly correlated with histological grading, but not with the fibrosis stage . Thereafter, at least 6 months after the successful treatment of AIH, the area under the receiver operating curve of VCTE reached 1.0 . Sustaining biochemical remission and the use of VCTE help monitor and manage the disease course of AIH.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Open Access License / Drug Dosage / Disclaimer
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License . Usage and distribution for commercial purposes requires written permission. Drug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug. Disclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor. The appearance of advertisements or/and product references in the publication is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval of the products or services advertised or of their effectiveness, quality or safety. The publisher and the editor disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements.
The Impact Of Immunosuppressant Therapy On Prognosis
Prior to the 1970s, most individuals diagnosed with autoimmune hepatitis died from their disease. Multiple studies in the early 1970s demonstrated the positive impact of corticosteroid therapy on disease outcomes. Sherlock and colleagues looked at the long-term impact of prednisolone therapy on survival and found that 63% of treated patients were alive at 10 years compared with only 27% of untreated patients in the control group . The median survival in the treatment group was 12.2 years versus 3.3 years in the control group.
More recent literature described markedly improved outcomes with immunosuppressive treatment. Czaja and colleagues reported a 90% transplant-free survival at 10 years for patients without cirrhosis at presentation and 89% for patients with cirrhosis at presentation. These survival rates were similar to those of the general population.
Studies utilizing serial liver biopsies have demonstrated how successful immunosuppressive therapy can improve both liver inflammation and fibrosis, potentially preventing the development of cirrhosis.
Read Also: What Is The Medication For Hepatitis C
Exacerbation Recrudescence And Relapse
During the course of maintenance therapy with corticosteroids/AZA, a substantial number of AIH patients spontaneously and asymptomatically experience biochemical exacerbation or recrudescence, i.e., an elevation of ALT coupled with or without an increase in IgG. The 2019 AASLD practice guidance and guidelines strictly define relapse as disease exacerbation that occurs after remission and drug withdrawal or by nonadherence . Multiple relapses have been shown to be associated with worse outcomes , but the definitions of relapse in the literature differ from that issued by the AASLD, including the concept that biochemical remission may not have proceeded relapse. Following the AASLD rules regarding biochemical remission-induction with first-line or even second-line drugs could result in fewer exacerbations. Relapse after drug withdrawal and exacerbation should be managed appropriately to induce re- remission with an increase in dosage or the reinstitution of immunosuppressive agents, or with the add-on of second-line drugs. In a case-control study, psychological stress was associated with relapse after drug taper-off or recrudescence .
Also Check: Pcr Quantitative Test For Hepatitis C
Association With Other Autoimmune Diseases Or Induction By Biologic Agents
Biologic agents: Biologic agents are increasingly being used for rheumatological and systemic autoimmune diseases. The BIOGEAS project, created by the Spanish Society of Internal medicine, has retrieved more than 800 cases of AI diseases secondary to biological therapies. In this study, 19 cases of AIH have been reported. Statins have been reported to induce AI diseases, typically in patients with other AI diseases.
Spontaneously: AI diseases frequently appeared to be associated between them. Multiple examples are published in the literature.
You May Like: How Do You Get Infected By Hepatitis C
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
The liver is a large organ that sits up under your ribs on the right side of your belly . It helps filter waste from your body, makes bile to help digest food, and stores sugar that your body uses for energy. Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when your bodys infection-fighting system attacks your liver cells. This causes swelling, inflammation and liver damage.
It is a long-term or chronic inflammatory liver disease.
Autoimmune hepatitis:
- May occur at any age
- Affects women more than men
- Is often linked to other diseases where the body attacks itself
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated

Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Flexure Polyp
Key Points About Drug
- Drug-induced hepatitis is a redness and swelling of the liver.
- It is a rare condition caused by harmful amounts of certain medicines, vitamins, herbal remedies, or food supplements.
- In most cases, you may be taking a medicine for several months before it reaches a toxic level and affects your liver.
- You may also get the condition if you take too much of some medicines, such as acetaminophen. This can happen quickly.
- You must stop taking the medicine that is causing the disease.
Three Clinical Settings Of Drug
Based on the drug-induced autoimmune liver disease, three clinical settings have been put forward
- Autoimmune hepatitis with drug-induced liver injury,
- drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis, and
- Immune-mediated drug-induced liver injury.
