Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
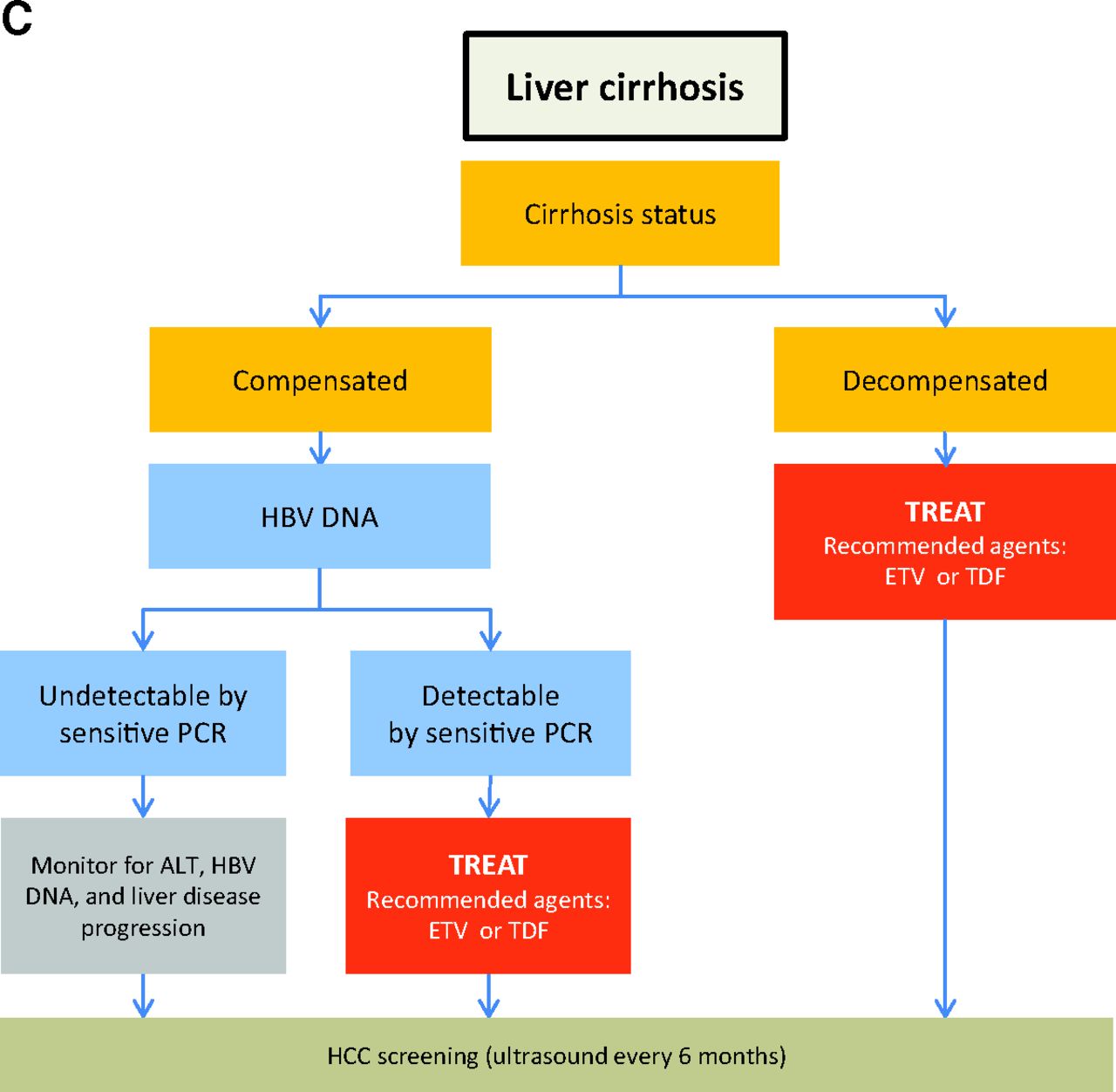
Phases Of Chronic Hbv Infection
The course of chronic HBV infection is characterized by fluctuations in HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels, reflecting variations in the balance between HBV replication and host immune response. Traditionally, three clinical parameters are used to define the four phases of chronic HBV infection .
Phases of chronic HBV infection.3 Traditionally, phases of chronic HBV infection are defined by HBeAg status, serum HBV DNA, and ALT levels. Quantitative HBsAg levels are different in each phase and are generally highest in the immune tolerant phase and lowest in the inactive carrier phase. Although most patients progress from one phase to the next, not all patients go through each phase reversion to an earlier phase can occur. Immune tolerant: HBeAgpositive, high serum HBV DNA but normal ALT levels. Immune clearance/HBeAgpositive chronic hepatitis: HBeAgpositive, high serum HBV DNA, and elevated ALT levels HBeAg seroconversion to antiHBe occurs after varying durations. Inactive carrier: HBeAgnegative, serum HBV DNA low or undetectable. Reactivation/HBeAgnegative chronic hepatitis: HBeAgnegative, elevated levels of HBV DNA and ALT in serum, HBV precore and/or basal core promoter variant often present. Abbreviation: HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen.
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
You May Like: How To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis B
There are two types of hepatitis B infection: acute and chronic.
Acute
An acute infection happens at the beginning, when you first get infected with hepatitis B. Many people are able to clear it from their bodies and recover. In fact, this is true of about 4 in 5 adults who are infected.
Chronic
If you are not able to clear the infection within six months or longer, you have chronic hepatitis B. It is chronic hepatitis B that leads to inflammation and the serious, and possibly fatal, illnesses of cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer. Treatment can slow disease progress, reduce the chance of liver cancer and increase your chances of surviving.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Hepatitis Vaccine Last
Mechanisms Of Action Of Na And Ifn
NAs inhibit reverse transcription of pregenomic RNA and synthesis of HBV DNA in the cytoplasm and have no direct effect on cccDNA. IFN has both antiviral and immunomodulatory activities, although the precise mechanisms of action remain unclear. Recent studies suggest that IFN may enhance cccDNA degradation and exert epigenetic modification of cccDNA transcription,4 explaining its greater effect on viral protein production and higher rates of HBeAg and hepatitis B surface antigen loss compared to NAs.
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis C Ab Non Reactive Mean
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Because their immune systems arent fully developed, infants and young children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B, so its important to limit their exposure to the virus. All expecting women should be screened for hepatitis B. If a high viral load is detected through testing, your doctor will initiate treatment during your third trimester to reduce the likelihood that your baby will contract the disease during delivery.
Additionally, the infants of mothers with hepatitis B should receive the hepatitis B vaccination series and immune globulins at birth so they do not develop hepatitis B.
Clearing Acute Hepatitis B
Some studies suggest that up to 95% of adults with acute HBV infection will spontaneously clear the virus, usually within six months, with no lasting repercussions.
Chronic hepatitis B occurs when the immune system does not clear the virus. Around one of every 20 people acutely infected with HBV will progress to this persistent stage of infection.
Chronic hepatitis B is a slowly progressive disease in which ongoing inflammation causes the gradual scarring of the liver. This can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma .
However, the course of chronic HBV infection is not set. Some people may progress faster than others, while others may never develop overt symptoms.
Statistically speaking:
- The risk of cirrhosis in people with chronic hepatitis B is approximately 10% to 20% over 20 years, increasing to 40% after 30 years.
- The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma increases by 2% and 3% per year in people with HBV and cirrhosis. People without cirrhosis can also get it, but the annual risk drops to around 0.02%.
Read Also: What Is Severe Hepatic Steatosis
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Virological Testing For Hbv
HBV DNA quantification
This is mainly used to assess the level of virus replication in HBV-infected patients. In addition, it can be used as a crucial component to select the indications and assess the efficacy of antiviral therapy. During antiviral therapy, obtaining a sustained virological response could significantly control the progression of cirrhosis and lower the risk of HCC.53,54 The quantitative detection of HBV DNA utilizes real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction however, the detection limit varies between manufacturers reagents.
HBV genotyping
To date, at least nine HBV genotypes and one undefined genotype have been identified. Some genotypes are further divided into subtypes. The detection of HBV genotypes could help to predict the efficacy of IFN and determine the disease prognosis.5558
Detection of resistant mutants
Read Also: Signs Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Treatment Of Children With Acute Hbv Infection
Children with acute HBV infection are usually asymptomatic. Those with fulminant hepatitis, severe acute hepatitis and protracted acute hepatitis might benefit from NA treatment. Lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir and tenofovir are considered acceptable options. IFN is contraindicated . Although an optimal duration of NA treatment has not been established, it is recommended that NA treatment be continued until HBsAg clearance, or at least 3 months after HBsAg seroconversion, or 1 year after HBeAg seroconversion without HBsAg loss .
Hepatitis B And Liver Cancer
Having hepatitis B increases the risk of liver cancer. Liver cancer may develop from long-term inflammation and damage caused by a chronic HBV infection. When your liver remains in a long-term state of inflammation, cirrhosis may develop.
As scar tissue takes over the liver, the DNA in healthy cells can also change, allowing malignant tumors to develop.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a primary form of liver cancer. It occurs in about leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
While liver cancer itself has been declining in the United States, it is still a deadly cancer. According to the CDC , about 25,000 new cases of liver cancer are diagnosed in men each year, and 11,000 new cases in women. Of these, an estimated 19,000 men and 9,000 women die from the disease.
Liver cancer alone has a 10% to 14% 5-year survival rate, reports the Hepatitis B Foundation. Early detection and treatment can significantly boost this rate to 60% to 70%.
You May Like: How Can Hepatitis Be Transmitted
Inactive Hbsag Carrier State105106
This is also known as HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection. Patients are in the immune control phase. They are positive for HBsAg and anti-HBe and negative for HBeAg. HBV DNA levels are < 2,000 IU/mL, and HBsAg levels are < 1,000 IU/mL. ALT and AST levels are persistently normal . Imaging examination shows no signs of cirrhosis. Liver biopsy shows a histological activity index score < 4, or lesions are mild using other semi-quantitative scoring systems.
Patients with hepatitis B can be monoinfected or coinfected. The most common hepatitis B coinfections are:
Coinfection with HDV
A) HBV/HCV coinfection
Because they share similar transmission routes, HBV/HCV coinfection is more common in regions endemic for both viruses. The global prevalence of this coinfection ranges from 1% to 15%. Some studies have shown that HCV is usually dominant and HBV can be serologically evident or occult.
Recommendations
1 Before starting therapy with DAAs, patients infectedwith HCV should be tested for HBV coinfection usingHBsAg and for past infection using anti-HBs and anti-HBc .
2 HBsAg-positive patients who do not meet the criteriafor HBV treatment should receive antiviral prophylaxisfor HBV for at least 12 weeks after hepatitis C treat-ment .
3 In HBsAg-negative and anti-HBc-positive patients,serum ALT levels should be monitored monthly. If ALTis elevated, the patient should be retested for HBsAgand HBV DNA .
B) HBV/HIV coinfection
Recommendations
References
Clinical Guidelines For Children With Chronic Hepatitis B
In general, the clinical guidelines for children are the same as for adults – visits are usually scheduled every six months or once a year. Most children do not need drug treatment, but they still need to be monitored regularly to make sure they remain healthy and to detect any problems with their liver as soon as possible. Visits will include a physical exam, blood tests, and possibly an imaging study of the liver .
AASLD guidelines provide guidance for treating children under the Updated Recommendations on the Treatment of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B, section 9A.
The Hepatitis B Foundation convened the first Pediatric HBV Workshop and invited the nations leading pediatric liver specialists to develop the first national recommendations for children living with hepatitis B to ensure that they receive the best care possible. These recommendations have been published in highly respected, peer-reviewed journals and provide expert guidance for the care of infected children.
Hepatitis B Foundations Clinical Guidelines for Pediatric HBV
HBF’s Pediatric HBV Screening and Monitoring Recommendations Published in Pediatrics in November 2009Haber BA, Block JM, Jonas MM, Karpen SJ, London WT, McMahon BJ, Murray KF, Narkewicz MR, Rosenthal P, Schwarz KB. Recommendations for screening, monitoring, and referral of pediatric chronic hepatitis B. Pediatrics 124:e1007-13.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Efficacy And Safety Of Available Treatments
Currently, two types of treatment, IFNs and NAs, are approved for chronic HBV infection. The virologic responses to these therapies are summarized in Table Table11.13, 24, 25 Pegylated IFNs have a more convenient dosing schedule and improved efficacy. Among the NAs, entecavir , TDF, and tenofovir alafenamide are preferred because of their potent antiviral activity and high barrier to antiviral resistance. A 1year course of pegylated IFN results in higher rates of HBeAg seroconversion and HBsAg loss than the same duration of ETV, TDF, or TAF therapy in patients who are HBeAgpositive despite lower rates of undetectable HBV DNA . Similarly, in patients who are HBeAgnegative, a 1year course of pegylated IFN results in a higher rate of HBsAg loss than the same duration of ETV, TDF, or TAF therapy despite a lower rate of undetectable HBV DNA . Response to IFN is more durable, and rates of HBeAg and HBsAg loss continue to increase after cessation of treatment, whereas viral relapse is universal when NA is discontinued after 1 year of therapy.
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Also Check: When Should You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Is Hepatitis B Preventable
Chronic hepatitis B infection affects at least 250 million people worldwide, causing over 880,000 deaths annually. It is also the major cause of liver cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States.
Unlike its cousin hepatitis C, hepatitis B can be prevented with vaccines. If you are accidentally exposed to the virus, there are also drug therapies you can takeâcalled postexposure prophylaxisâto avert the infection.
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
Also Check: What Can Cause Hepatitis B
Optimal Duration Of Na Treatment
There is no finite duration of NA treatment. In the clinical trials, NAs are usually administered for 48 weeks or more. HBeAg seroconversion is widely accepted as a therapy endpoint. The 2012 EASL guidelines and 2015 APASL guidelines recommend that NA treatment be continued for at least one year after HBeAg seroconversion occurs . In the patients with HBeAg-negative hepatitis, the continuation of NA treatment until HBsAg loss is recommended due to the high relapse rate after discontinuation .