How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis C Infection
If you dont have hepatitis C, you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
Hepatitis C can spread from person to person during sex, but the chances are low. People who have multiple sex partners, have HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases, or who engage in rough or anal sex have a higher chance of getting hepatitis C. Talk with your doctor about your risk of getting hepatitis C through sex and about safe sex practices, such as using a latex or polyurethane condom to help prevent the spread of hepatitis C.
If you had hepatitis C in the past and your body fought off the infection or medicines cured the infection, you can get hepatitis C again. Follow the steps above, and talk with your doctor about how to protect yourself from another hepatitis C infection.
If you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent liver damage.
Facts You Need To Know About Hepatitis C
According to the reports of the World Health Organization, approximately 325 million people worldwide are living with viral hepatitis. Many of them are passing on the infection to others unknowingly. Looking at the staggering numbers of people contracting hepatitis C every year, it has become a major public health concern for all health organizations.
There are several misinformation and false beliefs about the virus, which make seeking treatment all the more challenging for the people. World Hepatitis Day, observed on July 28 each year, aims to raise awareness and educate people about the disease and its treatment. Here are a few important facts about hepatitis C that you must know about
-
People having hepatitis C can still live a healthy and long life
A major concern for patients recently diagnosed with the type C virus is the outlook. The HCV or hepatitis C virus was discovered first in the late 1980s and there have been significant advances in treatment ever since. Currently, nearly 25% of all infected people are able to recover from acute hepatitis C without any complications. Moreover, several modern treatment options in the form of medications and pills have made it less painful than the older methods.
-
There are multiple ways that a person can be exposed to the virus
-
You are less likely to have liver cancer or a transplant
-
An asymptotic person can still transmit the virus
-
There is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
Recommended Reading: Medication For Hepatitis C Cure
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Myth: Most People Infected With Hepatitis C Contracted The Virus During Unprotected Sex
In most cases hepatitis C is spread when blood from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person. Before the virus was screened from the nations blood supply, hepatitis C was commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Today most people become infected by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
Only about 1 to 2 percent are infected through unprotected sex, Nguyen said.
Recommended Reading: Gilead Sciences Hepatitis C Cure
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Also Check: Where To Get Tested For Hiv And Hepatitis
Myth: All Hepatitis C Drugs Have Terrible Side Effects
Fact: Newer antiviral medicines have made treatment shorter, more effective, and with fewer side effects. The goal of these drugs is to clear the virus from your body. Some get the job done in only 8 weeks. Youâll see your doctor regularly while you take these drugs to make sure your body is responding well to treatment.
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Certain foreign substances that enter your body trigger your immune system to make antibodies. Antibodies are specifically programmed to only target the foreign substance they were made to fight.
If youve ever had a hepatitis C infection, your body will make hepatitis C antibodies as part of its immune response.
Your body only makes these antibodies if you have hepatitis C or had it in the past. So the hepatitis C antibody test can confirm whether you have the virus by testing for these specific antibodies.
It may take 2 to 3 months after exposure for the test to detect antibodies. If needed, your healthcare professional may order an HCV RNA test, which can detect the virus after just 1 or 2 weeks.
If the antibody test is positive, an HCV RNA test can show whether the infection is current.
While people of any gender experience the same hepatitis C symptoms, 2014 research suggested some effects of the virus may differ, depending on the sex you were assigned at birth.
Researchers noted that:
- women have a higher chance of clearing the virus without treatment
- liver disease may progress more rapidly in men
- men have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis A And How Do You Get It
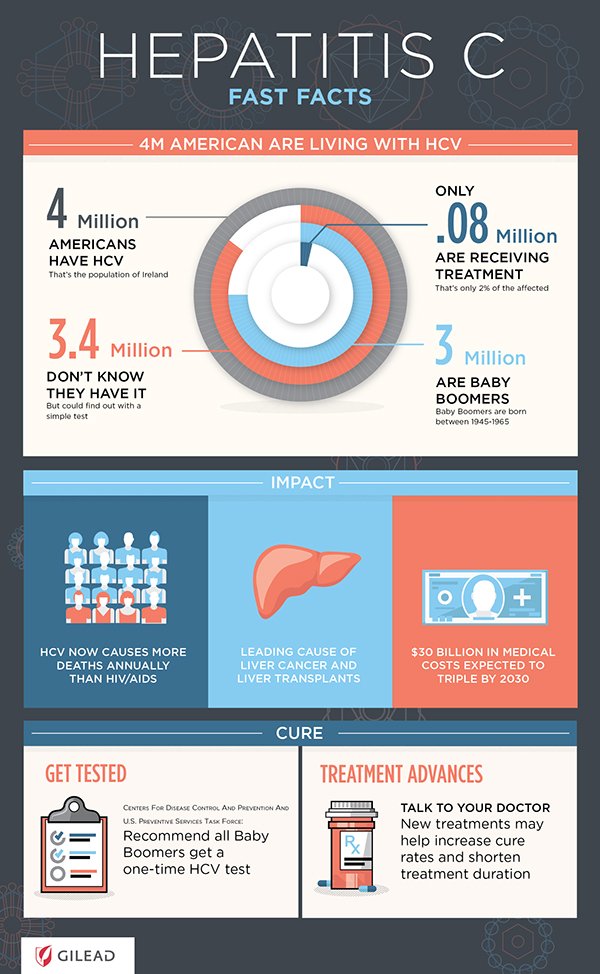
All Baby Boomers Need To Be Tested For Hepatitis C
People born between 1945 and 1965 are five times more likely to have hepatitis C than other adults, according to the CDC. Many of them were infected during the 1960s to 1980s from contaminated blood, or blood products like those used to treat hemophilia, before widespread screening for the virus began.
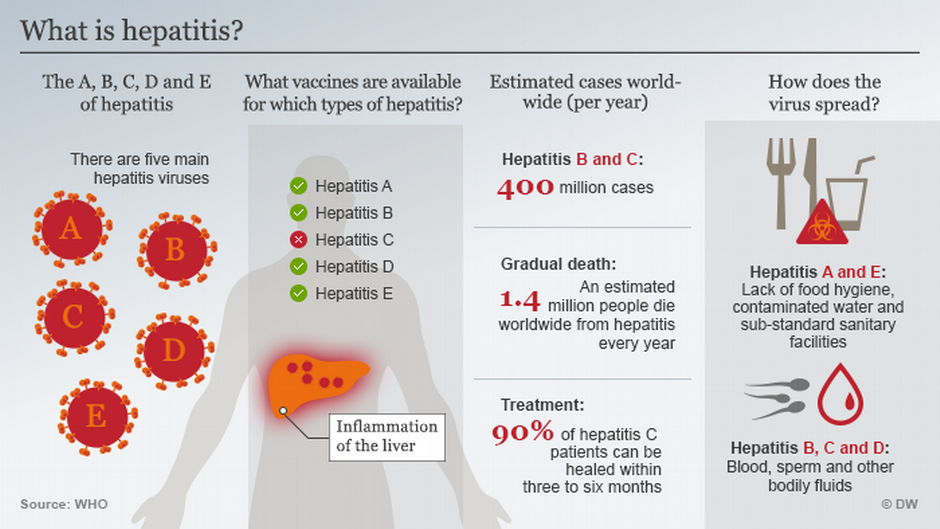
How Is Hepatitis Transmitted
Hepatitis viruses are transmitted in different ways.
- Contact with infected body fluids.
- Contaminated injection drug needles.
- Sharing personal items with someone who has hepatitis .
- Sexual contact with someone who has hepatitis.
- Close personal contact, living in a household with someone who is infected.
- HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during birth.
- Contaminated food or water is the most common cause of HAV and HEV infection.
