What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with acute hepatitis C do have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- Dark yellow urine
- Pain in your abdomen
- Jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
What Is Acute And Subacute Hepatic Failure Without Coma
What is acute liver failure without hepatic coma?
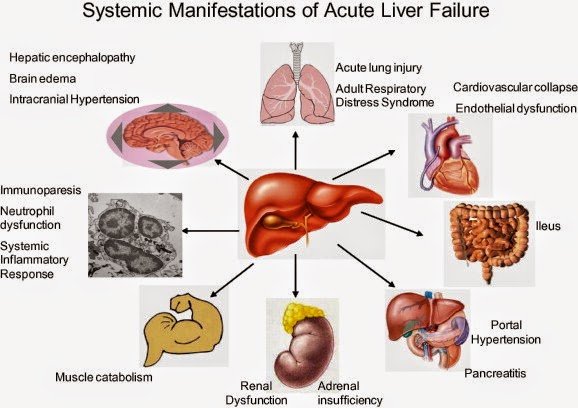
Acute liver failure is loss of liver function that occurs rapidly in days or weeks usually in a person who has no preexisting liver disease. Its most commonly caused by a hepatitis virus or drugs, such as acetaminophen. Acute liver failure is less common than chronic liver failure, which develops more slowly.
What is acute and subacute hepatic failure?
Acute liver failure is a rare disorder defined by the clinical progression of jaundice to hepatic encephalopathy in the absence of preexisting liver disease in fewer than 28 days. Subacute liver failure is defined as the occurrence of this progression in 2872 days.
How long can you live with acute liver failure?
Studies show one-year survival of 61%, two-year of 54%, and 45.4% at five years.
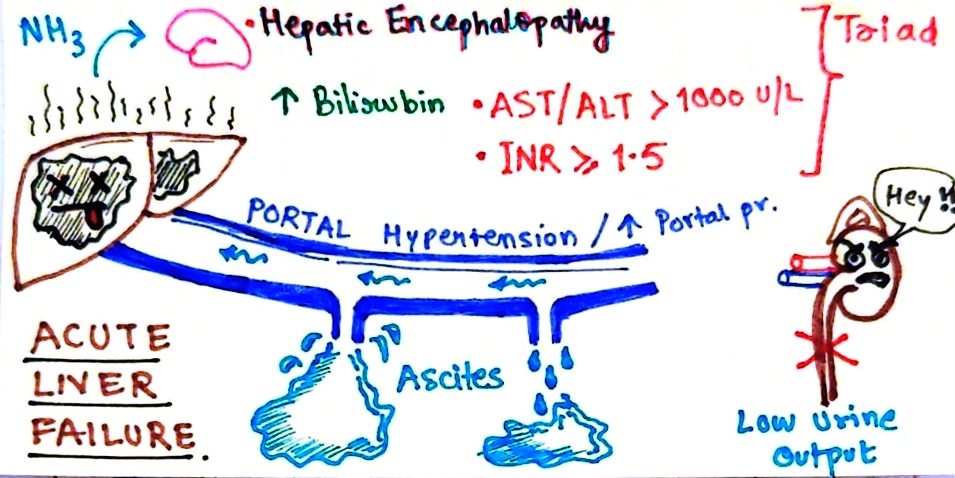
Can liver failure put you in a coma?
Hepatic encephalopathy is an altered level of consciousness as a result of liver failure. Its onset may be gradual or sudden. Other symptoms may include movement problems, changes in mood, or changes in personality. In the advanced stages it can result in a coma.
Prevention Of Hepatic Failure
One of the easiest ways to prevent liver failure is to moderate your drinking. The Mayo Clinic recommends that healthy women limit their alcohol consumption to one drink per day. Healthy men over the age of 65 should also limit their alcohol consumption to one drink a day. Men under 65 should consume no more than two drinks per day.