In addition, there are occurrences of mixed features like drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis and immune-mediated drug-induced liver injury. Sometimes positive autoantibodies are seen in drug-induced liver injury cases.
Read Also: How Do You Get Infected With Hepatitis B
When The Liver Is Under Attack
In people with autoimmune hepatitis, immune cells inappropriately mistake the liverâs normal cells as abnormal and attack them. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, scarring , impaired liver function, and even cirrhosis , which can result in liver failure, and death if not treated. Some people may eventually need a liver transplant. The liver disease specialists at NewYork-Presbyterians Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation are experienced in diagnosing and treating autoimmune hepatitis.
Fda Clears Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment Zetomipzomib As Investigational New Drug
The FDA cleared zetomipzomib as an Investigational New Drug. A phase 2 clinical trial is the next step for this autoimmune hepatitis treatment.
This week, Kezar Life Sciences, Inc. announced their autoimmune hepatitis treatment had received clearance of an Investigational New Drug application by the US Food and Drug Administration .
The therapy, zetomipzomib, is a first-in-class, selective immunoproteasome inhibitor, intended for the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis . AIH is a rare chronic disease that causes the immune system to attack the liver. This leads to inflammation and tissue damage that ultimate severely burdens patients health and quality of life.
AIH affects approximately 140000 persons in the US, with incidence rates 4 times higher in women than men. Left untreated, AIH can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
While there are AIH treatments currently available, these chronic corticosteroids can increase the burden of morbidity and mortality. With zetomipzomib, Kezar Life Sciences seeks to provide a treatment regimen to reduces the need for chronic immunosuppression via corticosteroids.
The primary efficacy endpoint will evaluate the proportion of patients who achieve a complete response, measured as normalization of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels with a successful corticosteroid taper by Week 24.
Related Content:
Donât Miss: Hepatitis C Causes Liver Damage
Don’t Miss: What Type Of Doctor Treats Hepatitis C
Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Life
Autoimmune hepatitis can become life-threatening when it isnt properly treated. Without treatment, you can end up developing cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver. Over time, liver failure can also occur when this condition is left untreated. Its important to seek a diagnosis and treatment if you think you might have this disease.
How To Use Prednisone And Azathioprine
There is no treatment schedule applicable to all AIH patients. The suggested algorithms and treatment schedules must be tailored to the single patient, taking into account the severity of the disease, age and co-morbidities.
The AASLD guidelines published in 2010 recommend two alternative schedules: either prednisone alone at a dose of 60 mg/d or a combination of prednisone 30 mg/d and azathioprine 50 mg/d as initial treatment, favouring the latter because of fewer steroid side-effects. However, as azathioprine can be hepatotoxic, particularly in cirrhotic and jaundiced patients, the more recent guidelines by the European Association for the Study of the Liver recommend that it is added after two weeks of steroid monotherapy , when partial disease control has been achieved. In addition, this approach avoids the problem of distinguishing between azathioprine-induced hepatotoxicity and non-response, this distinction being an important issue in clinical practice. A retrospective series of 133 adult patients reports better results with a combination of steroids and another immunosuppressant from disease presentation compared to steroids alone or steroids followed by the addition of azathioprine/other immunosuppressants. Of note, only 2% of the patients included in this study were jaundiced at presentation, possibly explaining the high remission rate on azathioprine, without hepatotoxicity.
Also Check: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
Also Check: Herbal Medicine For Hepatitis B
What Foods Should You Avoid With Autoimmune Hepatitis
You should include more fruits and vegetables in your diet, and avoid drinking alcohol since this can make liver problems worse. If you already have cirrhosis, you should avoid eating meats and seafood that are undercooked or raw. You should also follow your doctors recommendations for dietary changes, such as limiting salty and fatty foods.
