Hcv Lipoproteins And Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein
In infected patients, HCV particles circulate as low-density lipoprotein -virus complexes rich in triglycerides. These so-called lipo-viral particles were found to contain viral RNA, the viral structural proteins, core and envelope glycoproteins E1 and E2, but surprisingly also host-derived apolipoproteins B and E , which are the components of apoB-lipoproteins . The reasons for the circulation of the virus with lipoproteins are not clear. It is possible that this allows the virus to avoid recognition by leukocytes and also provides a mechanism to enter cells as a surrogate along with lipoproteins.
The Typical Treatments Can Hepatitis C Cause Cirrhosis Of The Liver
The primary treatment for fatty liver disease is surgery. This involves removing or dissolving the fatty liver cell. Surgery can be used for treating both severe and moderate cases. But the downside to surgery is that it can leave you with scarring that could impede your progress in losing weight and even your ability to stand up.
A more common way to diagnose fatty liver disease is through the use of liver function tests called a CT scan and an MRI. These tests will show whether or not your liver is functioning to its fullest capacity. If it shows signs of inflammation then your doctor may want to prescribe medication that will reduce inflammation. If there is fluid buildup in your abdomen, then your doctor may use a procedure called a liposuction to remove some of the fluid and reduce the swelling in the abdominal area.
===> How To Cure A Fatty Liver In Just Days < < <
The diagnosis of fatty liver is a little more tricky. A biopsy of your liver from the abdominal area will reveal inflammation, but it might not be fatty liver. It could be something else like hepatitis B or C, or even HIV if it is contained in its early stages. If the biopsy indicates the presence of fatty liver, then your doctor will conduct a trial of anti viral medication to make sure that the hepatitis does not develop into cirrhosis of the liver which would be very serious.
Characteristics Of The Study Population
Five hundred and ninety-eight consecutive patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria. A reliable elastography result could not be obtained in 24 of them. Thus, 574 patients were finally analyzed. Among them, 328 were HCV-monoinfected patients and 246 were HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals. The demographic, anthropometric and laboratory characteristics of these patients are shown in Table . BMI and plasma total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol values were lower in HIV/HCV-coinfected than in HCV-monoinfected patients . Nearly all of HIV/HCV-coinfected patients were under antiretroviral therapy with undetectable viral load in 78.9% of the cases .
Table 1 Characteristics of study populations .
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Incidence Of Cirrhosis Hcc And Hbsag Seroclearance In The Overall Chb Cohort
In the overall FL-CHB cohort, a lower cumulative 10-year incidence for cirrhosis and HCC and a higher cumulative 10-year incidence of HBsAg seroclearance was observed compared with non-FL CHB patients .
Cumulative 10-year incidence of cirrhosis , hepatocellular carcinoma , and hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in the overall chronic hepatitis B cohort. Number at risk values are presented as the number of patients at risk at the given time points .
When stratified by antiviral treatment status, within the unmatched, untreated CHB cohort, both the FL-CHB and non-FL CHB groups had low and similar rates of cirrhosis and HCC development, but the FL-CHB group had a significantly higher 10-year cumulative incidence of HBsAg seroclearance . Within the unmatched, treated cohort, compared to the FL-CHB group, the non-FL CHB group had a higher 10-year cumulative incidence for cirrhosis and HCC , but there was no difference in the rates of seroclearance .
Cumulative 10-year incidence of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma , and hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in the overall chronic hepatitis B cohort, by antiviral treatment status. Number at risk values are presented as the number of patients at risk at the given time points .
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have Hepatitis B
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Subgroup And Sensitivity Analyses
The results of the subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses are shown in Table âTable2.2. When the analysis was stratified by study quality, study design and adjustment for cholesterol level or diabetes in the models, there was a significant difference between subgroups .2). For example, HBV infection was significantly associated with the risk of NAFLD in cohort and cross-sectional studies , but not in case-control studies .2). According to the sensitivity analyses, despite excluded the study using MRS, the results of the relationship between HBV infection and NAFLD remained stable . Additionally, the overall results remained consistent when the pooling model was changed .
