Is Mild Hepatomegaly Serious
Rather than a disease in itself, hepatomegaly is a symptom or complication of other liver conditions, some of them life-threatening. For this reason, hepatomegaly is something to take seriously, as it points to an underlying problem that could be quite serious. Liver disease can develop for years with no overt symptoms at all.
Can Hepatic Steatosis Cause Complications
When NAFLD is not noticed soon enough, damage to the liver can occur. This could lead to physical and mental symptoms. Sometimes treatments can fix the problem, but when hepatic steatosis goes on too long, the entire organ can fail, or liver cancer can develop.
Liver transplant and further treatments are required but are not guaranteed to bring you back to perfect health. The liver is in charge of a lot of essential things, and when it stops working correctly, the entire body suffers.
How Common Is This Condition
NAFLD affects up to 25% of people worldwide. Most people wont have symptoms, and some may never know they have the condition. But 2% to 5% of people will experience complications from the fat in their liver. When fat leads to inflammation and cell damage in your liver, its called steatohepatitis. The non-alcoholic version is called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis .
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Garlic To Improve Overall Health
This vegetable not only adds flavor to food, but small experimental studies also show that may help reduce body weight and fat in people with fatty liver disease.
In a recent , patients with NAFLD that took 800 mg of garlic powder per day for 15 weeks saw reductions in liver fat and improved enzyme levels.
When it comes to whole food consumption, a
If you have fatty liver disease, your doctor may recommend avoiding certain foods or at least eating them sparingly. These foods generally contribute to weight gain and can increase blood sugar.
Fatty Steatosis Of The Liver
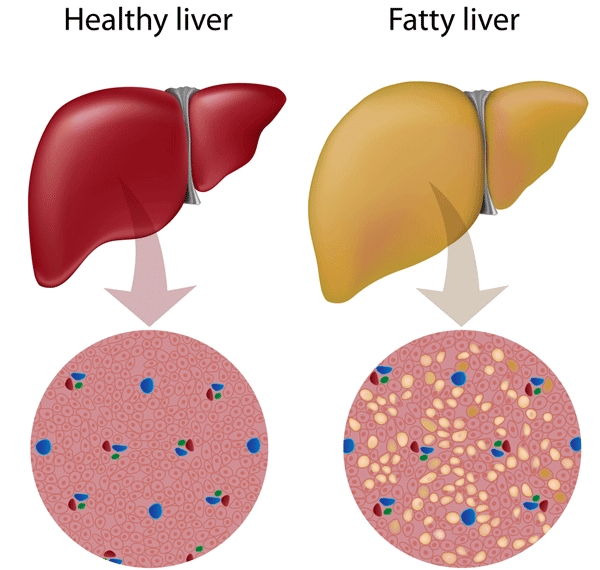
Fatty steatosis of the liver leads to an increase in the body, changes the color of the liver to yellowish or dark red. Because of the defeat of the liver with fat, the cells of the organ die, the body produces fatty cysts, the connective tissue begins to grow.
Often fatty steatosis occurs without visible symptoms, in most cases the disease is detected during ultrasound.
Progression of fatty steatosis is quite rare. If steatosis occurs together with inflammation of the liver, 10% of patients may develop cirrhosis, and in 1/3 – connective tissue grows and compacts in the organ.
, , , , , , , ,
Don’t Miss: How Can You Contact Hepatitis B
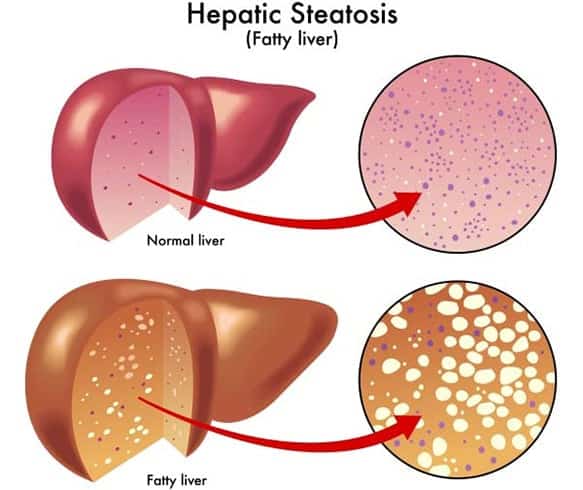
Steatosis Of The Liver
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Steatosis of the liver unites several pathological processes, which as a result lead to the appearance of fatty inclusions in the liver tissues.
