How To Get Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
All babies in the UK born on or after 1 August 2017 are given 3 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine as part of the NHS routine vaccination schedule.
These doses are given at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age.
Babies at high risk of developing hepatitis B infection from infected mothers are given extra doses of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, 4 weeks and 1 year of age.
If you think you’re at risk and need the hepatitis B vaccine, ask your GP to vaccinate you, or visit any sexual health or genitourinary medicine clinic.
If your job places you at risk of hepatitis B infection, it’s your employer’s responsibility to arrange vaccination for you, rather than your GP. Contact your occupational health department.
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
Before Taking This Medicine
Hepatitis A and B vaccine will not protect you against infection with hepatitis C or E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It will also not protect you from hepatitis A or B if you are already infected with the virus, even if you do not yet show symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you are allergic to yeast or neomycin, or if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A or hepatitis B.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system .
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
How Is The Vaccine Given
Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB® are given in 3 or 4 shots over a 6-month period. Infants should get their first dose at birth and usually complete the series by 6 months of age. Older children and teenagers who were not vaccinated as infants should also be vaccinated, as well as unvaccinated adults who are at risk of infection with hepatitis B.
You May Like: July 28 World Hepatitis Day
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
How To Take Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccine
Use Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccine exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
This vaccine is given as an injection into a muscle. You will receive this injection in a doctor’s office or other clinic setting.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is given in a series of 3 shots. The booster shots are given 1 month and 6 months after the first shot.
If you have a high risk of hepatitis infection, you may be given 3 shots within 30 days, and a fourth shot 12 months after the first.
Your individual booster schedule may be different from these guidelines. Follow your doctor’s instructions or the schedule recommended by the health department of the state you live in.
Contact your doctor if you miss a booster dose or if you get behind schedule. The next dose should be given as soon as possible. There is no need to start over.
Be sure to receive all recommended doses of this vaccine or you may not be fully protected against disease.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B And What Causes It
How Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Work
The Hepatitis B vaccine works by exposing the bodys immune system to the viral components without causing the disease. This allows the body to recognise, target, and eliminate the actual virus if it comes in contact with it. Only one part of the virus is isolated and cultivated to prepare the vaccine.
One of the ways by which immunity is created is by the production of antibodies. Antibodies are chemical components that are produced by the immune system which act against the disease and eliminate it. Checking the levels of these antibodies is a good way to know the immune status after taking the vaccine. This helps in understanding if the vaccine was effective or not.
Who Should Be Immunised Against Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B immunisation is recommended and funded for the following groups:
- all children up to their 18th birthday
- babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection
- people who live in close contact with someone infected with hepatitis B
- anyone undergoing renal dialysis
- people who have hepatitis C infection, or who are HIV positive, or who have had a needle stick injury.
- anyone who has received immunosuppression therapy of at least 28 days or has had solid organ or bone marrow transplant.
Hepatitis B immunisation is also recommended, but not funded, for:
- workers who are likely to come into contact with blood products, or who are at increased risk of needlestick injuries, assault, etc.
- people who change sex partners frequently such as sex workers
- people who regularly receive blood transfusions such as people with haemophilia
- current or recent injecting drug users
- migrants and travellers from or to areas with intermediate or high rates of hepatitis B such as the Asia and Pacific region.
Don’t Miss: How You Contract Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Are There Any Side Effects Associated With Combination Vaccines
These vaccines are very tolerable or have very mild side effects. You won’t need to be worried about mild symptoms like pain and swelling in the area where the shot has been given. On the other hand, if your child takes individual shots then, they will have to go through the pain and swelling multiple times, and thus, combination vaccines are preferred. The side effects that can come with it include swelling, pain, or fever that can last 2-3 days. In some cases, doctors can prescribe medication to ease the symptoms. We must make sure that you are following all the instructions carefully for the vaccine to be effective.