Other preventive measures include:
Recommended Reading: What Does Chronic Hepatitis C Mean
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C
Causes Associated With Chronic Liver Failure
Chronic liver failure is usually a result of cirrhosis or alcohol-related liver disease . The American Liver Foundation states that alcoholism is the most common cause of cirrhosis in the United States.
Usually, your liver breaks down any alcohol that you consume. But if you drink too much, your liver cant break down the alcohol fast enough. Also, toxic chemicals in alcohol can trigger inflammation in your liver and cause your liver to swell. Over time, this damage can lead to cirrhosis.
If you have hepatitis C, youre at greater risk of developing chronic liver failure or cirrhosis. The hepatitis C virus is spread through the blood. If the blood from a person with the infection enters your body, you can catch it. Needle sharing and using dirty needles for tattoos or piercings can spread hepatitis C.
According to the American Liver Foundation, around 25 percent of people in the United States with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis. Its the second leading cause of cirrhosis in the country.
Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
For clinicians treating chronic hepatitis C infection. Material covered includes recommendations for treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced persons with chronic HCV infection genotypes 1-6, based on the Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and Infectious Diseases Society of America HCV Guidance.
Track your progress and receive CE credit
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Patient Assistance Programs
What Might Complicate It
Individuals who survive one or more episodes of hepatic coma are occasionally left with residual neurologic abnormalities, such as tremor of the head or arms, asterixis, grimacing, choreatic twitching of the limbs, dysarthria, ataxia of gait, or impairment of intellectual functioning. These symptoms may worsen with repeated attacks of stupor and coma.
What Happens If Someone Has Hepatitis C And Hiv
When someone has both Hepatitis C and HIV, it is often referred to as HCV-HIV co-infection. This means that you have two infections in your body at the same time. HIV, the term for human immunodeficiency virus, is the virus that causes AIDS. You can find more detailed information about HIV and AIDS on several Web sties, including:
HCV-HIV co-infection is fairly common. Overall, about one-third of all Americans infected with HIV also have Hepatitis C. And the rate of co-infection is much higher among injection drug users. More than half of people who have HIV and use injection drugs are also infected with Hepatitis C.
People that are co-infected can be effectively treated. However, since there are two infections to deal with managing them is more complicated. There is no cure for HIV, but it can be controlled. Hepatitis C can be treated successfully. Working closely with a doctor who specializes in managing co-infections will give you the best chance for successful treatment.
There are specific risks associated with co-infection. Having HIV, in addition to Hepatitis C, does the following:
- Quickens Hepatitis C disease progression
- Triples the risk for liver disease, liver failure and liver-related death
- Increases the chance that Hepatitis C will be sexually transmitted
- Increases the chance that a mother will infect her unborn child with Hepatitis C
Read Also: Do You Ever Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Viral Hepatitis
The period of time between exposure to hepatitis and the onset of the illness is called the incubation period. The incubation period varies depending on the specific hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A virus has an incubation period of about 15 to 45 days Hepatitis B virus from 45 to 160 days, and Hepatitis C virus from about 2 weeks to 6 months.
Many patients infected with HAV, HBV, and HCV have few or no symptoms of illness. For those who do develop symptoms of viral hepatitis, the most common are flu-like symptoms including:
Also Check: Hepatitis C Symptoms How Do You Get It
Recommendations For Medical Management And Monitoring Of Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING After the initial diagnosis of acute HCV with viremia , HCV treatment should be initiated without awaiting spontaneous resolution. I, B Counseling is recommended for patients with acute HCV infection to avoid hepatotoxic insults, including hepatotoxic drugs and alcohol consumption, and to reduce the risk of HCV transmission to others. I, C Referral to an addiction medicine specialist is recommended for patients with acute HCV infection related to substance use. I, B
Patients with acute HCV infection should be treated upon initial diagnosis without awaiting spontaneous resolution, using a test and treat strategy and according to the simplified approach, if eligible. Real-world data have demonstrated a reduction in HCV viremia prevalence and incidence with unrestricted access to HCV therapy . In addition, mathematical modeling suggests that DAA treatment scale-up, especially among those at highest risk of transmission, can reduce HCV incidence and prevalence . Moreover, delay introduced by waiting for spontaneous clearance may be associated with loss to follow up.
There is no need to alter concomitant medications that are metabolized by hepatic enzymes unless there is concern for developing acute liver failure . Acetaminophen and alcohol consumption should be avoided during acute HCV infection .
What Is Hepatic Coma
Hepatic coma can be defined as the sum of neuropsychiatric disorders during liver failure of different origin. According to the patho-genesis hepatic coma can be divided in exogenous hepatic coma as sequelae of liver cirrhosis and endogenous hepatic coma caused by severe viral hepatitis or by intoxication.
Also Check: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis C
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
What About Sex And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be spread through sexual intercourse, but the risk is considered to be low. It is extremely rare among monogamous couples, meaning couples who only have sex with one another. The risk increases if you:
- Have multiple sex partners
- Have a sexually transmitted disease
- Are infected with HIV
There is no evidence that Hepatitis C is spread by oral sex.
To reduce the chance of getting or giving Hepatitis C through sexual contact, follow these guidelines:
- Use latex condoms every time you have sex, particularly if you have:
- More than one partner
- Rough sex that might make one of you bleed
- Sex during your or your partners menstrual period
- Sex when you or your partner has an open sore on either of your genitals
Don’t Miss: What Is The New Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as types of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Management Of Acute Hcv Infection
Acute hepatitis C infection is most often asymptomatic and frequently develops into chronic infection. Case reports of acute hepatitis C have increased in the US since 2010 and have most often been associated with parenteral exposures to blood or body fluids . Although HCV infection is primarily associated with injection drug use, certain behaviors primarily among men who have sex with menare risk factors for transmission . The syndemic of opioid use disorder and HCV and HIV transmission contributes to the burden of disease in certain populations .
Read Also: Which Hepatitis Is The Worst
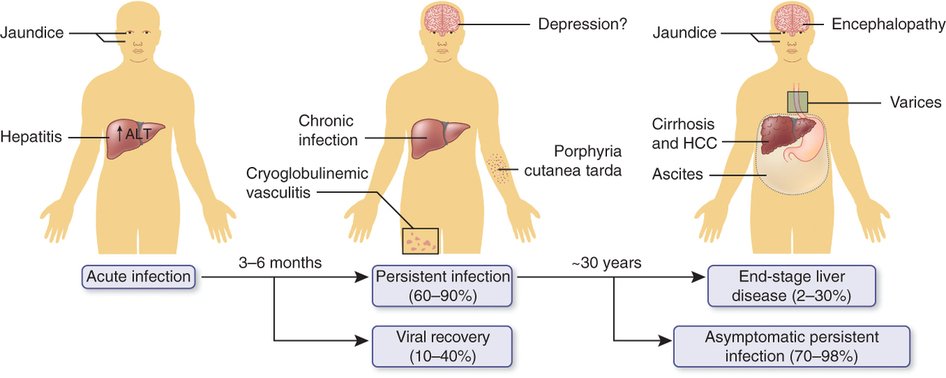
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Relationship Of Symptoms And Spontaneous Clearance
Overall, when combining data from multiple historical studies, approximately 25 to 35% of person with acute HCV infection have spontaneous clearance of HCV. The rates of spontaneous clearance are significantly lower in persons who are Black and in those individuals who have HIV coinfection. In contrast, rates of spontaneous clear are higher in females and in persons who acquired HCV in childhood. It has also been demonstrated that patients who present with symptomatic acute HCV infection and jaundice have higher rates of spontaneous clearance of HCV, in the range of 35 to 50%. The presence of jaundice is believed to reflect hepatic inflammation caused by a more robust initial immune response against HCV.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Test Kit Walgreens
You Have An Inflammation Of The Liver That Is Caused By Viruses
If the liver is inflamed, this can cause various symptoms. The skin and eyes may turn yellow. The stool may be colorless and urine may be very dark. You may feel feeble and tired. You may be seriously ill. You may feel nauseous. You may also get a high temperature and sore muscles. It is also possible to have other symptoms. The liver inflammation also sometimes causes no symptoms at all.