What Are The Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
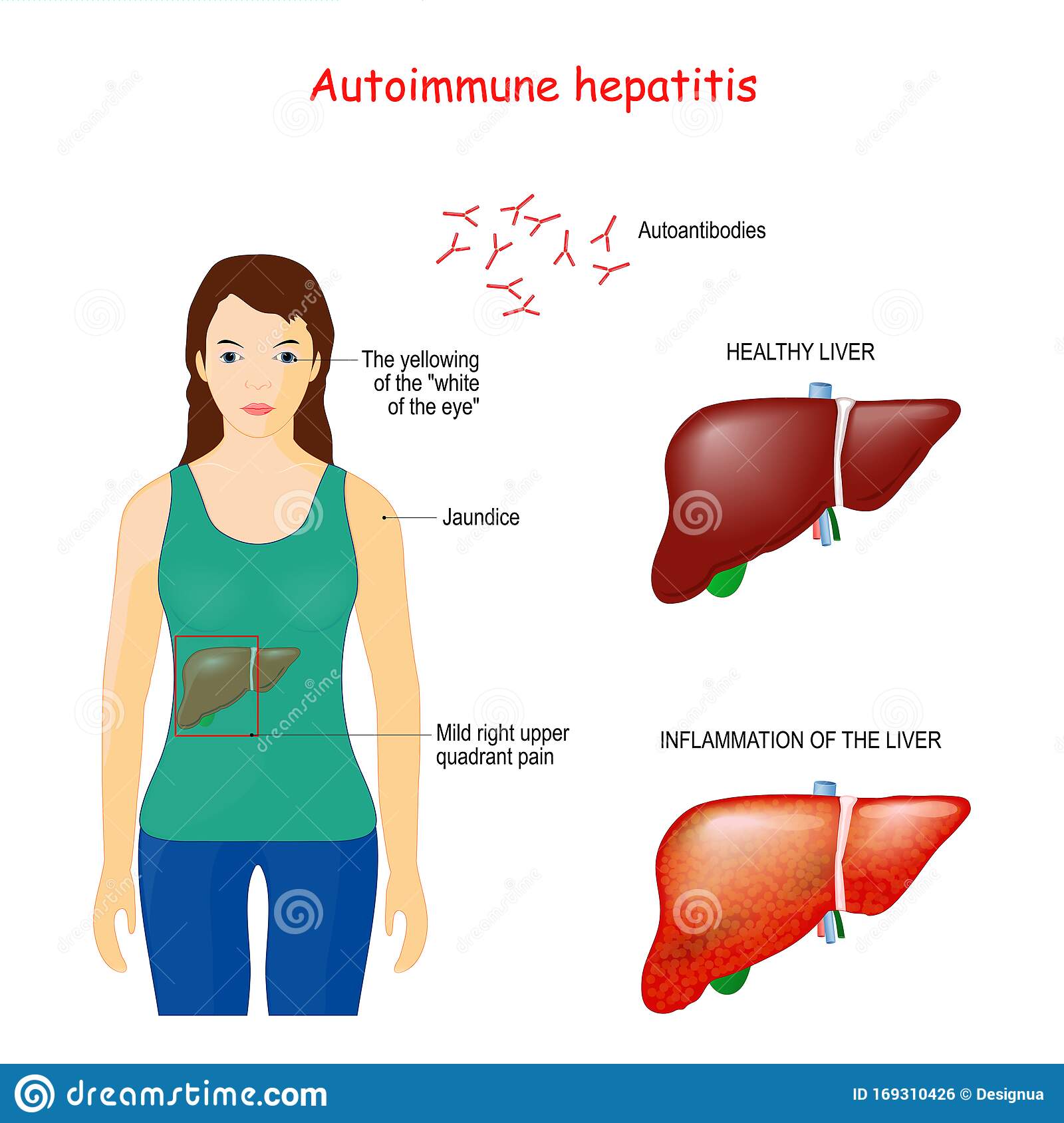
People with autoimmune hepatitis may have some of the following symptoms
- pain over the liver, in the upper part of the abdomen
- yellowish color of the whites of the eyes and skin, called jaundice
- darkening of the color of urine
- lightening of the color of stools
- skin conditions, such as rash, psoriasis, vitiligo, or acne
When symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are present, they can range from mild to severe.
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have no symptoms. In such cases, doctors may find evidence of liver problems during routine blood tests that leads to a diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. People without symptoms at diagnosis may develop symptoms later.
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis dont have symptoms until they develop complications due to cirrhosis. These symptoms include
- feeling tired or weak
- bloating from a buildup of fluid in the abdomen, called ascites
- swelling of the lower legs, ankles, or feet, called edema
Read Also: How Do They Test For Hepatitis C