What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
What Is In The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Vaccines are given by a course of three injections, usually as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine scheme.
Although there are different types of vaccines, they usually contain one of the proteins from the surface of the hepatitis B virus thats then inserted in to the genetic code into yeast cells which stops the risk of viral DNA getting into the final product.
They also contain small amounts of sodium chloride and aluminium, and can contain yeast and formaldehyde.
Also Check: Colloidal Silver And Hepatitis C
Are There Any Side Effects To Twinrix
Like any drug, the Twinrix vaccine can trigger side effects, but the chance of severe side effects is exceptionally low.
Very Common side effects felt in more than 10% of people receiving the vaccine are:
- Headache
- Pain and redness at the injection site
Common side effects felt between 1% and 10% of people receiving the vaccine are:
- Diarrhea
- Nerve disorders
Very rare in less than 0.01% of people receiving the vaccine are hives.
Still, you should call your doctor or hospital if you have critical or unusual reactions after receiving the vaccine.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A How Do You Get It
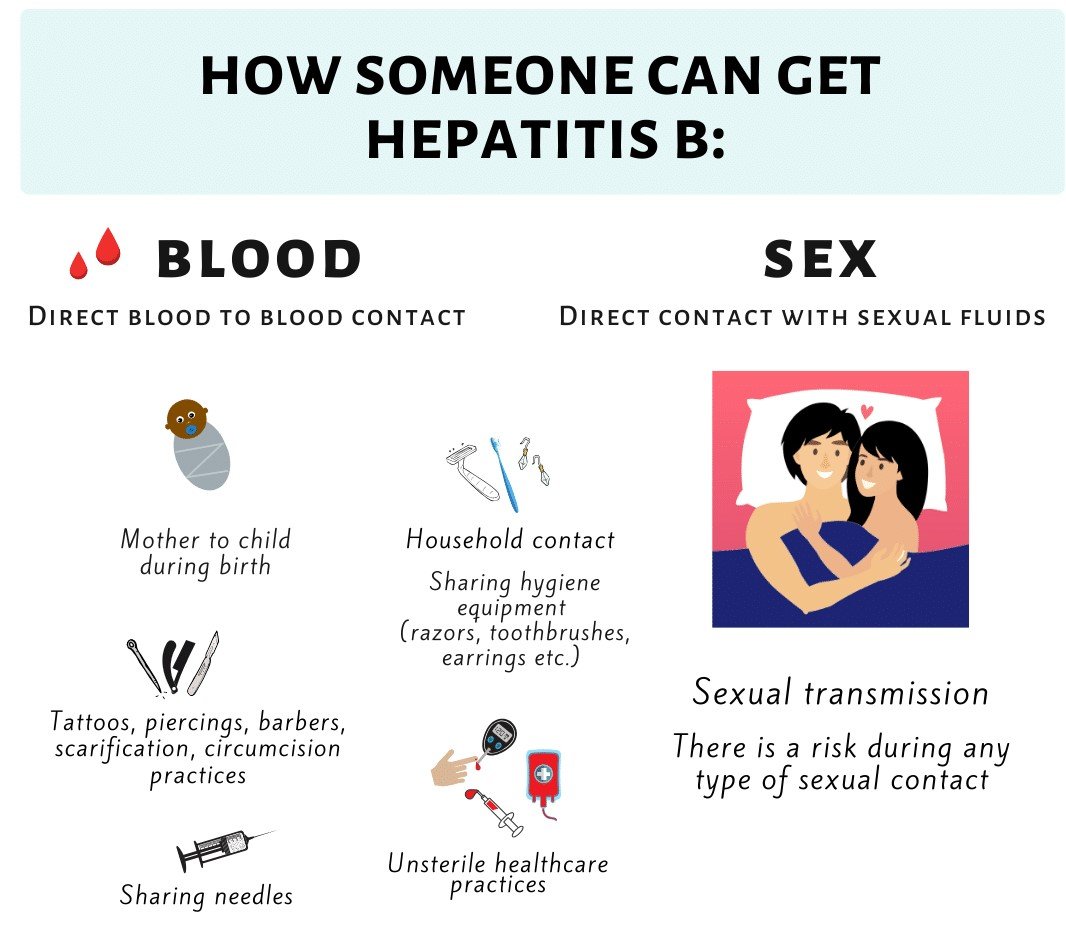
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Immunisation Against Hepatitis A
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis A infection and is recommended for people in high-risk groups, and for unvaccinated people who have been in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A.
Immunisation against hepatitis A includes a course of injections over a 6 to 12-month period. Healthy people 12 months of age and over receive 2 doses of hepatitis A vaccine, or 3 doses if the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are given as a combination.
You can complete any missed vaccine doses, even if the recommended time frame has passed. You do not need to start the vaccine course again.
If you are in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A be sure to have the hepatitis A vaccine if you have not already completed a vaccine course.
Babies under 12 months of age and people who have a weakened immune system who are also in close contact with a person with hepatitis A can have an injection of normal human immunoglobulin instead of the hepatitis A vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis A is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children who live in high-risk areas .
Also Check: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Other Reported Adverse Events And Conditions
While serious events and chronic illnesses such as chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and sudden infant death syndrome have been alleged or reported following HB vaccination, no evidence of a causal association has been demonstrated in a number of studies.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Recommended Reading: Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis C
Primary Hepatitis B Vaccinations For Children In The Uk
In the UK, children born after August 2017 are eligible to be given hepatitis B vaccines when they are young.
This consists of three doses of a hepatitis B vaccine. These doses are given at eight, 12 and 16 weeks of age. Babies at high risk of developing the hepatitis B infection from infected mothers are given additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine at birth, four weeks and one year of age.
However, if your child was born before this time, they are likely unvaccinated. If you are unsure which vaccinations your child has received, you should consult your doctor.
Routine Child Hepatitis B Immunisation
In August 2017, a routine vaccine programme was introduced for all infants born in the UK :
- They will be offered a hexavalent vaccine .
- The new vaccine will replace the existing pentavalent vaccine to extend its protection against hepatitis B virus in addition to diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, and Haemophilus influenzae type b disease.
- There will not be any change to the timing of the routine childhood immunisation schedule, with the hexavalent vaccine replacing the vaccine previously given at 8, 12, and 16 weeks of age.
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Cause Cirrhosis Of The Liver
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Side Effects Of Immunisation Against Hepatitis A
Immunisations against hepatitis A are effective and safe. All medications can have side effects.
For most people, the chance of a serious side effect from a vaccine is much lower than the chance of serious harm if you catch the disease.
Common side effects from the hepatitis A vaccine include:
- localised pain, redness and swelling at the injection site
- low-grade temperature
- headache.
Read Also: How Does Hepatitis C Start
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Recommended Reading: Do You Die From Hepatitis C
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Hepatitis B
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
If blood tests show that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis B and regular tests to assess the health of your liver.
Treatment is usually offered if:
- your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B by itself
- there’s evidence of ongoing liver damage
Hepatitis B medications can help keep the virus under control and stop it damaging your liver, although they won’t necessarily cure the infection and some people need lifelong treatment.
The main medicines for chronic hepatitis B are outlined below.
Does The Hepatitis Vaccine Expire
The hepatitis B vaccination provides lifelong protection . Therefore, there is no need to renew the vaccination once it has been administered.
In addition, the hepatitis A and B vaccines can also provide protection against other types of hepatitis. Thus, even if you develop antibodies against one type of virus, you will still be protected against other types of hepatitis if you are also vaccinated against them. There are separate guidelines regarding when vaccination should be given after exposure to another type of hepatitis virus. For example, people who have recently received a dose of the hepatitis A vaccine should not receive a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine until at least six months have passed since their last dose of the hepatitis A vaccine.
Similarly, those who have recently received a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine should not receive a dose of the hepatitis A vaccine for at least twelve months after their last dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Those who have not yet received a dose of either vaccine should discuss with their doctor how long to wait before being vaccinated with the other vaccine.
Although the hepatitis A and B vaccines do not expire, repeated doses over time may not be effective in certain individuals or for certain viruses.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For People At Risk
In Victoria free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk, including:
- Men who have sex with men.
- People living with HIV.
- People living with hepatitis C.
- Prisoners.
- People no longer in a custodial setting who commenced, but did not complete, a free vaccine course while in custody.
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
- People born in priority hepatitis B endemic countries who arrived in Australia in the last 10 years priority countries include China, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, Afghanistan, Thailand, South Korea, Myanmar , Indonesia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Cambodia.
- Vulnerable citizens people who have experienced hardship that prevented them from accessing the vaccine earlier. Vulnerable citizens are vaccinated based on an individual assessment by an immunisation provider.
Immunisation is also recommended, but not free, for people who are at increased risk including:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment that, in some instances, can greatly reduce your risk of infection with hepatitis B.
Remember that being immunised against hepatitis B does not protect you against HIV, hepatitis C or other diseases spread by blood or bodily fluids. It is important that you take precautions to make sure you are not exposed to these diseases.
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
Recommended Reading: Can You Donate Blood If You Had Hepatitis A
Managing Fever After Immunisation
Common side effects following immunisation are usually mild and temporary . Specific treatment is not usually required.There are a number of treatment options that can reduce the side effects of the vaccine including:
- Drinking extra fluids to drink and not overdressing if there is a fever.
- Although routine use of paracetamol after vaccination is not recommended, if fever is present, paracetamol can be taken check the label for the correct dose or speak with your pharmacist .
Who Publishes Updated Guidance On Validation Of Elimination Of Mother

WHO has updated its Global guidance on criteria and processes for validation: elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B virus. This third version of global guidance incorporates EMTCT of HBV towards validation of triple elimination and provides standardized processes and criteria to both validate EMTCT of HIV, syphilis and HBV, and to recognize high burden countries that have made significant progress on the path to elimination .
The similarity of the critical interventions necessary to prevent transmission adds to the feasibility and benefit of an integrated approach to EMTCT of all three infections as triple elimination. Building on an integrated maternal and child health platform, WHO has moved to operationalize universal health coverage in the context of integrated communicable disease prevention.
The guidance strongly emphasizes country-led accountability, rigorous analysis, intensive programme assessment and multilevel collaboration, including the involvement of communities of women living with HIV or HBV, or affected by syphilis. A harmonized approach to triple elimination is encouraged within a public health, rights-based and person-centred approach but depending on readiness, countries may choose to pursue validation of single, dual or triple EMTCT.
Reference
1. Ending AIDS: progress towards the 909090 targets. Global AIDS update 2017. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS 2017
Also Check: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
How Does Hiv Spread
HIV spreads when blood or certain bodily fluids that have high amounts of active virus are exposed to ones bloodstream.
For a person to contract HIV, there must be enough active virus in the fluid that encounters the bloodstream. This can occur through:
- a mucous membrane, or moist skin, such as in the mouth, rectum, penis, or vagina
- a significant opening in the skin
- injection
Transmission of the virus most often happens during anal or vaginal sex, but it can also occur by sharing needles.
Factors that affect the survival of HIV outside the body include:
- Temperature. HIV stays alive and active when kept in the cold but is killed by heat.
- Sunlight. Ultraviolet light in sunshine damages the virus, so its no longer able to reproduce.
- Amount of virus in the fluid. Generally, the higher the level of HIV virus in the fluid, the longer it will take for all of it to become inactive.
- Level of acidity. HIV survives best at a pH around 7 and becomes inactive when the environment is even just a little more or less acidic.
- Environmental humidity. Drying will lower the viral concentration of active virus as well.
When any of these factors arent perfect for HIV in its environment, survival time of the virus goes down.
Dont Miss: Can Alcohol Cause Hepatitis C