How A Liver Becomes Fatty
It is unclear how a liver becomes fatty. The fat may come from other parts of your body, or your liver may absorb an increased amount of fat from your intestine. Another possible explanation is that the liver loses its ability to change fat into a form that can be eliminated. However, the eating of fatty foods, by itself, doesnt produce a fatty liver.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Virus Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology
You May Like: How To Test For Hepatitis C At Home
Experimental Models: Steatosis And Fibrosis Development
In animal models, such as the leptin deficient ob/ob mouse or the leptin receptor deficient mouse and rat , there is very marked hepatic steatosis but little steatohepatitis or fibrosis. Development of steatohepatitis in these models depends on additional factors, such as endotoxin exposure, acute liver injury , alcohol, excess dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids, or aging. A unifying hypothesis envisages that all causes capable of changing the redox equilibrium of the hepatocyte may result in liver inflammation and fibrogenesis activation. For example, ROS may promote hepatic stellate cell activation and collagen fibre deposition. Lipid peroxidation products, such as 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal, may elicit activation and nuclear translocation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases, upregulate c-Jun and increase AP-1 binding, all of which may lead to procollagen type I overexpression. Furthermore, these phenomena are efficiently prevented by antioxidants.
Prevention Of Hcc In Chronic Hepatitis B: Anti
Prevention is the best treatment for any condition and HCC is not an exception to the rule, especially in view of the high mortality. Development of HBV vaccine has been a major success in reducing the incidence of HBV and subsequent development of HCC. Benefits of vaccination have been demonstrated by the countries like Taiwan, where 25 years after the adoption of the universal hepatitis B vaccination program, HBV carrier rate among children has decreased to 1.2% and incidence of HCC among vaccinated children decreased by 70% . Vaccine is recommended for all newborns, pregnant women at their first neonatal visit and high-risk individuals. Neonates of HBV-infected mothers should get a dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin in addition to vaccination. It is estimated that > 90% of countries routinely vaccinate newborns against HBV, and approximately 70% are now delivering 3 immunization doses .
Analyzing the Taiwan National Health Research database, Wu et al. demonstrated that nucleoside analogues reduce the risk of recurrent HBV-related HCC following liver resection . Authors demonstrated a 6-year HCC recurrence rate of 45.6% compared to 54.6% in untreated individuals, as well as a 6-year reduction in overall mortality , with number needed to treat 12 to prevent one HCC over 6 years, and 6 to prevent 1 death over that same period of time.
Don’t Miss: How Can Someone Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C And Steatosis: What Is Fatty Liver Disease
Hepatitis C is a viral disease of the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus. This disease is usually transmitted via contact with infected blood, although it is also possible to contract it during sexual intercourse. After infection, the virus is cleared out of the organism within six months with little to none complications in about 30 percent of cases. On the other hand, in about 70 percent of patients, hepatitis C takes a chronic form. The chronic form of the disease can last for years and sometimes even be lifelong.
While patients suffering from the acute form of hepatitis C usually show little to no symptoms, the chronic form, which causes a much more serious deterioration of the liver, presents with a number of symptoms, such as:
- Prolonged bleeding time
- Getting bruises easily
These symptoms suggest a gradual loss of liver function. If untreated, hepatitis C can, in time, cause more serious damage to the liver, which can manifest as complications such as fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer. The most common complication of the chronic form of this disease is steatosis, or fatty liver, which affects 55 percent of patients.
Evaluation Of Liver Disease Based On Enzyme Levels
It is customary and useful to categorize liver diseases into three broad categories: Hepatocellular, in which primary injury is to the hepatocytes cholestatic, in which primary injury is to the bile ducts and infiltrative, in which the liver is invaded or replaced by non-hepatic substances, such as neoplasm or amyloid. Although there is a great deal of overlap in liver test result abnormalities seen in these three categories, particularly in cholestatic and infiltrative disorders, an attempt to characterize an otherwise undifferentiated clinical case as hepatocellular, cholestatic, or infiltrative often makes subsequent evaluation faster and more efficient. The AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase tests are most useful to make the distinction between hepatocellular and cholestatic disease.
The normal range for aminotransferase levels in most clinical laboratories is much lower than that for the alkaline phosphatase level. Accordingly, when considering levels of elevations, it is necessary to consider them relative to the respective upper limit of normal for each test compared. Consider a patient with an AST level of 120 IU/mL and an alkaline phosphatase of 130 IU/mL . This represents a hepatocellular pattern of liver injury because the AST level is three times the upper limit of normal, whereas the alkaline phosphatase level is only marginally higher than its upper limit of normal.
Table 2: Category of Liver Disease by Predominant Serum Enzyme Abnormality
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Lifestyle Modifications For Nafld
Although there have been many breakthroughs in understanding epidemiology and pathophysiology of NAFLD, weight loss remains the cornerstone treatment for NAFLD . The AASLD suggests a weight loss goal of 35% of total body weight for improvement in steatosis. In addition, 710% weight reduction is required to improve fibrosis and other histological features of NASH . Weight loss can lead to remission of NAFLD in patients with a BMI < 25%. .
Generally, low calorie diets are recommended for patients with NAFLD/NASH . Nguyen, V. and George, J. recommend a hypo-caloric diet , with the aim of achieving 57% reduction in baseline weight over a year for NAFLD management this resulted in histological improvement of steatosis and steatohepatitis .
Intake of simple carbohydrates is associated with NASH development. Fructose, being a simple carbohydrate, is associated with increased hepatic fibrosis due to its rapid metabolism in the liver, leading to a decrease in hepatic ATP level and hepatic oxidative damage . Polyunsaturated fatty acids such as n-3 PUFA have been reported to reduce systemic inflammation and oxidation . The WELCOME study demonstrated a mild reduction in liver fat, with omega-3 fatty acids used at a dose of 4 g/day for 15 to 18 months, but did not result in an improvement in fibrosis scores .
Viral Factors Of Hepatocarcinogenesis In Hbv Infection
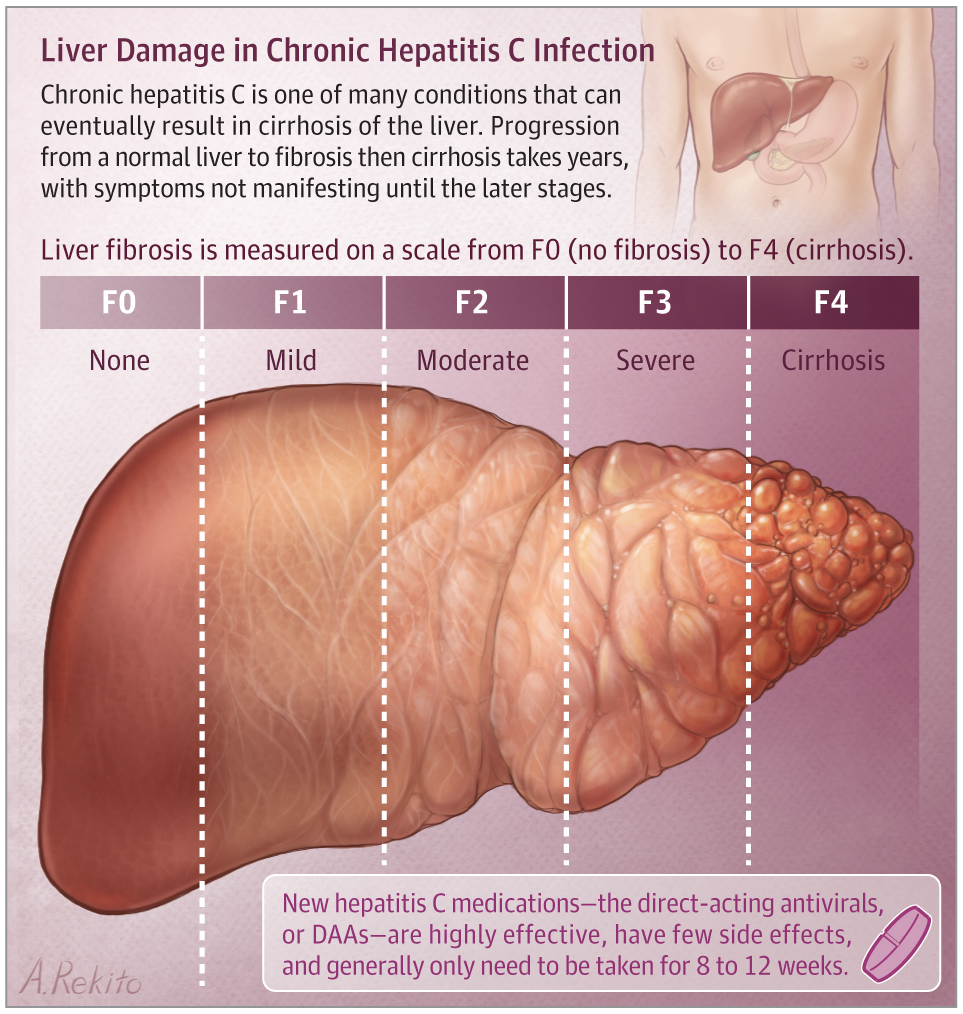
Although cirrhosis is the major risk factor for HCC in the setting of chronic hepatitis B, over the years several other risk factors have been identified, including the viral load, the presence of hepatitis B e antigen , and hepatitis B surface antigen .