This pathology is focal and diffuse. In focal steatosis, fat accumulation of fat is observed, and in case of diffuse fat, fat is located throughout the surface of the organ.
Steatosis occurs irrespective of age, but is most often diagnosed after 45 years, when the organism has been exposed to various negative factors for quite some time. From non-alcoholic steatosis, mostly women suffer, usually because of obesity. Men who abuse alcohol are more likely to be exposed to alcoholic steatosis.
Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms
Now that you know what is fatty liver, its time to take a look at some of the ways you can identify this disease by knowing the common nonalcoholic fatty liver disease symptoms. First, its important to note that it is possible to have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and exhibit no symptoms. This is actually quite common. When symptoms do occur, there are several possibilities.
Signs of a fatty liver can include:
- A build up of fluid and swelling of the legs and abdomen
- Mental confusion
Read Also: Best Medication For Hepatitis C
How To Treat Fatty Liver
We have to disconnect the mobile from the battery charger, i.e. introduce less energy, and use it more, i.e. increase energy consumption.
Diet and exercise are therefore the cornerstones of therapy. The aim should not be a rapid weight loss , but a lasting change in eating habits and lifestyle.
The patient should be taught to reduce the calories in the diet , but also to choose appropriate foods.
Saturated fats and rapidly absorbed simple sugars should be reduced.
A useful tip is to Google Glycemic index of foods and prefer those with a low index.
Another important measure is to reduce foods high in fructose , as fructose greatly increases hepatic steatosis.
How A Liver Becomes Fatty
It is unclear how a liver becomes fatty. The fat may come from other parts of your body, or your liver may absorb an increased amount of fat from your intestine. Another possible explanation is that the liver loses its ability to change fat into a form that can be eliminated. However, the eating of fatty foods, by itself, doesnt produce a fatty liver.
Recommended Reading: Is There Medicine For Hepatitis B
Hepatic Steatosis Hepatic Resection And Liver Transplantation
Macrovesicular steatosis is an important criterion defining extended-criteria donor organs. Several studies have reported a poor impact of steatosis on postoperative morbidity and mortality after liver resection. A national analysis of the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients demonstrated that macrovesicular steatosis of greater than 30% was an independent predictor of reduced 1-year graft survival. Steatotic livers are particularly vulnerable to ischemia/reperfusion injury, resulting in an increased risk of postoperative morbidity and mortality after liver surgery, including liver transplantation. In a retrospective review of 450 living liver donors who underwent right hepatectomy, a mild degree of hepatic steatosis was associated with higher postoperative peak aspartate and alanine aminotransferase values. Furthermore, biliary complications remain a persistent problem in orthotopic liver transplantation. The presence of macrovesicular steatosis in 20% to 50% of a liver graft emerged as a newly defined risk factor for postoperative biliary complications in 175 adult patients undergoing living donor liver transplantation. Thus, hepatic steatosis poses a challenge after liver resection or transplantation.
Metabolic Syndrome And Fatty Liver Disease
Many researchers now believe that metabolic syndrome a cluster of disorders that increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease and stroke plays an important role in the development of fatty liver.Signs and symptoms of metabolic syndrome include:
- obesity, particularly around the waist
- high blood pressure
- one or more abnormal cholesterol levels high levels of triglycerides, a type of blood fat, or low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, the good cholesterol
- resistance to insulin, a hormone that helps to regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
Of these, insulin resistance may be the most important trigger of NASH. Because the condition can remain stable for many years, causing little harm, researchers have proposed that a second hit to the liver, such as a bacterial infection or hormonal abnormality, may lead to cirrhosis.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody Mean
Symptoms Of Fatty Liver Disease
A fatty liver produces no symptoms on its own, so people often learn about their fatty liver when they have medical tests for other reasons. NASH can damage your liver for years or even decades without causing any symptoms. If the disease gets worse, you may experience fatigue, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, weakness and confusion.
Hepatic Steatosis: Lifestyle And Prevention
Liver diseases can be prevented primarily by avoiding a sedentary lifestyle, practicing regular physical activity and following a balanced diet, rich in vegetable proteins, whole grains, fish and white meat, low in red meat and free of sweets and alcohol.
The Mediterranean diet is particularly indicated to decrease weight and reduce the amount of steatosis.
There are no drugs on the market able to block the degenerative process of non-alcoholic steatosis in liver fibrosis.
The modification of lifestyle is therefore a fundamental intervention and must pass through an improvement of diet, the regular practice of physical activity and the elimination of alcohol.
Also Check: How Much Does It Cost To Treat Hepatitis C
Greens To Prevent Fat Buildup
Compounds found in spinach and other leafy greens may help fight fatty liver disease.
A 2021 study found that eating spinach specifically lowered the risk of NAFLD, possibly due to the nitrate and distinct polyphenols found in the leafy green. Interestingly enough, the study focused on raw spinach, as cooked spinach did not have the same strong results. This could be because cooking spinach may result in lowered polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity.
Limit Your Contact With Environmental Toxins
Not only does your liver process chemicals that enter your body through your mouth, but it also processes chemicals that enter through your nose and skin.
Some everyday household products contain toxins that can damage your liver, especially if you come into contact with them regularly.
To prevent long-term damage to your liver, opt for organic cleaning products and techniques to clean your home. Avoid using pesticides and herbicides in your yard, or take precautions to avoid inhaling chemical fumes.
If you must use chemicals or aerosols inside the house to paint, for instance make sure your space is well ventilated. If thats not possible, wear a mask.
Also Check: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Can Fatty Liver Disease Make It Harder For Me To Lose Weight
Fatty liver disease should not make it harder for you to lose weight. However, you will have to follow a strict eating and exercise plan in order to lose weight. The doctors at Johns Hopkins may need to treat your fatty liver disease with a combination of medications in order to achieve adequate glucose control and normal cholesterol levels.
Request an Appointment
Ways To Reverse A Fatty Liver
Fatty liver occurs when excess fat accumulates inside liver cells. This means normal, healthy liver tissue becomes partly replaced with fatty tissue. The fat starts to invade the liver, gradually infiltrating the healthy liver areas, so that less and less healthy liver tissue remains. The fatty liver has a yellow greasy appearance and is often enlarged and swollen with fat.
Fatty liver is now recognised as the most common cause of abnormal liver function test results in the USA, UK and Australia. Around one in five people in the general population, in the USA and Australia has a fatty liver. Fatty liver is usually associated with abdominal obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. If severe, it can eventually lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Cause Fatty Liver
Expression Of The Fatty Liver Disease Gene Depends On Environment
Your DNA an abbreviation short for deoxyribonucleic acid is a code that makes you human and determines your individual traits. Some traits, such as eye color, are influenced by just two genes and based on your inherited genes, will remain set in stone for your lifetime.
Other traits, such as personality, are much more complex and described as polygenic traits since they are influenced by a large number of different genes. An individuals personality like introversion or open-mindedness is highly influenced by both genes and the environment. For example, a naturally introverted child may become more extroverted over time in response to positive experiences with family and peers.
The expression of the genes contributing to fatty liver disease is comparable to more complex traits, like personality. Inheriting certain forms of the gene may predispose you to fatty liver disease under certain environmental conditions.
Living With Fatty Liver Disease
If you are living with fatty liver disease, learn as much as you can about your condition and work closely with your medical team. Since many medications can harm your liver, always let all your health care providers know about any medications you are taking. These include OTC drugs, dietary supplements, and vitamins. Other ways to manage fatty liver disease include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and continuing to avoid alcohol.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis From Saliva
The Fatty Liver: How It Accumulates And Why Its Dangerous
It is normal for a certain amount of fat to accumulate in the liver, but when the percentage exceeds 5% of the organs weight, then the disease develops.
Fat accumulates because too much energy reaches the liver in the form of fatty acids, which come from excess sugar and fat .
These acids are toxic to the liver because they oxidise and damage the mitochondria, the batteries that produce the energy needed for the life of the cell.
The liver tries to protect itself by neutralising and accumulating the fatty acids in the form of triglyceride droplets.
Why Is Fatty Liver Disease Bad
In most cases, fatty liver disease doesnt cause any serious problems or prevent your liver from functioning normally. But for 7% to 30% of people with the condition, fatty liver disease gets worse over time. It progresses through three stages:
Cirrhosis of the liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is a result of severe damage to the liver. The hard scar tissue that replaces healthy liver tissue slows down the livers functioning. Eventually, it can block liver function entirely. Cirrhosis can lead to liver failure and liver cancer.
You May Like: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis B
The Most Effective Fatty Liver Treatment: Lifestyle Changes
The good news is that the most effective treatment so far for fatty liver disease does not involve medications, but rather lifestyle changes. The bad news is that these are typically hard to achieve and maintain for many people. Heres what we know helps:
- Lose weight. Weight loss of roughly 5% of your body weight might be enough to improve abnormal liver tests and decrease the fat in the liver. Losing between 7% and 10% of body weight seems to decrease the amount of inflammation and injury to liver cells, and it may even reverse some of the damage of fibrosis. Target a gradual weight loss of 1 to 2 pounds per week, as very rapid weight loss may worsen inflammation and fibrosis. You may want to explore the option of weight loss surgery with your doctor, if you arent making any headway with weight loss and your health is suffering.
- It appears that aerobic exercisealso leads to decreased fat in the liver, and with vigorous intensity, possibly also decreased inflammation independent of weight loss.
- Eat well. Some studies suggest that the may also decrease the fat in the liver. This nutrition plan emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, replacing butter with olive or canola oil, limiting red meat, and eating more fish and lean poultry.
- Drink coffee, maybe? Some studies showed that patients with NAFLD who drank coffee had a decreased risk in fibrosis. However, take into consideration the downsides of regular caffeine intake.
Image: magicmine/Getty Images
What Are The Possible Complications Of Non
- Steatohepatitis. Up to 20% of people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may develop non-alcoholic steatohepatitis , a state of chronic inflammation of the liver. This can do progressive damage to your liver, eventually resulting in scarring of the tissues .
- Pregnancy complications. NAFLD in pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of complications for both mother and baby. In particular, pregnant mothers are three-to-four times more likely to experience hypertensive complications such as preeclampsia.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
How Is It Treated
There are no medical treatments yet for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly may help prevent liver damage from starting or reverse it in the early stages.
- See a doctor who specializes in the liver regularly
- Talk to your doctor about ways to improve your liver health
- Lose weight, if you are overweight or obese
- Lower your cholesterol and triglycerides
- Control your diabetes
Maintain A Healthy Weight
Sticking to a healthy, plant-based diet and getting regular exercise can keep fat from building up in your liver. That’s because the major risk factors for NAFLD are obesity and diabetes, both of which are tied to our weight.
It’s estimated that rates of NAFLD may be 90% in obese people and 50% in people with diabetes. Because obesity and diabetes are so prevalent in developed countries, approximately 30% of adults in the developed world have NAFLD. Fortunately, some of this damage appears to be reversible if you take off the extra pounds.
If you are overweight or obese, the American College of Gastroenterology advises that losing 10% of your body weight will have a positive impact on your liver.
Also Check: Hepatic Artery Infusion Survival Rate
Fate Of Fatty Acids In The Liver
In the fasting state, adipocyte TAG is hydrolyzed to release FFAs, which are transported to the liver where they can serve as substrates for mitochondrial -oxidation. -oxidation of fatty acids is a major source of energy needed to maintain liver viability during fasting. It is also the source of the ketone bodies, acetoacetate and acetone. These are released into the blood and are essential fuel sources for peripheral tissues, when glucose is in short supply. Defects in hepatic -oxidation cause microvesicular steatosis of the liver, increase in oxidative stress due to extramitochondrial oxidative stress. ROS and peroxidation products lead to cytotoxic events, release of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of hepatic stellate cells and fibrosis.