How Do My Healthcare Professional And I Decide On Treatment
Your healthcare professional will look at your health history and decide if treatment is right for you. The treatment you receive and the length of treatment may depend on:
- how much virus is in your body
- your genotype of hep C
- whether you have liver damage
- whether or not youve been treated previously
Next:
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis
Hepatitis C Recurrence: What Are The Risks And Treatment
Hepatitis C Recurrenceis of the various types major division is based on the acute or the chronic. In the later stages of the infection with this virus, the infections stay for the whole lifetime. The studies also suggest that 70-85% of the patients infected with this virus are curable.
The treatment is better than the previous conditions, and also, the average risk of the occurrence of the disease is less than 1%. But it is also important to take the proper precautions to prevent the occurrence of the disease.
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis C
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.Clin Infect Dis.
Nat Med.
J Viral Hepat.
J Clin Microbiol.
Antivir Ther.J Clin Virol.J Viral Hepat.
Ann Intern Med.
de novoJ Hepatol.
- All patients with suspected HCV infection should be tested for anti-HCV antibodies in serum or plasma as first-line diagnostic test .
- In the case of suspected acute hepatitis C, in immunocompromised patients and in patients on haemodialysis, HCV RNA testing in serum or plasma should be part of the initial evaluation .
- If anti-HCV antibodies are detected, HCV RNA should be determined by a sensitive molecular method with a lower limit of detection 15IU/ml .
- In low- and middle-income countries, and in specific settings in high-income countries, a qualitative HCV RNA assay with a lower limit of detection 1,000IU/ml can be used to provide broad affordable access to HCV diagnosis and care .
- Anti-HCV antibody-positive, HCV RNA-negative individuals should be retested for HCV RNA 12 and 24weeks later to confirm definitive clearance .
- HCV core antigen in serum or plasma is a marker of HCV replication that can be used instead of HCV RNA to diagnose acute or chronic HCV infection when HCV RNA assays are not available and/or not affordable .
Also Check: Hepatitis B What Is It
Edema Symptoms Lead To Diagnosis
The Baltimore resident found out he had the disease in 2018 after his feet swelled up. My feet were so bad, I had to take the shoestrings out of my shoes so I could walk, he says.
When he visited nearby Johns Hopkins Hospital to get help, the medical team conducted a simple blood test to see if Pannell had hepatitis C.
Edema, a swelling of the feet, ankles, or legs due to a buildup in fluids, is a common symptom of cirrhosis.
I couldnt believe I tested positive, says Pannell, 64. I was mad, but I figured that I probably got the disease from sharing needles because I was an addict at one time. Today, Im going on 17 years clean.
After completing eight weeks of antivirals, Pannell was retested. He still had hepatitis C. I was frustrated and discouraged that it didnt work, says Pannell, but my care provider said lets try it again.
After a second round of therapy, Pannell was cured.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Adults
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Overview Of Hepatitis B And C Management
Justin Hooper, PharmD, BCPS
Tyler, Texas
US Pharm. 2009 34:32-41.
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that is often caused by one of five hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, or E. Hepatitis A and E are commonly contracted by ingestion of contaminated food or water, while transmission of hepatitis B and C occurs by parenteral contact with infected body fluids. No specific drug therapy is available for the treatment of hepatitis A or E. Hepatitis B and C infections are worldwide concerns because they often lead to chronic liver disease and even death. Much effort has been dedicated to global eradication of these diseases through education and vaccination. Still, viral hepatitis is a major public health concern. While both hepatitis B and C are associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the therapeutic approach to treatment varies by virus type, and each will be discussed separately.
Read Also: Chronic Hepatitis C With Hepatic Coma
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
- Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
- The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high risk areas include North Africa, the Middle East and Central and East Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often doesn’t have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged. This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition. Symptoms can include:
- flu-like symptoms, such as muscle aches and a high temperature
- feeling tired all the time
- loss of appetite
Read more about the complications of hepatitis C.