The landmark REVEAL study , a large community-based study in Taiwan that included 3,653 HBsAg-positive and HCV-negative patients enrolled between 1991 and 1992, demonstrated that the risk of HCC was much greater in individuals with high serum levels of HBV DNA compared to those with low levels . In this relatively young cohort , at enrollment, 85% were HBeAg-positive, 94% had normal ALT levels, and only 2% had cirrhosis. During a mean follow-up of 11 years, HCC developed in 164 patients , with higher incidence of HCC associated with a higher HBV DNA at the study entry. Cumulative incidence of HCC of 14.9% was noted among those with HBV DNA > 1 million copies/mL, while it was much lower at 1.3% among those with an HBV DNA level < 300 copies/mL, at baseline. The HBV DNA level remained an independent predictor for HCC even after adjusting for sex, age, cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, HBeAg status, serum ALT level, and the presence of cirrhosis at the baseline, i.e., all the other known risk factors for development for HCC. It is important to keep in mind, however, that most of the individuals in this study, likely acquired HBV perinatally it is not clear if these data can be applied to those who acquired HBV as adults.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Caused By A Virus Or Bacteria
Factors Associated With Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C Patients
Patients with HCV infection may have coexisting obesity, diabetes, alcohol abuse, etc., which contribute to the development of fatty liver . In many studies a link between steatosis and a high body mass index has been reported . Adinolfi et al reported that overall, steatosis was not significantly associated with BMI, but when analysis was done by single genotype, a significant association was shown between high visceral fat distribution and grade of steatosis in HCV genotype 1 patients . This led to the idea that in patients with HCV infection there is a metabolic fat and a viral fat . Epidemiological studies have suggested a link between type 2 diabetes and chronic HCV infection. However, the presence of confounding factors such as obesity, aging, or cirrhosis precludes the establishment of a definite relationship between these two conditions.
Corticosteroids, amiodarone, methotrexate, etc.
What You Need To Know About Fatty Liver Disease
If a fatty liver disease diagnosis is made, your doctor will perform a series of tests to identify the cause of the condition. These may include a CT scan, blood test, liver enzymes test, albumin level, serum creatinine, and urine test. Blood tests may also reveal symptoms such as high calcium, low albumin, or polydipsia. Once these symptoms are present, your doctor will evaluate them to determine if you do have fatty liver disease and what course of treatment is appropriate.
Some factors that are known to cause fatty liver disease include being overweight or obese, being a woman, and being over 50 years of age. People who smoke cigarettes or use other tobacco products are at increased risk of developing this condition. There are also other risk factors that are not well understood but include genetic tendencies toward obesity and polydipsia. Other risk factors that are associated with this disease include being older than 50 years of age and having an unhealthy body mass index. Obese people are at greater risk than thinner people for developing fatty liver disease because obese people have excess fat deposits around their bellies, hips, and thighs.
About one of every five Americans has a fatty liver, which is also called steatosis. In fact, up to 9 of every 10 diabetics and people with obesity have fatty liver.
Here are the details of each of these disorders:
Recommended Reading: What Happens To Your Body When You Have Hepatitis C
The Typical Treatments Difference Between Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver And Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
If you have a fatty liver, you might be wondering what to do to treat it. Although the treatment options are limited, some of them can actually be beneficial. These include diets rich in raw vegetables, which contain many antioxidants. Eating these foods regularly also minimizes your risk of developing inflammation in the hepatic lining and the liver. Additionally, eating more vegetables helps you maintain a low glycemic index and develop a strong metabolically functioning organ.
Exercise is crucial in reducing the fat deposits in the liver. It can help with cholesterol levels and shed excess weight. Unlike other diseases, exercising does not require expensive equipment. Walking, jogging, dancing, cycling, and yoga are all effective exercises. In addition, its important to avoid alcohol, which is one of the leading causes of fatty hepatitis. This will not only improve your general health, but will allow your liver to heal and regenerate.
===> How To Cure A Fatty Liver In Just Days < < <
A high-carb diet can damage your liver and make it harder for it to perform its functions. The most common cause of liver disease is alcohol. It causes inflammation and damages the livers cells, and lowers the metabolism. As a result, the livers ability to perform its functions is weakened and eventually fails. A healthy diet will not only prevent the damage that alcohol can cause, but also help you recover from it.