How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed
Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
Are Hepatitis B And C Preventable
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable disease.
There is a three-shot vaccination series that is very effective in protecting people against the virus if theyre exposed. In the United States, all newborns are vaccinated for hepatitis B and all pregnant women are screened for hepatitis B during pregnancy. This way, mothers infected with hepatitis B can take protective steps to decrease the risk of transmission of the virus to the child.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Latest Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Could There Be A Link With Covid
The COVID-19 virus is one of the possible infections under scrutiny. Some of the children who have contracted hepatitis have recently been infected with COVID-19, although experts caution that this is to be expected given the high COVID-19 infection rates in this age group.
Experts are also stressing that there is no link between these incidences of hepatitis and the COVID-19 vaccine2. This is because no vaccinations were given to the children who were under 5 years of age – the age group which makes up over 75% of current hepatitis cases.
Why has there been an increase of hepatitis in children?
- 8min
Can Hepatitis B Be Treated What Treatments Are Available
Good treatments are available for all adults who hold Medicare cards. Treatment aims to prevent liver damage but is not an actual cure. Not everyone will need
treatment and there are short- or long term options. Please phone the Hepatitis Infoline on 1800 803 990 for more information. Read more about monitoring and treatment of hep B.
Read Also: Confirmatory Test For Hepatitis C
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
- older adults
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Knowing Your Risk For Chronic Hepatitis C
Because chronic hepatitis may have no symptoms, it is important to know your risk for chronic hepatitis C virus . Risk factors include:
- Those who had a transfusion of blood or blood products before 1992 .
- Those born between the years of 1945-1965.
- Those who have or are experimenting with intravenous drugs.
- Those who have snorted or are snorting cocaine.
- Those who have gotten tattoos with a non-sterile needle.
- Those who have had unprotected multiple sexual partners.
- Those with HIV.
- Children born to mothers with HCV infection.
Although these are the most common ways to acquire Hepatitis C, there are other risk factors that can lead to infection. Thus, in 2020 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention updated its screening guidelines to recommend all adults 18 years or older get screened at least once in their lifetime for HCV.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Viral Load Quest
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
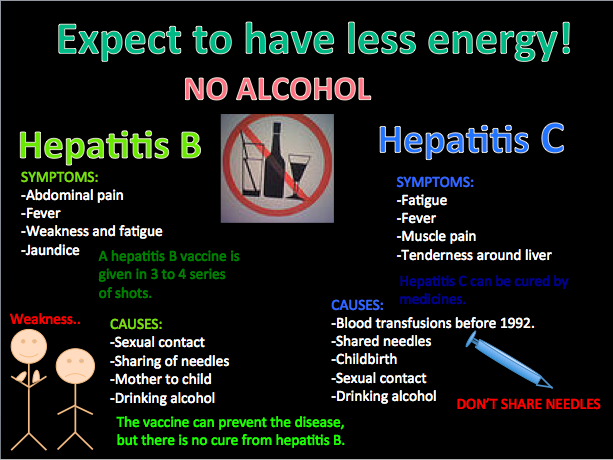
What’s The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B and C have some similarities to each other, but also a number of important differences. Like any form of hepatitis they both attack the liver, sometimes causing serious liver damage. They can both be transmitted by blood to blood contact with an infected person. They are both treatable with medication, which is improving all the time and this means that those infected with either hepatitis B or C can usually live a long and healthy life with a few lifestyle changes. There are similarities in the some of the ways in which you might become infected, including sharing needles or equipment used to inject drugs through infected blood products passed on from mother to child and more.
However, there are also a number of important differences between hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Contagious By Touch
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
The first step in diagnosing a hepatitis infection is to receive a medical exam from your doctor. The doctor will perform a physical to look for signs of the illness. All the varieties of hepatitis present with a very similar set of symptoms, which includes:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
You may also experience jaundice or a yellowing of the skin and eyes and bowel movements that appear gray. Michael says, Fortunately, most patients are asymptomatic. If you have hepatitis B and its an active condition, meaning youre sick from it, your skin and eyes are going to have a yellow tint.
The doctor will look for these telltale signs and then order blood work to spot the viral load for the type of hepatitis and whether the infection is dormant or active. If the virus is active, you are contagious. The blood test can also determine if the infection is acute or chronic .
If the blood test confirms hepatitis, the doctor may also order an ultrasound of the liver to see if it is inflamed. The ultrasound should also show if the liver is scarred with cirrhosis. You may also have a CT or MRI to look more closely at the liver or signs of liver cancer. This is especially important if you have a family history of the disease.
Finally, in the unusual event that the imaging tests arent shedding light on the situation, the clinician may order a liver biopsy.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis B Do To You
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Symptoms for HCV may not appear for 20 to 30 years, and that is why it is so important to get tested. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control now recommends that all adults 18 years and older are tested at least once for HCV. Some high risk groups may need more frequent testing, and all pregnant women should be tested during every pregnancy.
HCV can actually clear itself from the body in about 15% of people, but most people become infected with the virus chronically.
Early symptoms of acute HCV occur within 1 to 3 months and may last several weeks. These may include:
- yellow-colored skin or eye sclera
- weakness
- nausea and stomach pain
- joint or muscle pain
Chronic, long-term symptoms of HCV can include weight loss, fluid build-up and swelling, poor appetite, fatigue, easy bruising and bleeding, itchy skin, jaundice, dark-colored urine, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech , and spider-like blood vessels on the skin .
Which Organ Is Affected By Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters blood and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol consumption, toxins, certain medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis.
You May Like: What Does Non Reactive Mean On A Hepatitis C Test
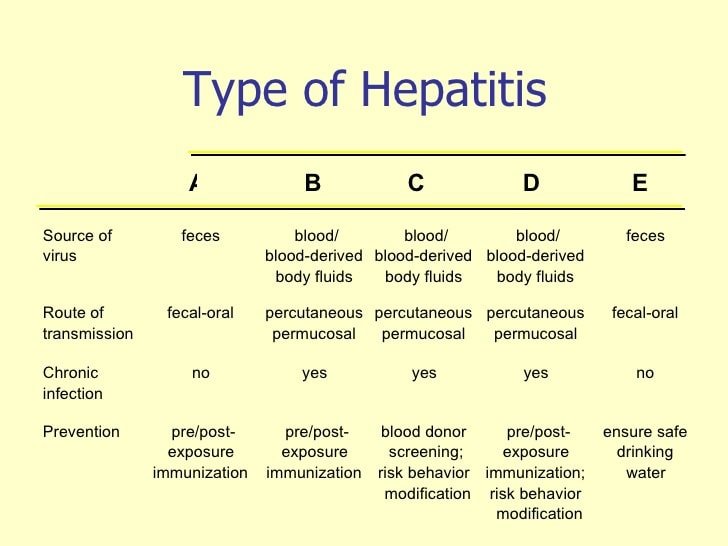
The A B Cs Of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus causes acute inflammation of the liver that almost always gets better on its own, although it can be more serious if you get it when you are older or if you already have liver disease. It is easily spread from person to person, in food and water, and can infect many people at once. For example, if a food handler at a restaurant is infected with hepatitis A, those who eat food prepared by that handler may be infected. Hepatitis A can be prevented by getting vaccinated.
Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus can be both acute and chronic and is spread through blood or other body fluids in various ways. Hepatitis B is very common in Asia and Africa and those who were born or lived in these areas should be checked for hepatitis B. Like hepatitis A, a vaccine is available to prevent HBV infection as long as you have not been previously exposed. Although chronic HBV cannot be cured, there are oral medications available to treat and control the virus.
Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is almost always chronic and spreads mostly by direct blood to blood contact. Although hepatitis A and B can be prevented by vaccination, hepatitis C cannot. However, there are currently oral medications available that are able to cure Hepatitis C in 95% of all cases regardless of prior treatment history.
Which Hepatitis Is Acute
Hepatitis A virus is the most common cause of acute hepatitis, followed by hepatitis B virus.
What is acute about chronic hepatitis?
Acute-over-chronic liver failure is a common pattern of end-stage liver disease in clinical practice and occurs frequently in patients with chronic hepatitis B or HBV-related cirrhosis. New advances in recent years have led to a better understanding of this disease.
Is hepatitis A chronic or acute?
Hepatitis A Hepatitis caused by HAV is an acute illness that never becomes chronic. At one time, hepatitis A was called infectious hepatitis because it could spread easily from person to person like other viral infections.
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Demographics Age Distribution And Underlying Comorbidities
A total of 149 HCC patients were enrolled during the study period: 89 with HBV-associated cancers, 38 with HCV-associated cancers, 4 with cancers associated with both HBV and HCV, and 18 patients with cancers not associated with either hepatitis virus . HCC patients with HBV and HCV co-infection, as well as those without underlying viral hepatitis were excluded from the present analysis. HCC developed more commonly among males in both groups, however the association to male gender was stronger in the HBV group. Only 5% of HBV-associated HCCs developed in female patients compared with 21% of HCV-associated HCCs . The majority of HBV-associated HCC patients were of Asian race , compared with only 5% in HCV-associated HCC patients .
Figure 1
HCC incidence according to underlying etiology . Underlying risk factors for HCC in current series closely resembles global demographic: worldwide epidemiologic data estimate HCC due to HBV in 53-54% of total cases, and due to HCV in 25%-31% of cases
As a group, patients who developed HCC associated with underlying HBV had fewer systemic comorbidities than those with underlying HCV. A mean of 1.0 underlying systemic comorbidity was present in HBV patients at the time of initial cancer diagnosis, compared with a mean of 2.9 associated systemic comorbidities in HCV patients . A coincident history of alcohol abuse was also less frequent in the HBV group , as was the frequency of HIV co-infection .
A Rise In Hepatitis In Children
As of 4th July 2022, 263 children under 10 years of age have been diagnosed with hepatitis in the UK this year1. Thankfully, no children have died, but this unusually high number of hepatitis in children has caused the UK Health Security Agency to jump into action to figure out the cause of this recent hepatitis outbreak.
There are many types of hepatitis in children, and these have various causes. Depending on the hepatitis type, this liver condition can be very treatable, but it can also sometimes be life-threatening. Most types – hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E – are caused by an infection with a virus. However, according to the UKHSA, these known hepatitis viruses have not been found in the children recently affected2.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
Whats The Difference Between Hepatitis A B And C
Chronic Illness, Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatology, Liver Health
Youve probably seen stories in the news about hepatitis A outbreaks linked to infected restaurant workers, or how a rising rate of hepatitis C infections is causing increased health care costs.
But you might not know the difference between hepatitis A, B and C, or why you should be concerned about them.
Heres why: Hepatitis, or inflammation of the liver, affects more than 50,000 new people each year and is a leading cause of liver cancer and liver transplants. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates as many as 6 million people in the U.S. are living with hepatitis.
Having hepatitis can be dangerous and uncomfortable. Symptoms are similar for hepatitis A, B and C and may include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, gray-colored stools, joint pain and jaundice . Even worse, chronic hepatitis often has no symptoms, and people dont know theyre infected until they get very sick.
Michael Fried, MD, director of the UNC Liver Center, explains the difference between the types of hepatitis and how to protect yourself.
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Virus Symptoms And Treatment
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is the most common liver infection in the world. Globally, hepatitis B has infected about 350 million people. In the United States, there are roughly 0.8 million cases. It is responsible for more liver-related cancer and deaths than hepatitis C .
Hepatitis B infection is also considerably more contagious. Some statistics suggest that it might be five to ten times more infectious than hepatitis C. Part of that comes from how stable the virus is, which contributes to its ability to survive on surfaces for longer periods of time .
While it is not strictly a sexually transmitted infection, you can get the hepatitis B virus through sexual contact. As mentioned, it travels easily through blood, but it can also be transmitted through semen and vaginal fluids. This means that you can potentially get it from anal, vaginal, or oral sex, along with any exposure to infected blood .
Hepatitis B is considerably more preventable than hepatitis C. Along with safer sex, a hepatitis B vaccine exists to largely protect most people from infection. There is no hepatitis C vaccine .