You May Like: Facts About Hepatitis B Vaccine
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
Twinrix Side Effects List For Healthcare Professionals
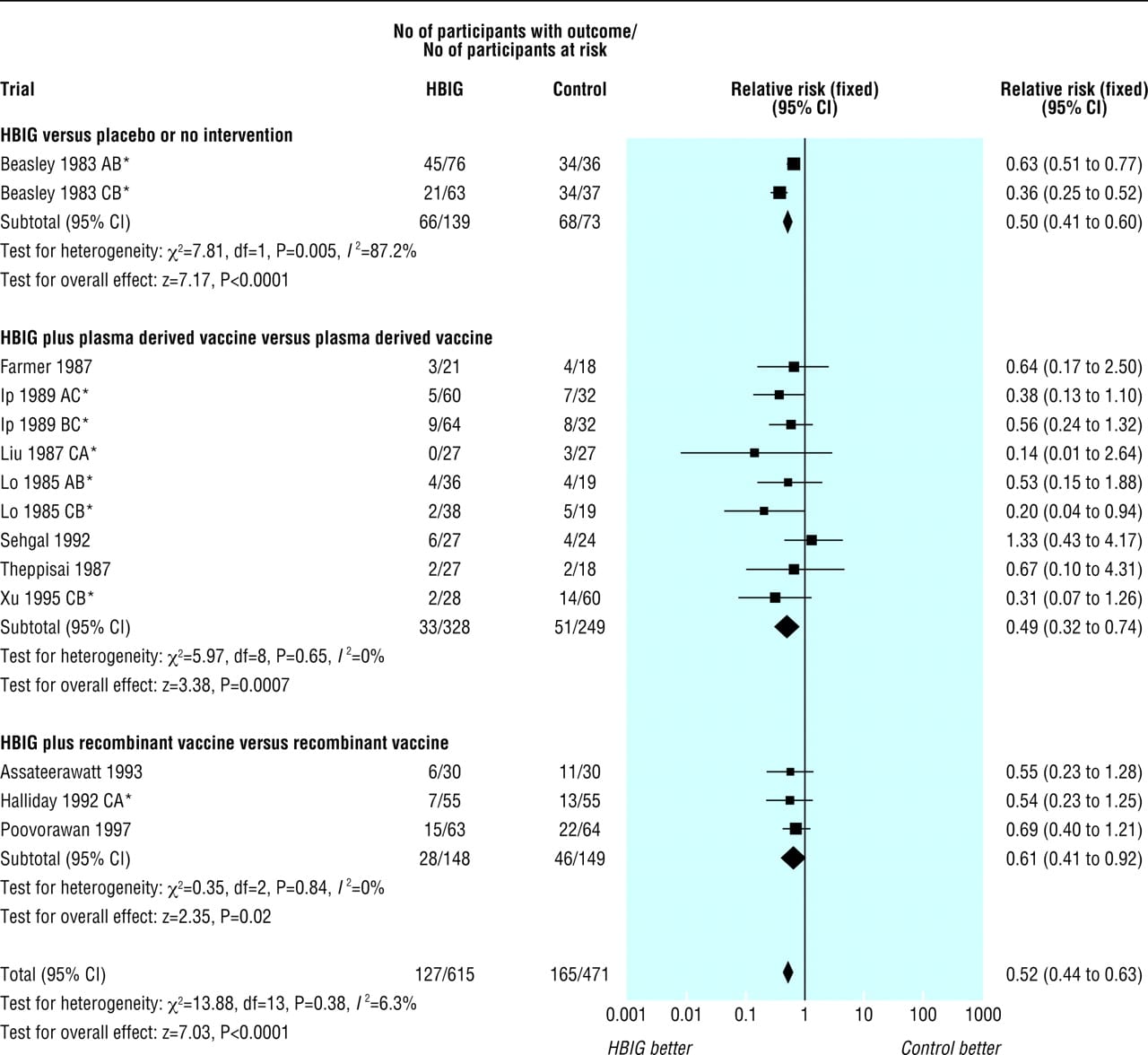
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a vaccine cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another vaccine and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Following any dose of Twinrix, the most common solicited injection site reactions were
- injection site soreness and redness
- the most common solicited systemic adverse reactions were
The safety of Twinrix has been evaluated in clinical trials involving the administration of approximately 7,500 doses to more than 2,500 individuals.
- In a U.S. study, 773 subjects were randomized 1:1 to receive Twinrix or concurrent administration of Engerix-B and Havrix .
- Solicited local adverse reactions and systemic adverse events were recorded by parents/guardians on diary cards for 4 days after vaccination.
- Unsolicited adverse events were recorded for 31 days after vaccination.
- Solicited reactions reported following the administration of Twinrix or Engerix-B and Havrix are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Rates of Local Adverse Reactions and Systemic Adverse Reactions within 4 Days of Vaccinationawith Twinrixb or Engerix-B and Havrixc
Most solicited local adverse reactions and systemic adverse reactions seen with Twinrix were considered by the subjects as mild and self-limiting and did not last more than 48 hours.
Incidence 1% To 10% Of Injections, Seen In Clinical Trials With Twinrix
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
What Is The Most Important Information I Should Know About Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis A and B vaccine will not protect you against infection with hepatitis C or E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It will also not protect you from hepatitis A or B if you are already infected with the virus, even if you do not yet show symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you are allergic to yeast or neomycin, or if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A or hepatitis B.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
- an allergy to latex rubber or
- a weak immune system .
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Recommended Reading: What If You Have Hepatitis B
Who Should Take The Hepatitis B Vaccine
As such, it is recommended that everyone be vaccinated against Hepatitis B. The following groups are especially recommended to get vaccinated at the earliest as they are at higher risk of exposure to infection.
-
People whose partners have hepatitis B
-
Healthcare workers
-
People who use/ have recently used injectable drugs
-
People living with HIV/ Hepatitis C/Chronic Liver disease
-
Diabetic patients at the discretion of their doctors
-
Individuals who are in prison/ jail
This vaccine is safe for use in individuals with compromised immune systems. It is also safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
WHO recommends vaccination for all age groups. It is recommended for:
-
All newborns within 24 hours of life
-
All children & adolescents below the age of 19 with no prior history of hepatitis vaccination
-
All adults up to the age of 60
-
All adults over the age of 60 with risk factors for hepatitis B infection
Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives difficult breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
You may feel faint after receiving this vaccine. Some people have had seizure like reactions after receiving this vaccine. Your doctor may want you to remain under observation during the first 15 minutes after the injection.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have:
-
numbness, pain, tingling, weakness, burning or prickly feeling, vision or hearing problems, trouble breathing
-
red or blistering skin rash or
-
easy bruising or bleeding .
Common side effects of hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine may include:
-
redness or tenderness where the shot was given
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B Treated
How Do Inactivated Viral Vaccines Work
Inactivated viralvaccines are sterile biologic products that provide immunity against viral infections. Inactivated viral vaccines work by stimulating the bodys immune system to produce antibodies against specific types of viruses, and protect a person from becoming infected when exposed to these viruses.
In the case of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes respiratory illness and has led to the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines do not entirely prevent infection but protect vaccinated individuals from serious illness and hospitalization from the disease.
Inactivated viral vaccines contain particles of proteins or genetic material from viruses. Inactivated viral vaccines may also contain substances that preserve and stabilize the vaccine, and enhance immune response. Some viral vaccines are delivered in inactivated harmless viruses such as human adenovirus.
Inactivated viral vaccines may be made from:
- Surface proteins of the viruses enable the virus to hold on to a human cell, enter inside and replicate.
- Modified RNA particles from the virus can enter host cells and induce the production of viral antigen, which stimulates an immune response from the body.
- Recombined DNA material from multiple strains and subtypes of viruses, killed to eliminate disease-causing capability.
Currently, inactivated viral vaccines approved by the FDA protect against viral infectious diseases that include:
- Coronavirus disease , caused by SARS-Cov-2 virus
Adults
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For Children
Vaccination is the best protection against hepatitis B infection and is recommended for all infants and young children, adolescents and those in high-risk groups. Vaccination can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule.
In Victoria, vaccination against hepatitis B is free for all babies and children including:
- Babies at birth vaccinate with hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 20 years of age.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Be Transferred Through Saliva
Rare Side Effects After Immunisation
There is a very rare risk of a serious allergic reaction to any vaccine. This is why you are advised to stay at the clinic or medical surgery for at least 15 minutes following immunisation, in case further treatment is required.
If you think your child may be having a serious allergic reaction and you are no longer at the clinic where they were immunised, take them immediately to your doctor or to the nearest hospital, or call 000 for an ambulance.
Another rare side effect is the hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode . If they are experiencing HHE, a baby may be:
This may occur from one to 48 hours following vaccination. The whole episode may last from a few minutes to 36 hours.
If you think your child may be having an HHE episode, take them immediately to your doctor or to the nearest hospital.
Follow-up of children with HHE shows no long-term neurological or other side effects.
What Drugs Interact With Twinrix
Concomitant Administration With Vaccines And Immune Globulin
- Do not mix Twinrix with any other vaccine or product in the same syringe.
- When concomitant administration of immunoglobulin is required, it should be given with a different syringe and at a different injection site.
- There are no data to assess the concomitant use of Twinrix with other vaccines.
Immunosuppressive Therapies
- Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids , may reduce the immune response to Twinrix.
Interference With Laboratory Tests
- Hepatitis B surface antigen derived from hepatitis B vaccines has been transiently detected in blood samples following vaccination. Serum HBsAg detection may not have diagnostic value within 28 days after receipt of a hepatitis B vaccine, including Twinrix.
You May Like: Signs Of Hepatitis C In Women