What Are The Types Of Hepatitis
There are many types of hepatitis which cause symptoms that range from mild to very serious.
Five types of viral hepatitis are:
- hepatitis A an illness that can last from a few weeks to 6 months
- hepatitis B a serious infection that can lead to liver damage
- hepatitis C a disease that is now easily treatable
- hepatitis D a disease that only affects people infected with hepatitis B, and is a rarer type of hepatitis in Australia
- hepatitis E a short-term illness that can be severe in pregnant women, but is rare in Australia
There are other types of hepatitis that are not infectious, including:
- autoimmune hepatitis
Having one type of hepatitis doesnt stop you from getting other types.
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute infection with hepatitis viruses. Acute infection is a short-term condition, lasting under six months. Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months.
Hepatitis B infection can be either acute or chronic. Most people who get acute hepatitis B dont end up progressing to chronic hepatitis B. By contrast, acute hepatitis C tends to develop into chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 7585 percent of adults newly infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection, according to the CDC . Others clear the infection.
When you get acute hepatitis C you may or may not have symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic, meaning people dont notice the symptoms. Symptoms are only noticeable in 15 percent of cases of acute hepatitis C.
Also Check: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Understanding Changes In Biomarkers During Disease Progression
Understanding the changes in HBV biomarkers over the course of a persons infection and recovery is key to interpreting the test results. Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 depict the typical biomarker changes over the course of hepatitis B disease.
Figure 3-1. Typical serologic course of acute hepatitis B to recovery
Figure 3-2. Typical serologic course of the progression to chronic hepatitis B
Acute, resolved, and chronic hepatitis BApproximately 90% of people > 5 years of age with acute hepatitis B will spontaneously clear their infection . People with resolved hepatitis B will remain positive for total anti-HBc and develop anti-HBs that protect against future HBV infection . Chronic hepatitis B is defined as an HBV infection lasting > 6 months. During the typical course of chronic infection, the total anti-HBc and HBsAg markers will always be present, whereas anti-HBc IgM will disappear . Hepatitis B envelope antigen and hepatitis B envelope antibody are variably present. HBV DNA levels vary during the course of chronic infection. Any detectable HBV DNA level is considered positive for surveillance purposes.
Among people with previously inactive hepatitis B , laboratory evidence of reactivation includes meeting any one of the following criteria:
- HBV DNA is now detectable or
- HBsAg test conversion occurs .
You May Like: Hepatitis C Rapid Test Kit
Are There Complications From Hepatitis A
In extremely rare cases, hepatitis A can lead to acute liver failure. This complication is most common in older adults and people who already have chronic liver disease. If this occurs, you will be hospitalized. Even in cases of liver failure, a full recovery is likely. Very rarely is a liver transplant required.
What Is Hepatitis C
Like hepatitis B, the hepatitis C virus spreads from person to person through blood or other body fluids, and can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer. The most common way people become infected is by sharing drug paraphernalia such as needles and straws. People also can get hepatitis C from unprotected sex with an infected partner. And it can be passed from an infected mother to her unborn baby.