Also Check: How Do You Spread Hepatitis C
Myth: Teenagers Are More Likely To Have Hepatitis C
Fact: Baby boomers — those born between 1945 and 1965 — are most likely to get hep C. It could be because they were infected years ago when blood wasn’t screened as well as it is now.
The CDC recommends that all baby boomers be tested for the hep C virus. They also suggest testing for anyone who:
- Has problems with their liver
- Had a blood transfusion before 1992
Children born to mothers with hep C should also be tested.
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C

If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Having Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C
Since there is no vaccine for hepatitis C, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to avoid contact with the blood of infected people. This includes:
- If you shoot drugs, never share works with anyone. This includes all drug injection equipment that can get blood on or in it . Sterile syringes can be purchased over the counter in most pharmacies in Massachusetts by anyone 18 years of age or older. Find out about drug treatment programs that can help you stop using drugs.
- Only get tattoos or body piercings at places using sterile equipment and supplies.
- Never share razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers
- The risk of sexual transmission is low, but use of latex condoms during vaginal or anal sex will reduce the risk even more
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Go Away
If I Have Hepatitis C What Should I Know And Whats Next
What does hepatitis C do to the body?
Hepatitis C can cause swelling and scarring in the liver. After 20 to 30 years, the liver can become quite damaged and unable to work properly. This can cause many different health problems because the liver does so many important jobs for the body.
Anyone with signs of liver damage should be checked to see if they can get hepatitis C treatment as it could stop further liver damage.
How can I know if my liver is damaged?
Health care providers cannot predict who will have liver damage, so it is important to regularly see a provider who can monitor your health.
Your health care provider can complete a detailed health assessment. This assessment will help to find out if the hepatitis C infection has caused any problems in how well your liver works. It may include:
- a physical examination
Patient Book: Using your voice
A skills building workbook to help people get the care and support they need .
Patient Card: Tips to getting your message heard
6 tips on how to get people to hear you and what to do when people say no.
What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C An Std
Fact #: Theres More Than One Way You Can Be Exposed To The Virus
A common misconception is that only people who use drugs can get hepatitis C. While some people whove had a history of using intravenous drugs have been diagnosed with hepatitis C, there are many other ways you can be exposed to the virus.
For instance, baby boomers are considered the population most at risk for hepatitis C simply because they were born before accurate blood screening protocols were mandated. This means anyone born between 1945 to 1965 should be tested for this virus.
Other groups at increased risk for hepatitis C include people who have had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992, people on hemodialysis for their kidneys, and people living with HIV.
80 percent of people with acute hepatitis C infection dont develop any symptoms. Chronic hepatitis C infection does not cause symptoms until cirrhosis develops. This means that precautions should be taken regardless of how you feel physically.
Although theres a relatively small chance of spreading the virus sexually, its best to always practice safe sex measures. Also, though the risk of transmission from razors or toothbrushes is very low, avoid sharing either of these grooming tools.
A Liver Transplant Is Not A Cure For Hepatitis C
Irreparable damage from hepatitis C is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the United States, Hanouneh says. But even after the diseased liver is removed, you still need medication to eliminate the virus from the body. Fortunately, Graham notes, medication can cure hepatitis C after a liver transplant.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis A And B And C
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
- All people born between 1945 and 1965
- Anyone who has ever injected drugs, even if once or many years ago
- People with HIV infection
- People who had a blood transfusion organ transplantation before 1992
- People who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or other injury
- People receiving hemodialysis
- People who have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
Don’t Miss: Tenofovir Hepatitis B Side Effects
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Hepatitis Isnt Just An Std
Viral hepatitis can be transmitted through sexual contact, but there are many other ways to get hepatitis. HAV is most commonly transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food or drink. HCV is mostly transmitted through exposure to contaminated blood this can occur during blood transfusions, contaminated medical equipment, and injection drug use.
Recommended Reading: What Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria