No Identifiable Source Of Infection
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, injection drug use accounts for approximately 60% of all HCV infections in the United States, while other known exposures account for 20-30%. Approximately 10% of patients in most epidemiological studies, however, have no identifiable source of infection. HCV exposure in these patients may be from a number of uncommon modes of transmission, including vertical transmission, and parenteral transmission from medical or dental procedures prior to the availability of HCV testing. There are no conclusive data to show that persons with a history of exposures such as intranasal cocaine use, tattooing or body piercing are at an increased risk for HCV infection based on these exposures solely. It is believed, however, that these are potential modes of HCV acquisition in the absence of adequate sterilization techniques.
Preparation And Use Of Drugs
Washing hands and using sterile water to prepare and use drugs lower the risk of catching hepatitis A. The use of new paraphernalia for the preparation, injection and inhalation of drugs lowers the risk of catching hepatitis B and C through blood.
Never share drug paraphernalia. To know the location of distribution points for drug injecting material, call Info-Santé 811.
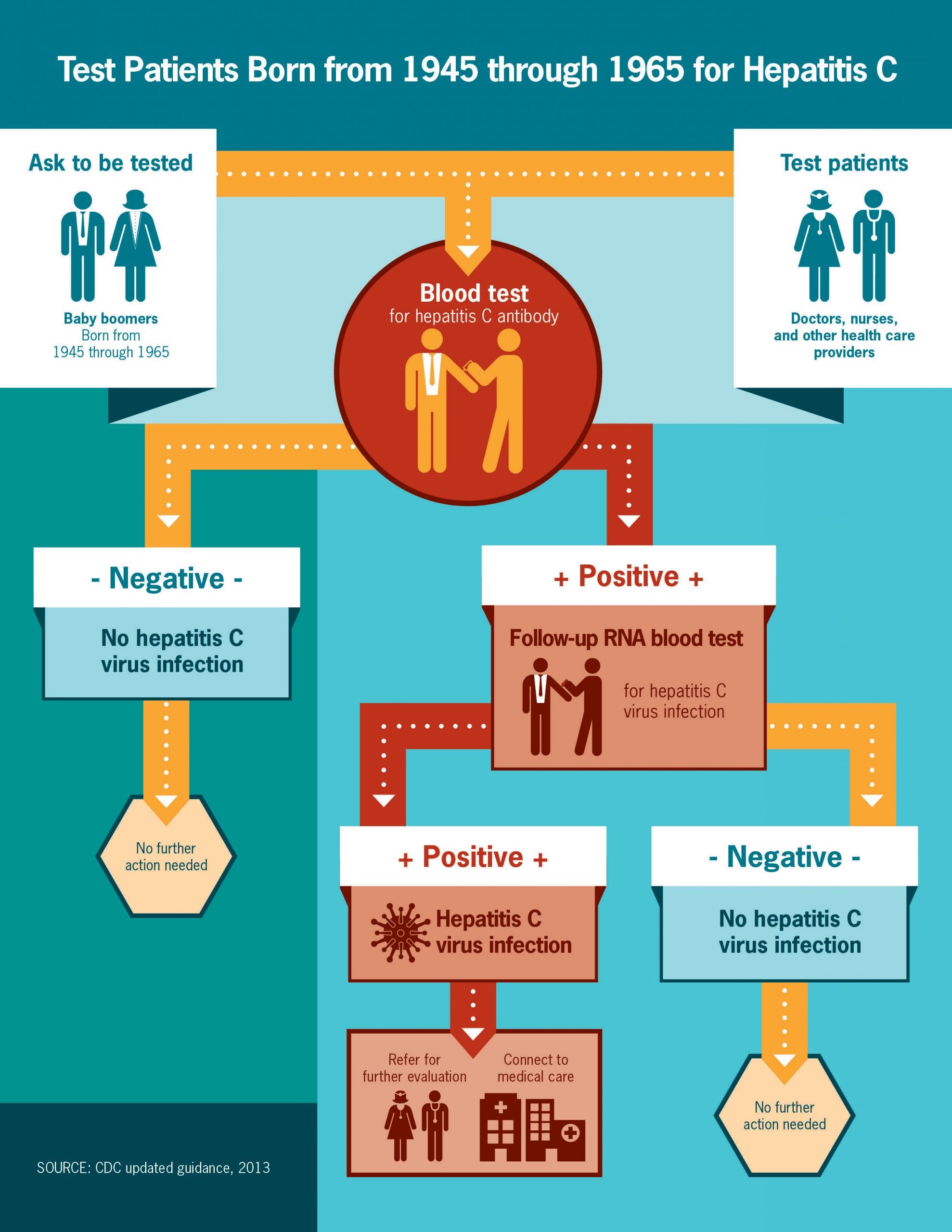
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis A After Vaccination
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is really contagious. Its transmitted through contact with semen , vaginal fluids, and blood. You can get it from:
-
having vaginal, anal, or oral sex
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Hepatitis C And The Hep C Virus
Hepatitis C is a liver infection that can lead to serious liver damage. Its caused by the hepatitis C virus. About 2.4 million people in the U.S. have the disease. But it causes few symptoms, so most of them don’t know. The virus spreads through an infected persons blood or body fluids.
There are many forms of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. The most common in the U.S. is type 1. None is more serious than any other, but they respond differently to treatment.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis C
Epidemiology And Natural History
The number of cases of chronic HBV infection has been estimated at almost 400 million worldwide . HBV has 8 genotypes which are associated with moderate differences in response to therapy. Children with chronic hepatitis B have a high frequency of HBeAg positivity and high HBV DNA levels compared to those with other genotypes and the timing of HBeAg seroconversion in genotype C is more delayed compared to genotype B. Genotype C results in more aggressive hepatitis and is associated with an increased risk of HCC. However the development of HCC was associated with genotype B in a single Taiwanese pediatric study. The prevalence of chronic HBV infection in pregnant women in urban areas of the USA varies by race and ethnicity. While the highest rate was observed in Asian women , the rates in black, white and Hispanic women were 1, 0.6 and 0.14%, respectively.
The spontaneous seroconversion rates of HBeAg for children infected via perinatal transmission are less than 2% per year for those under age 3 years, and 4 5% per year in those older than 3 years, whereas children infected after the perinatal period have higher rates of spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion, up to 70 80% over 20 years. The time to HBeAg clearance for individuals with HBV genotype C is longer than in patients with other genotypes . Since the early 1990s, the incidence of acute HBV in the United States has declined .
Undercooked And Raw Shellfish
Shellfish are animals that filter the water from their surroundings. Because of this, they can become contaminated with hepatitis A virus if they are grown in polluted waters. To be safe, cook shellfish thoroughly before eating it. Undercooked shellfish like oysters, mussels, and clams may harbor and transmit hepatitis A. You may prefer the taste of raw oysters, but cooked shellfish really is safer. Protect your health and skip the raw oyster bar.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Screening
Evaluation Of The Current Policy
An HPA audit of infants eligible for HBIG in the UK confirmed chronic infection in around 26/543 of their infants rate despite receiving HBIG and vaccination .
The chance of a baby becoming infected with hepatitis B depended on year of birth, maternal HBeAg status and ethnic group. There was a higher risk of infection in the babies born to mothers who were HBeAg seropositive and anti-HBe seronegative compared with other groups eligible for HBIG . The role of gestational age or birthweight was not examined.
A more recent audit of HBsAg seropositive women in Bradford documented chronic infection in 4/57 infants born to HBeAg positive women compared to 0/219 infants born to anti-HBe positive women who were given vaccine alone . In addition to infants who developed chronic infection, only a small proportion of babies had convincing evidence of resolved infection .
In total the transmission rate in was 11/57 and 1/211 in babies born to HBeAg seropositive and anti-HBe positive women respectively.
The single infection detected in the child of an anti-HBe positive woman was vaccinated on the date of birth but the second dose was delayed to 7 weeks of age. This suggests that vaccination alone is sufficient to largely prevent transmission and therefore to prevent cases of both chronic and acute infection in infants born to anti-HBe positive women. This data supports the effectiveness of the current UK policy when correctly implemented.
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Be Cured With Antibiotics
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute infection with hepatitis viruses. Acute infection is a short-term condition, lasting under six months. Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months.
Hepatitis B infection can be either acute or chronic. Most people who get acute hepatitis B dont end up progressing to chronic hepatitis B. By contrast, acute hepatitis C tends to develop into chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 7585 percent of adults newly infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection, according to the CDC . Others clear the infection.
When you get acute hepatitis C you may or may not have symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic, meaning people dont notice the symptoms. Symptoms are only noticeable in 15 percent of cases of acute hepatitis C.
Recommendation For Test Of Cure
-
Not relevant for these infections.