Severe Acute Liver Injury
Fifty severe acute liver injury events occurred during follow-up , with a median time from azole initiation of 22 days . We observed 41 severe acute liver injury events among fluconazole initiators , 6 among ketoconazole initiators , 0 among itraconazole initiators , 2 among voriconazole initiators , and 1 among posaconazole initiators . Among the 50 patients who developed severe acute liver injury, 1 was subsequently hospitalized for acute liver injury within 6 months of the event, and 9 died within 6 months.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
Read Also: What Medication Cures Hepatitis C
Drg Mapping Rules For B1710
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patient’s primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient’s primary diagnostic code is B17.10, look in the list below to see which MDC’s “Assignment of Diagnosis Codes” is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patient’s discharge date.
Recommended Regimens For Patients With Acute Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING Owing to high efficacy and safety, the same regimens that are recommended for chronic HCV infection are recommended for acute infection. IIa, C
A number of studies have evaluated DAA treatment of acute HCV infection. Small single-arm, uncontrolled studies have evaluated 6 or 8 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir. One such study demonstrated 100% SVR with 8 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir among 27 men with acute HCV and HIV-coinfection . Investigators conducting another study evaluated 6 weeks of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir in a similar cohort . Among participants with genotype 1 infection, 79% achieved SVR12 71% of those with genotype 4 infection achieved SVR12 with this shortened regimen. Among the 6 individuals whose treatment did not lead to SVR12, there were 3 relapses . Three participants achieved SVR4 but were lost to follow-up . A phase 2 study followed a similar treatment protocol among 20 individuals with genotype 1 HCV monoinfection, all of whom achieved SVR12 .
An open-label, single-arm, multicenter pilot study evaluated the efficacy of 6 weeks of the pangenotypic regimen glecaprevir/pibrentasvir among persons with acute/recent HCV infection . SVR12 was 90% a single virological failure occurred in a man with genotype 1a, HIV coinfection, and a viral load of 7.7 log10 IU/mL. This patient was successfully retreated .
- Related References
Recommended Reading: The Effects Of Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Life Expectancy And Prognosis
Can you die from hepatitis? Technically, the complications of chronic hepatitis C are fatal. About 30,000 people in the U.S. die each year from cirrhosis.
How long can you live with untreated hep C? The disease affects everyone differently, so thereâs no rule. But about 70% to 80% of people with will get chronic help C. Within 20 years, about 20% to 30% of those people will get cirrhosis. From there, it depends on what type of cirrhosis you have, your treatment, and if you can get a liver transplant.
Can hepatitis C go away on its own? Yes. From 15% to 20% of people with hep C clear it from their bodies without treatment. Itâs more likely to happen in women and people who have symptoms. But it usually happens between 4 and 18 months after symptoms start.
American Liver Foundation Hep C 123: âFrequently Asked Questions.â
Gastroenterology: âExtrahepatic morbidity and mortality of chronic hepatitis C.â
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âHepatitis C.â
Therapeutic Advances in Infectious Disease: âExtrahepatic Manifestations of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.â
The Hepatitis C Support Project: âAn Overview of Extrahepatic Manifestations of Hepatitis C.â
BioDrugs: âManagement of hepatitis C virus-related arthritis.â
Frontiers in Endocrinology: âDiabetes and Hepatitis C: A Two-Way Association.â
U.S. National Library of Medicine: âAtherosclerosis,â âPreventing Hepatitis B or C.â
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr