Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Also Check: How Does Hepatitis C Affect The Body
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Symptoms In Females
Try To Control Itching
People who have hepatitis sometimes have itchy skin. You can control itching by keeping cool and out of the sun, wearing cotton clothing, or using over-the-counter antihistamines such as a non-drowsy one like loratadine or one that may make you sleepy like diphenhydramine . Talk to your doctor before taking these medicines.
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
You May Like: What Virus Causes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
You May Like: Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
Jeong Eun Song, Do Young Kim
Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Contributions: Conception and design: DY Kim Administrative support: None Provision of study materials or patients: None Collection and assembly of data: None Data analysis and interpretation: None Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Hepatitis B virus infection is a major global health problems leading to severe liver disease such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma . HBV is a circular, partly double-stranded DNA virus with various serological markers: hepatitis B surface antigen and anti-HBs, anti-HBc IgM and IgG, and hepatitis B e antigen and anti-HBe. It is transmitted by sexual, parenteral and vertical route. One significant method to diminish the burden of this disease is timely diagnosis of acute, chronic and occult cases of HBV. First step of HBV diagnosis is achieved by using serological markers for detecting antigens and antibodies. In order to verify first step of diagnosis, to quantify viral load and to identify genotypes, quantitative or qualitative molecular tests are used. In this article, the serological and molecular tests for diagnosis of HBV infection will be reviewed.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus serology molecular diagnosis
Submitted Aug 01, 2016. Accepted for publication Aug 28, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.09.11
Recommended Reading: What Does Non Reactive Mean For Hepatitis C
What Causes Hepatitis B
It’s caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is spread through contact with the blood and body fluids of an infected person.
You may get hepatitis B if you:
- Have sex with an infected person without using a condom.
- Get a tattoo or piercing with tools that weren’t sterilized.
A mother who has the virus can pass it to her baby during delivery. Medical experts recommend that all pregnant women get tested for hepatitis B. If you have the virus, your baby can get shots to help prevent infection with the virus.
You cannot get hepatitis B from casual contact such as hugging, kissing, sneezing, coughing, or sharing food or drinks.
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Don’t Miss: What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C
How Does Hepatitis B Spread
The hepatitis B virus is known as a blood-borne virus because it is transmitted from one person to another via blood or fluids contaminated with blood. Another important route of transmission is from an infected mother to a newborn child, which occurs during or shortly after birth.
- Direct contact with blood may occur through the use of dirty needles during illicit drug use, inadvertent needle sticks experienced by healthcare workers or contact with blood through other means. Semen, which contains small amounts of blood, and saliva that is contaminated with blood also carry the virus.
- The virus may be transmitted when these fluids come in contact with broken skin or a mucous membrane of an uninfected person.
People who are at an increased risk of being infected with the hepatitis B virus include the following:
In some cases, the source of transmission is never known.
You cannot get hepatitis B from the following activities:
- Having someone sneeze or cough on you
- Hugging someone
Half of all people infected with the hepatitis B virus have no symptoms and may never realize that they have been infected. Adults are more likely to develop symptoms than children. For those who do get sick, symptoms usually develop within 1 to 4 months after exposure to the virus. The initial symptoms are often similar to the flu.
Common symptoms of hepatitis B include:
Other types of acute viral hepatitis such as hepatitis A and hepatitis C have symptoms that are indistinguishable from hepatitis B.
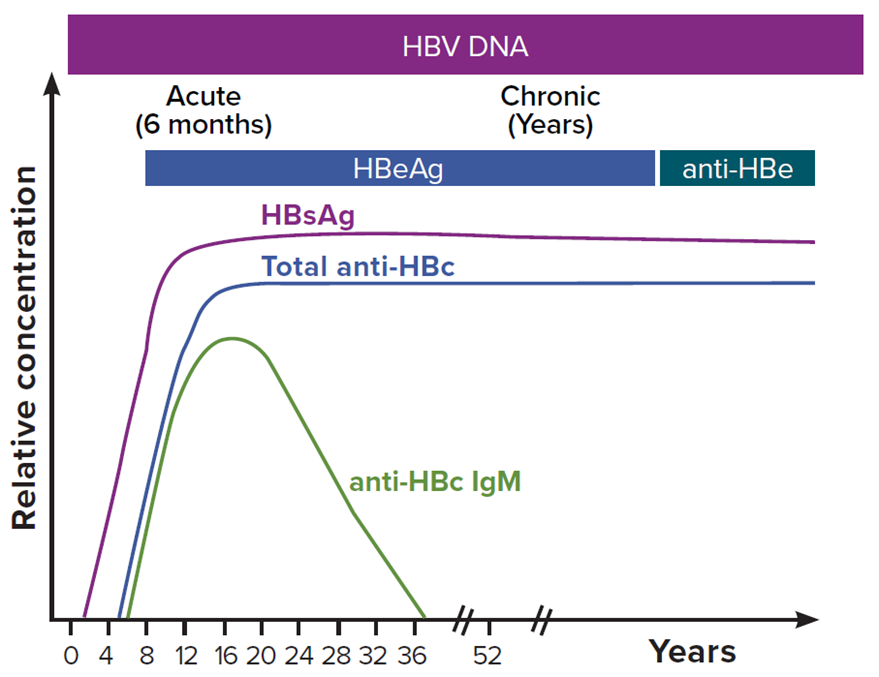
Recommended Tests To Investigate Chronic Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Chronic HBV infection is defined by the continued presence of HBsAg in the blood for longer than six months. Figure Figure11 and Table Table22 outline the tests used to diagnose most cases of chronic HBV. Test selection should be based on the person’s risk factors, vaccination history and findings from previous tests .
Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection . ALT Alanine aminotransferase Anti-HAV-IgM Immunoglobulin M class antibody to HAV Anti-HCV Antibody to HCV antigens HBsAg Hepatitis B surface antigen
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Go To Get A Hepatitis B Vaccination
What Is The Medical Treatment For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B infection
Acute hepatitis B infection is not treated with antiviral medications.
- If the infected person is dehydrated from vomiting or diarrhea, a doctor may prescribe IV fluids to help them feel better. Medications may also be used to control these symptoms.
- People with mild symptoms can be cared for at home.
Chronic hepatitis B infection
The degree of liver damage is related to the amount of active, replicating virus in the blood and liver. Regularly measuring the amount of HBV DNA in the blood gives your physician a good idea of how fast the virus is multiplying. The treatments now in use are classified as antiviral drugs because they work by stopping the virus from multiplying.
Treatment is usually started when blood tests indicate that liver functions are deteriorating and the amount of replicating HBV is rising. Many people never reach this point. For those who do, the interval between diagnosis and starting treatment is quite variable.
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Read Also: Where To Get Tested For Hiv And Hepatitis
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by a virus that is spread through blood, semen and vaginal fluids.
You can get hepatitis B from:
- having vaginal, anal or oral sex without using a condom or dam
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Is Surgery A Treatment For Hepatitis B
There is no surgical therapy for hepatitis B.
If liver damage is so severe that the liver starts to fail, liver transplant may be recommended:
- Liver transplant is a major process and surgery with an extended recovery period.
- It also depends on the availability of a matching donor liver.
- If liver transplant becomes a possibility for an individual, a health care practitioner will discuss the risks and benefits with them.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.