Hepatitis C is the most serious type of hepatitis. Its now one of the most common reasons for liver transplants in adults. Scientists have been trying for decades to develop a hepatitis C vaccine, but none has been successful yet. Fortunately, medicines can now treat people with hepatitis C and cure them in most cases.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Go Away By Itself
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis B And C Difference
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis From Donating Plasma
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
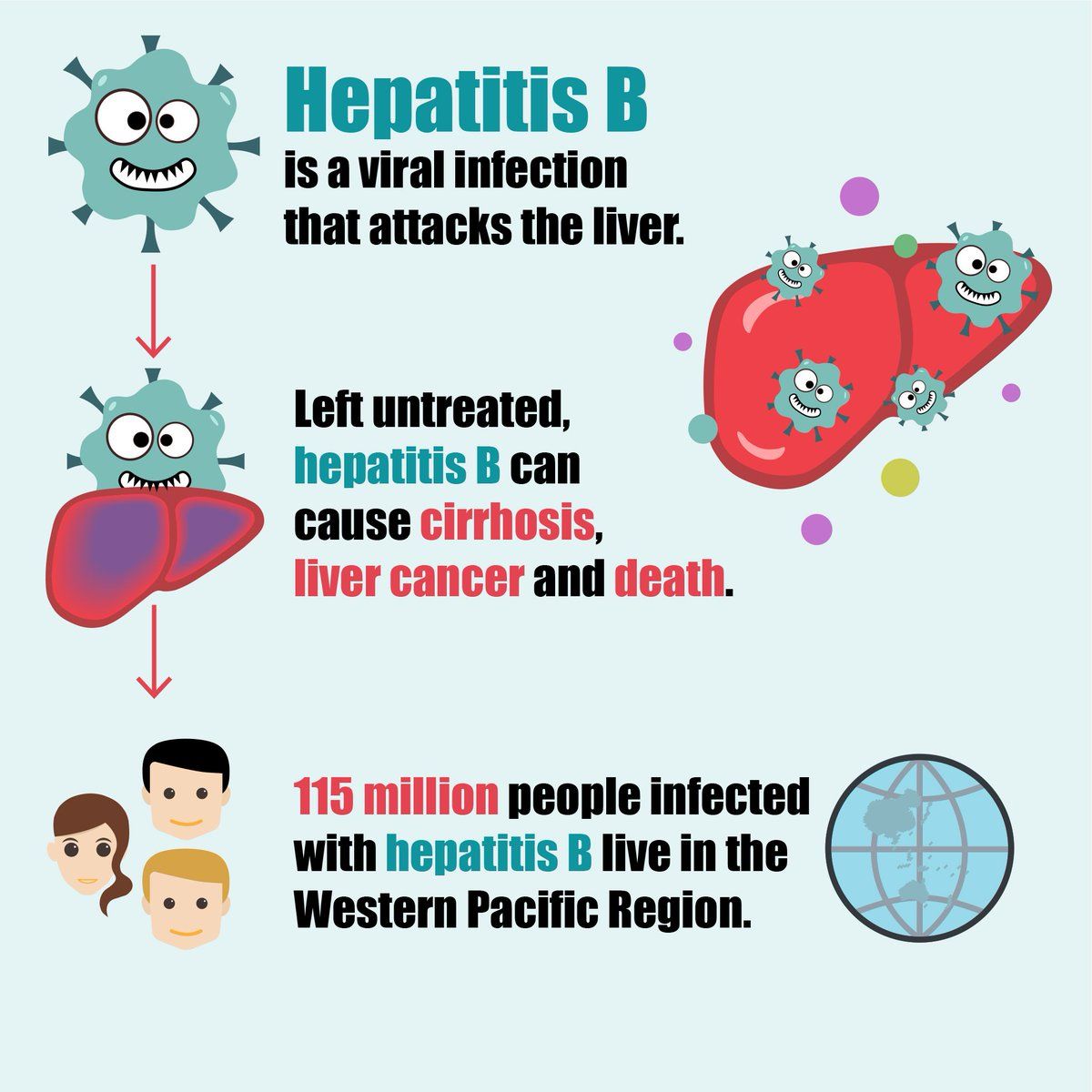
In the United States, an estimated 862,000 people were chronically infected with HBV in 2016. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2018, 3,322 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 21,600 acute hepatitis B infections. New HBV infections are likely linked to the ongoing opioid crisis in the United States.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 257 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Dont Miss: How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
What Is The Long
Children with chronic hepatitis B can lead completely normal lives, attend school, and play sports without any special arrangements, just like any other child.
A child with chronic HBV infection could be infected for life. Over the decades, the virus can cause progressive damage to the liver and lead to such complications as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
When they become older, children with hepatitis B should avoid drinking alcohol, as it can make the disease progress more quickly. Once they become sexually active, they should practice safe sex to protect their partners from infection.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis B Transferred
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
History And Physical Exam
To diagnose hepatitis, first your doctor will take your history to determine any risk factors you may have for infectious or noninfectious hepatitis.
During a physical examination, your doctor may press down gently on your abdomen to see if theres pain or tenderness. Your doctor may also feel to see if your liver is enlarged. If your skin or eyes are yellow, your doctor will note this during the exam.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis B Do
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Don’t Miss: What Is In The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Keep Personal Items Personal
Any tools or implements that may have a bit of blood on them from infected people are potential sources of hepatitis B or C transmission. Toothbrushes, nail clippers, razors, needles, and washcloths may all contain trace amounts of blood that can transmit infection. Keep personal items such as these to yourself and never use personal items that belong to others.
Causes Of Noninfectious Hepatitis
Although hepatitis is most commonly the result of an infection, other factors can cause the condition.
Alcohol and other toxins
Excess alcohol consumption can cause liver damage and inflammation. This may also be referred to as alcoholic hepatitis.
The alcohol directly injures the cells of your liver. Over time, it can cause permanent damage and lead to thickening or scarring of liver tissue and liver failure.
Other toxic causes of hepatitis include misuse of medications and exposure to toxins.
Autoimmune system response
In some cases, the immune system mistakes the liver as harmful and attacks it. This causes ongoing inflammation that can range from mild to severe, often hindering liver function. Itâs three times more common in women than in men.
Also Check: Where Do You Get Hepatitis B
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis Sexually
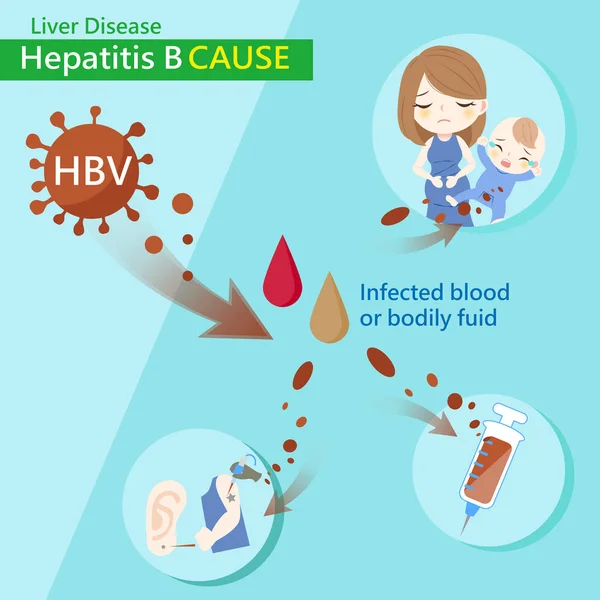
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .