How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Acute Hepatitis
Baby Boomers Are More Likely Than Other Age Groups To Have Hepatitis C
Baby boomers, a.k.a. people born between 1945 and 1965, are five times more likely to have hepatitis C than the rest of the population . Transmission of hepatitis C reached its peak in the 1960s through the 1980s, before regular screenings for the virus became common, which is when most Boomers living with the disease today likely contracted it. Health experts recommend that everyone in this age group be tested for hepatitis C even if they donât exhibit symptoms.
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do

Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Recommended Reading: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine 2 Dose
Hepatitis B Vaccination Within 24 Hours Of Birth Prevents Mother
- Women who are living with hepatitis B can transmit the virus to their newborns during birth .
- MTCT of the hepatitis B virus is the primary source of chronic infections worldwide.
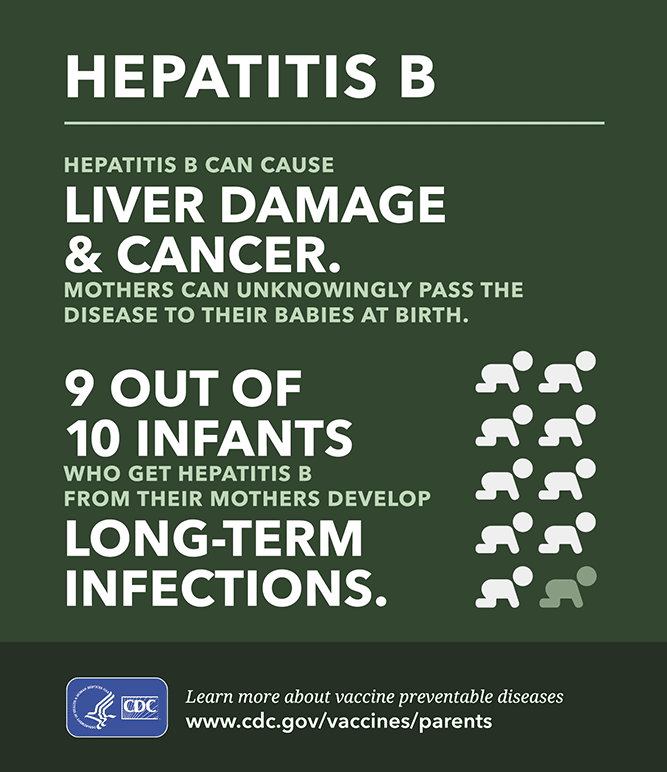
- If not vaccinated, 9 out of 10 infants infected with HBV at birth will progress to chronic HBV infections.
- In 2021, over half of all newborns worldwide were not protected by a universal hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
Yellow Eyes And Skin Are Common Symptoms Of Acute Hepatitis
Unlike chronic hepatitis, acute hepatitis quickly presents clear signs. These include pale stool, dark urine, fatigue, loss of appetite, and flu-like symptoms. One of the tell-tale symptoms of hepatitis is jaundice, which is characterized by yellowish skin or eyes. This occurs when bilirubin, an orange-colored waste material produced by the normal breakdown of red blood cells, builds up in the blood because the liver isnât functioning properly.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
How Can I Contract Hepatitis B
You can contract hepatitis B by coming into contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis B include:
Getting a manicure, pedicure, tattoo, piercing, or acupuncture with improperly sterilized tools
Having sexual contact with an infected partner
Giving first aid to, or receiving it from, an infected person
Receiving a medical or dental procedure with contaminated equipment
Sharing personal grooming items with an infected person
Hepatitis B Facts And Figures
Hepatitis B is a global public health threat and the worlds most common serious liver infection. It is up to 100 times more infectious than the HIV/AIDS virus. It also is the primary cause of liver cancer , which is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths in the world.
Hepatitis B Around the World
- Two billion people have been infected with the hepatitis B virus .
- Approximately 1.5 million people become newly infected each year.
- Almost 300 million people are chronically infected.
- Approximately 10% of infected individuals are diagnosed.
- An estimated 820,000 people die each year from hepatitis B and related complications such as liver cancer.¹
- Approximately two people die each minute from hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B In the United States
1. In 2019, there were approximately 820 000 people who died from hepatitis B-related causes globally: Web Annex 1. Key data at a glance. In: Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021. Accountability for the global health sector strategies 20162021: actions for impact. Geneva: World Health Organization 2021. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Recommended Reading: Genotype 3 Hepatitis C Treatment
Compliance With Accelerated Vs Standard Vaccination Schedules In Different Populations
Table 2Overview of hepatitis B vaccine uptake according to vaccination schedule, in different atrisk populations
| Ref. | |
|---|---|
| MSM, IVDU, CSW and STI | 0 1 6 |
*Schedule expressed in months 0 1/4 3/4 therefore corresponds to 0.7.21days type of vaccination schedule: coded as S , SS , A or SA parentheses indicate schedules without the final dose numbers and percentages either reported in the paper, or calculated from the reported values
SW/MSM/Multiple partners/STI clinic attendants
Several studies have reported being able to administer three doses of hepatitis B vaccine to a higher proportion of the population targeted, when an accelerated or a superaccelerated schedule was used, at least the primary part of it. Unfortunately, few of these studies report immunogenicity data this is mainly due to the difficulties to administer three vaccine doses, and thus the low proportion that can actually be tested afterwards.39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46
A recent paper that did report immunogenicity data studied a shortened standard schedule as an alternative option, in a setting where other strategies are used to improve the compliance. Even if the 0.1.4months schedule failed to significantly improve the compliance, it offered equal protection within a shorter interval.47
Drug users
Dosage varies according to age and type of vaccine used: follow manufacturers instructions.
Child: one dose = 5 to 10 micrograms
Adult: one dose = 10 to 20 micrograms
- Child, adolescent, adult: schedule 0-1-6
Who Is Most At Risk For Chronic Disease
The likelihood that an HBV infection will become chronic depends upon the age at which a person becomes infected, with young children who become infected with HBV being the most likely to develop chronic infections.
About 90% of infants infected during the first year of life develop chronic infections 30% to 50% of children infected between one to four years of age develop chronic infections. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood die from HBV-related liver cancer or cirrhosis. About 90% of healthy adults who are infected with HBV will recover and be completely rid of the virus within six months.
You May Like: How Hepatitis C Virus Spread
High Level Of Protection: The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is the mainstay of hepatitis B prevention. Safe and effective vaccines are available that offer high levels of protection and most countries in Europe have implemented a universal vaccination programme.
With evidence of on-going transmission and continuing importation of cases, these vaccination programmes are essential in order to achieve the target of hepatitis elimination by 2030.
In addition to vaccination programmes the implementation of blood safety strategies and safe injection practices can prevent transmission of HBV. Safer sex practices can also protect against transmission.
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Causes
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating viruses. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
What Are Warnings And Precautions For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Warnings
This medication contains the hepatitis b vaccine. Do not take Engerix B or Recombivax HB if you are allergic to the hepatitis b vaccine or any ingredients contained in this drug.
Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center immediately.
Contraindications
- See What Are Side Effects Associated with Using Hepatitis B Vaccine?
Long-Term Effects
- See What Are Side Effects Associated with Using Hepatitis B Vaccine?
Cautions
- Not protective against hepatitis A, C, or E
- Gluteal muscle injection is not recommended
- Heptavax B is no longer used in the US
Pregnancy and Lactation
- Use the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy with caution if the benefits outweigh the risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies are not available, or neither animal nor human studies were done.
- It is not known if the hepatitis B vaccine is excreted in breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
Hepatitis B C And D Can Lead To Chronic Liver Disease Cirrhosis And Liver Cancer
Many people can continue to have a healthy and normal life without realising their liver is being damaged. It is essential that, if you are at risk, you see your doctor regularly and get checkups. Taking care of yourself is also very important, in addition to getting vaccinated, avoid excess alcohol and do not smoke, take care not to take medications that can cause liver injury. Focus on a healthy diet, exercise and stay lean.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Baby
Does Hepatitis B Go Away
In most cases, hepatitis B goes away on its own. You can relieve your symptoms at home by resting, eating healthy foods, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding alcohol and drugs. Also, find out from your doctor what medicines and herbal products to avoid, because some can make liver damage caused by hepatitis B worse.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
You May Like: Lamivudine Dose In Hepatitis B
There Are Over 300 Million People In The World That Live With Viral Hepatitis
Less than 20% of the people with the virus are aware that they have the infection. The prevalence rates of hepatitis vary throughout the world, some areas have high rates of hepatitis B of over 10%. Higher rates of hepatitis B are seen in older Koreans born before vaccination programs were available.
Key Facts About Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic liver disease, including cancer.
- The virus is transmitted through contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person.
- About 2 billion people worldwide have been infected with the virus and about 370 million live with chronic infection and liver damage.
- Two thirds of those infected with HBV are unaware of their infection
- An estimated 800 000 people die each year due to HBV induced liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Despite there being a vaccine, globally HBV kills one person every minute
- About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood later die from liver cancer or cirrhosis caused by the chronic infection.
- The hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
- Hepatitis B is preventable with a safe and effective vaccine.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Related To Aids