Also Check: I Need Information On Hepatitis C
How Is The Hepatitis C Virus Transmitted
The following actions transmit the hepatitis C virus:
What Will My Doctor Need To Know To Treat Me
If you want to be assessed for treatment, you need to make an appointment with a doctor. They will be mostly interested in the condition of your liver. Your doctor will organise, if possible, for you to have a Fibroscan examination. If Fibroscan is not available, your doctor will probably use an APRI test. This is an online calculator that estimates the health of your liver. It involves a blood test called a liver function test.
Dont forget, its very important to get a PCR test 12 weeks after finishing treatment this will mean the doctor can make sure you are cured.
You May Like: Hepatitis A How Is It Spread
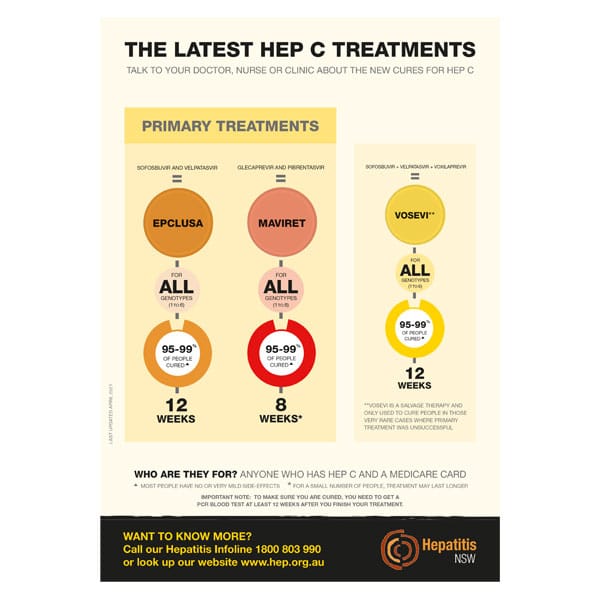
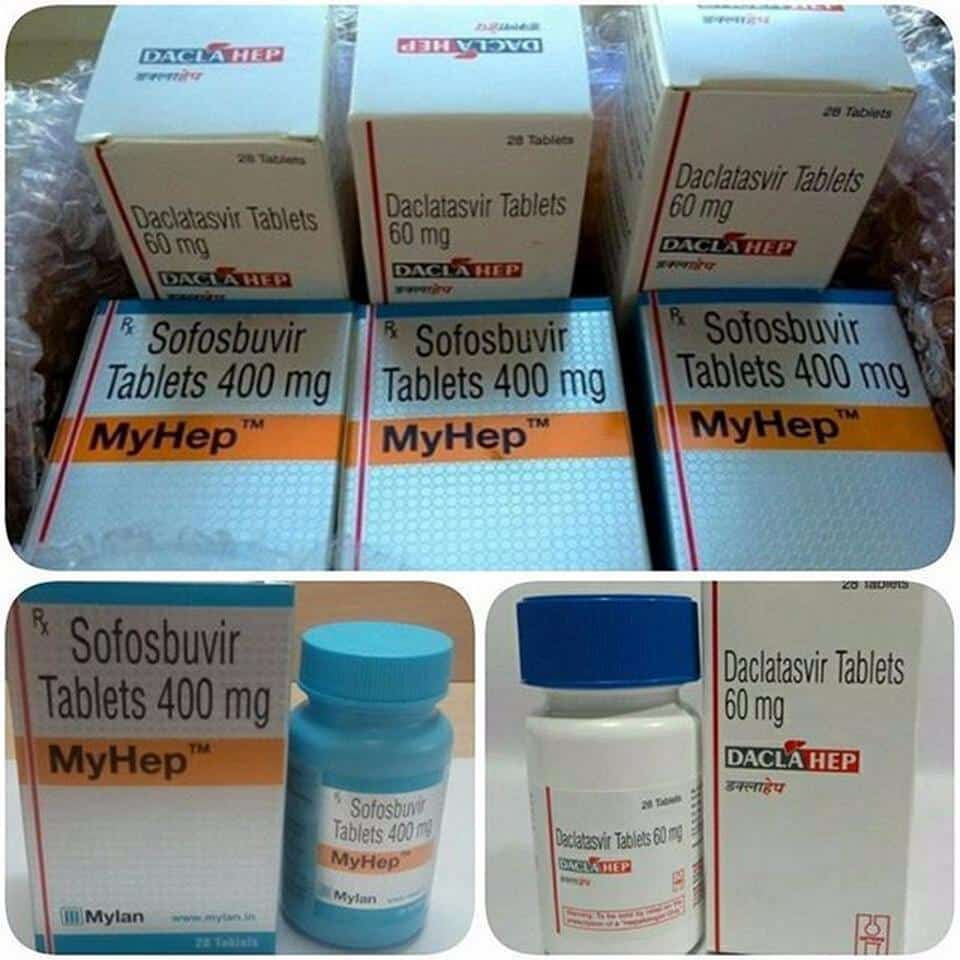
What Drugs Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Most hepatitis C is currently treated with all-oral medical regimens of direct-acting antivirals or DAAs. DAAs is a term used to distinguish these hepatitis C drugs from an older generation of injected medicines that act indirectly on the immune response to the hepatitis C virus. DAAs act directly on the virus to block different steps in its life cycle. There are several DAAs that are used in combinations that have been scientifically proven to cure hepatitis C. They are not interchangeable, and some are only available combined in one pill or dose pack as a specific combination. DAAs are not used as single-drug therapy because of the high risk of the virus developing resistance and because they work best in combinations. The choice of which regimen to use depends upon the genotype of the virus, the level of liver fibrosis , and any drug resistance that may be present .
Examples of combination DAAs with cure rates between 91%-100% include:
Genotype 1a and 1b are the commonest genotypes in the United States. Of all the genotypes, genotype 3 has been the most difficult to treat with DAAs alone and required the use of ribavirin, which has significant side effects. All genotypes can now be treated with oral DAAs without ribavirin. Some genotypes may still require the use of injected pegylated interferon and/or ribavirin if there is no response to DAAs.
Recommended Reading: How Does One Get Hepatitis B And C
Are There Ways To Cure Hepatitis C Other Than With Medications
Patients sometimes ask whether there are ways to treat hepatitis C other than taking medicines. Currently, there are no vaccines to prevent hepatitis C. Once a person is infected, the only way to treat it is with prescribed antiviral medications.
Some patients worry that having hepatitis C means they will need a liver transplant. Only a very small fraction of people with hepatitis C require a liver transplant. By far, most people with hepatitis C never need a liver transplant. A transplant is performedonlywhen damage to the liver is extremely advanced and the liver is unable to perform its basic functions. A transplant provides a new working liver, but a transplant does not get rid of the hepatitis C virus in the patient. Patients with a liver transplant still need antiviral medication to cure their virus.
Also Check: Low Protein Diet For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Importance Of Adhering To Your Treatment Plan
Once you begin treatment for your Hepatitis C infection, youll want to do everything you can to make it a success. Adherence to your Hepatitis C medication regimen is an important predictor of successful treatment. When it comes to medications, this means that you want to adhere to taking them as prescribed meaning taking the right dose, the right way, at the right time, for as long as prescribed.
The goal of using medications to treat Hepatitis C is to:
- Clear the Hepatitis C virus from your body
- Prevent or slow down scarring of your liver
- Reduce your chance of developing cirrhosis and liver cancer
Proper adherence to Hepatitis C therapy will increase your chance of being cured and decrease the long-term complications of Hepatitis C.
Adhering to other aspects of your treatment plan is also important. Keeping your medical appointments and getting the necessary lab tests will help to maximize your chance of treatment success and minimize potential problems.
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Hepatic Steatosis
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood.
Hepatitis C can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Although no vaccine for hepatitis C is available, you can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about treatment. Medicines can cure most cases of hepatitis C.
E Treatment Of Hepatitis C
The primary goal of HCV therapy is to achieve a SVR, defined as an undetectable HCV RNA 6 months after stopping antiviral therapy. Secondary goals of antiviral therapy include improvements in histology, quality of life and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Antiviral therapy is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for patients with persistently abnormal liver enzymes, detectable HCV RNA and an abnormal liver biopsy. Recent data have shown that patients with normal liver enzymes, detectable HCV RNA and an abnormal liver biopsy respond to therapy at similar rates as those with abnormal liver enzymes.55
The efficacy of HCV treatment has improved over the past decade. Initial treatment consisting of interferon alpha has been replaced by pegylated interferon and now by combination therapy using pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Efficacy varies depending on multiple factors especially viral genotype, but achieving sustained viral suppression in 50% of patients can be expected .
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Go Away
What Is The Outlook For Children With Hepatitis C
Most children acquire HCV at birth through vertical transmission from their mother. Around 1 in 20 babies born to mothers with hepatitis C acquire the virus, according to the American Liver Foundation.
Of those babies with an infection, some 40 percent may clear it without treatment by the time they are 2 years old .
The outlook for older kids who acquire an HCV infection through other means of transmission is more similar to the outlook for adults.
Up to 80 percent of those who have hepatitis C may go on to develop a chronic infection that may progress into chronic liver disease with scarring in 20 to 30 years.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Read Also: Causative Agent For Hepatitis C
Patient Evaluation And Treatment
Recommendations
Treatment should be considered for all patients with detectable HCV RNA and an abnormal liver biopsy, regardless of the presence or absence of liver enzyme elevation.
Prior to making a decision regarding treatment, patients should be evaluated with HCV RNA, HCV genotype, liver enzymes , and liver biopsy, unless contraindicated. The decision to initiate antiviral therapy should be made based upon the willingness of the patient to undergo therapy, ability to regularly attend appointments, and agreement to use contraception to prevent pregnancy. The decision to initiate antiviral therapy should be made on an individualized basis that considers severity of liver disease, co-morbid conditions, the potential for serious side effects and the likelihood of response.
Patients with HCV infection on methadone maintenance therapy should not be considered ineligible for treatment.
The treatment of the actively using injection drug user is not contraindicated and may be appropriate under some circumstances. Patients with a history of well-controlled psychiatric disorders may be excellent candidates for antiviral therapy and should be under the care of a qualified mental health professional.
All patients with CHC infection are candidates for antiviral therapy. These patients are defined by detectable serum HCV RNA and an abnormal liver biopsy consistent with chronic liver disease. Treatment is recommended for patients with significant inflammation or fibrosis.23
Managing Your Health While On Treatment
There are many things you can do to improve your health and feel better while on treatment for your Hepatitis C infection. And by taking good care of yourself, you will increase your chances of be able to take your medication as prescribed.
IMPORTANCE OF DIET AND NUTRITION
Contrary to some claims you might read on the Internet, there is no special Hepatitis C diet. However, a healthy diet can improve liver health in a person with Hepatitis C.
A well-balanced diet can lead to better liver functioning and lowered risk of cirrhosis of the liver. It can also help your immune system fight off illness. People with Hepatitis C tend to have higher rates of diabetes, but a good diet can help control blood sugar and reduce body fat, thereby lowering your risk for becoming diabetic.
Multiple studies have now demonstrated the benefit of drinking coffee to improve liver health in Hepatitis C. Studies suggest you need to drink more than two cups per day to gain this benefit. However, the research is not strong enough to make a recommendation to start drinking coffee and some people do not tolerate it well. But for those who currently do drink coffee enjoy!
General dietary recommendations include the following:
BE CAUTIOUS ABOUT DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS
Certain vitamins and minerals like vitamins A and D, iron and niacin can be harmful to your liver in high doses. Before taking a vitamin or supplement, its best to talk with your doctor, dietician or nutritionist.
ALCOHOL
Read Also: How Would You Know If You Had Hepatitis C