-
Patients with newly diagnosed infection caused by HBV or HCV should have serological markers of infection measured 3 and 6months later to establish whether the infection has become chronic,,, .
-
Serological follow up after antiviral therapy is beyond the scope of this guideline.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Titer Test Quest Diagnostics
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Jaundice
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
- Fever
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Ascites
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Jaundice
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A Virus
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all of the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. In addition to the 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, as of 2017, there is a 2-dose series given over 1 month.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or postexposure prophylaxis is available. The best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to never inject drugs or to stop injecting drugs by getting into and staying in drug treatment. If you continue injecting drugs, always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment.
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Read Also: Hepatic Arterial Infusion Side Effects
Special Considerations And Controversies
Compared to adults with CHC, children have different modes of transmission, spontaneous and treatment rates of clearance, slow progression of fibrosis. The accumulative duration of HCV infection since birth theoretically makes children with vertical transmission of HCV at risk for cirrhosis and HCC by the time of the transition to the adulthood. provides recommendations to pediatricians and pediatric gastroenterologists to monitoring and/or managing children with CHC. As the field of hepatitis C therapy is rapidly progressing, DAAs have proven to be efficient therapy even in HCV-infected adults with compensated cirrhosis. Pretreatment liver histology does not necessarily predict the response. A new IFN-free, DAA-based combination: sofosbuvir plus ledipasvir in one single tablet – was approved in 2014 in the United States for adults clinical trials are ongoing to improve tolerability and compliance in children.
Recommended Approach to Monitoring and/or Managing Children with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection indicated as having HCV infection for greater than 6 months
Other Steps You Can Take
Screening of all donated blood has reduced the chance of getting hepatitis B and C from a blood transfusion. People newly diagnosed with hepatitis B infection should be reported to state health care workers to track the population’s exposure to the virus.
The hepatitis B vaccine, or a hepatitis immune globulin shot, may help prevent infection if it is received it within 24 hours of contact with the virus.
Recommended Reading: Tell Me About Hepatitis C
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Other Body Fluids And Tissues
Hepatitis B is found in semen and vaginal secretions. The virus can be transmitted during unprotected sexual intercourse, and from mother to infant during birth.
Synovial fluid , amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and peritoneal fluid can contain the hepatitis B virus, but the risk of transmission to workers is not known.
Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomit have not been implicated in the spread of hepatitis B. Unless they are visibly contaminated with blood, the risk of contracting hepatitis B from these fluids in the workplace is very low.
Hepatitis B is not transmitted by casual contact. For example, hospital employees who have no contact with blood, blood products, or blood-contaminated fluids are at no greater risk than the general public. However, the virus can spread through intimate contact with carriers in a household setting, possibly because of frequent physical contact with small cuts or skin rashes. The virus can also spread through biting and possibly by the sharing of toothbrushes or razors. It is not spread through sneezing, coughing, hand holding, hugging, kissing, breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils, water or food.
Also Check: How To Contact Hepatitis C
Transmission To Hcw S
Over the past several decades, substantial effort has been devoted to preventing occupational exposures to bloodborne viruses and immunizing HCWs with hepatitis B vaccine . Among susceptible HCWs, in the absence of postexposure prophylaxis, the risk of HBV infection after a needlestick injury is 37%62% if the source patient is HBeAg positive and 23%37% if the patient is HBeAg negative . Many of the infections that occurred before widespread vaccination of HCWs likely resulted from inapparent exposures, such as inoculation into cutaneous scratches, lesions, or mucosal surfaces . The estimated number of HBV infections among HCWs in the United States has decreased from > 10,000 in 1983 to 400 in 2002 . This decrease is attributed to the implementation of standard precautions in health care settings, use of safety devices, increasing levels of hepatitis B vaccination coverage among HCWs, and postexposure prophylaxis .
Myth#: If You Have Hepatitis C Youll Know It Right Away
The center for disease control reports that approximately 20 to 30% of those infected with hepatitis C will show symptoms of the virus soon after infection. Moreover, symptoms like weariness or abdominal discomfort are often moderate or nonspecific, and you may be hesitant to seek medical help. In many cases, viruses are usually identified years after first infection. Most patients only find out they have it after being tested for hepatitis C or after having major health problems like cirrhosis , liver cancer, or kidney diseases.
You May Like: Tenofovir Hepatitis B Side Effects
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth. Itâs less likely to happen during your pregnancy.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Also Check: What Is The Cure For Hepatitis C