Postoperative And Rehabilitation Care
A diet consisting of 100 g/day of protein should be recommended. This should be supplemented with multivitamins including folate and thiamine. Protein-energy malnutrition is very common in alcoholics and associated with high mortality when compared to patients with no malnutrition. Unless the patient has encephalopathy, protein should not be restricted.
Is There A Safe Level Of Drinking
For most people, moderate drinking will not lead to alcohol-related liver disease. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, moderate drinking is one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men. Each of these alcoholic beverages, in the following amounts, is considered one drink and contains the same amount of alcohol:
- One 12-ounce bottle of beer
- One 4-ounce glass of wine
- One 1-ounce shot of hard liquor.
However, if you have chronic liver disease, even small amounts of alcohol can make your liver disease worse. People with alcohol-related liver disease and those with cirrhosis from any cause should abstain from alcohol completely.
Donât Miss: Hepatitis B How Is It Spread
How Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Diagnosed
Alcoholic hepatitis is not easy to diagnose. While the disease usually comes on after a period of fairly heavy drinking, it may also be seen in people who are moderate drinkers.
Blood tests may help in diagnosis.
Proof is best established by liver biopsy. This involves taking a tiny specimen of liver tissue with a needle and examining it under a microscope. The biopsy is usually done under local anesthesia.
Read Also: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
Portal Hypertension And Varices
Portal hypertension is a common complication of cirrhosis and, less commonly, alcoholic hepatitis. It occurs when the blood pressure inside your liver has risen to a potentially serious level.
When the liver becomes severely scarred, it’s harder for blood to move through it. This leads to an increase in the pressure of blood around the intestines.
The blood must also find a new way to return to your heart. It does this by opening up new blood vessels, usually along the lining of your stomach or oesophagus . These new blood vessels are known as varices.
If the blood pressure rises to a certain level, it can become too high for the varices to cope with, causing the walls of the varices to split and bleed.
This can cause long-term bleeding, which can lead to anaemia.
Alternatively, the bleeding can be rapid and massive, causing you to vomit blood and pass stools that are very dark or tar-like.
Split varices can be treated by using an endoscope to locate the varices. A tiny band can then be used to seal the base of the varices.
Recommended Reading: Physical Signs Of Hepatitis C
Causes And Risk Factors For Alcoholic Hepatitis
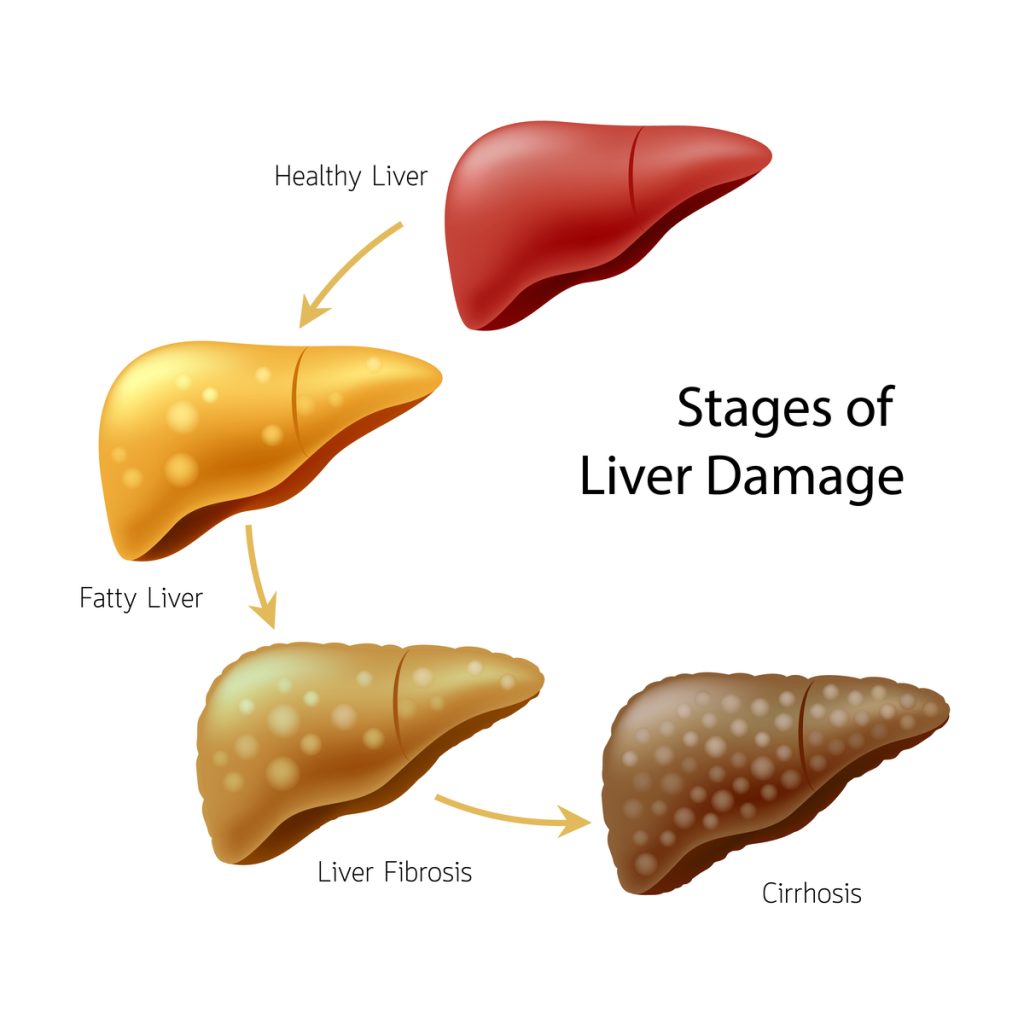
The main cause of alcoholic hepatitis is heavy drinking over an extended period of time. The process of breaking down alcohol in the liver causes inflammation that can destroy liver cells.
Over time, scars begin to replace functional liver tissue in the body. This interferes with how the liver works. Irreversible scarring, or cirrhosis, is the final stage of alcoholic liver disease.
Cirrhosis can quickly progress to liver failure once it develops. A damaged liver can also interfere with blood flow to the kidneys. This can result in damage and kidney failure.
Other factors can contribute to alcoholic hepatitis. For example, people with other types of hepatitis have a higher risk. As a result, it is not advisable for them to drink alcohol.
A person with alcoholic hepatitis may also experience malnourishment. Drinking significant amounts of alcohol can suppress the appetite. Alcohol may become the main source of calories for an individual. Malnutrition can also contribute to liver disease.
Other possible risk factors may include:
- sex assigned at birth, as females may have a
- electrolyte tests
- tests for other chemicals in the body
An ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI scan can show a more detailed view of the liver and any physical damage.
If other tests do not provide a clear answer, the doctor may conduct a liver biopsy. This involves taking a small tissue sample from the liver using a needle or through surgery for testing in a laboratory.
How Can Prevent Alcoholic Hepatitis
The best treatment is to stop drinking.
Treatment also may include:
- Hereditary defects in iron or copper metabolism
- Prolonged exposure to toxins
In children, the most frequent causes are biliary atresia â a disease that damages the bile ducts â and neonatal hepatitis. Children with these diseases often receive liver transplants.
Many adult patients who require liver transplants suffer from primary biliary cirrhosis. We do not yet know what causes this illness, but it is not in any way related to alcohol consumption.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Steatosis Of The Liver
Why Your Liver Is So Important
This vital organ is responsible for a number of essential functions from storing vitamins and minerals to the processing of fats, proteins, and carbs. One of which is to detox toxins from the blood. As the bodys primary method of processing alcohol and other drugs, the liver takes the brunt of drinkings toll on the body, and continued alcohol consumption can cause irreparable damage. The extent of which can range from impaired liver function to all-out failure. The consequences of either can cause a domino effect of other health issues.
How Can Alcohol Use Cause Hepatitis
Every food and drink you consume passes through your liver for processing. Your liver helps metabolize nutrients and filters out toxins. When alcohol goes to your liver for processing, it acts as a toxin. It offers no nutritional value and instead breaks down into poisonous chemicals.
Chronic heavy alcohol use can overload your liver with fat and toxins to process. When your liver can no longer keep up, these toxins and fat build up and begin to injure your liver. The injury produces an inflammatory response. This is your bodys way of attempting to heal and ward off further injury.
Like a fever, inflammation is supposed to be a temporary intervention. But when the assault is constant, the inflammation becomes constant. In your liver, this means swelling with fluid. If the swelling is severe and persistent, over time it will damage the tissues, causing cell death.
You May Like: How Can You Catch Hepatitis A
How Long Does It Take To Recover From Alcohol
People who quit drinking alcohol after diagnosis show great improvement after six to 12 months. Milder cases often resolve completely. More severe cases can continue to show gradual improvement over the following years. Some livers may bear permanent scarring, but as long as you avoid alcohol, there wont be ongoing damage.
Toxic Effects On Cell Membranes
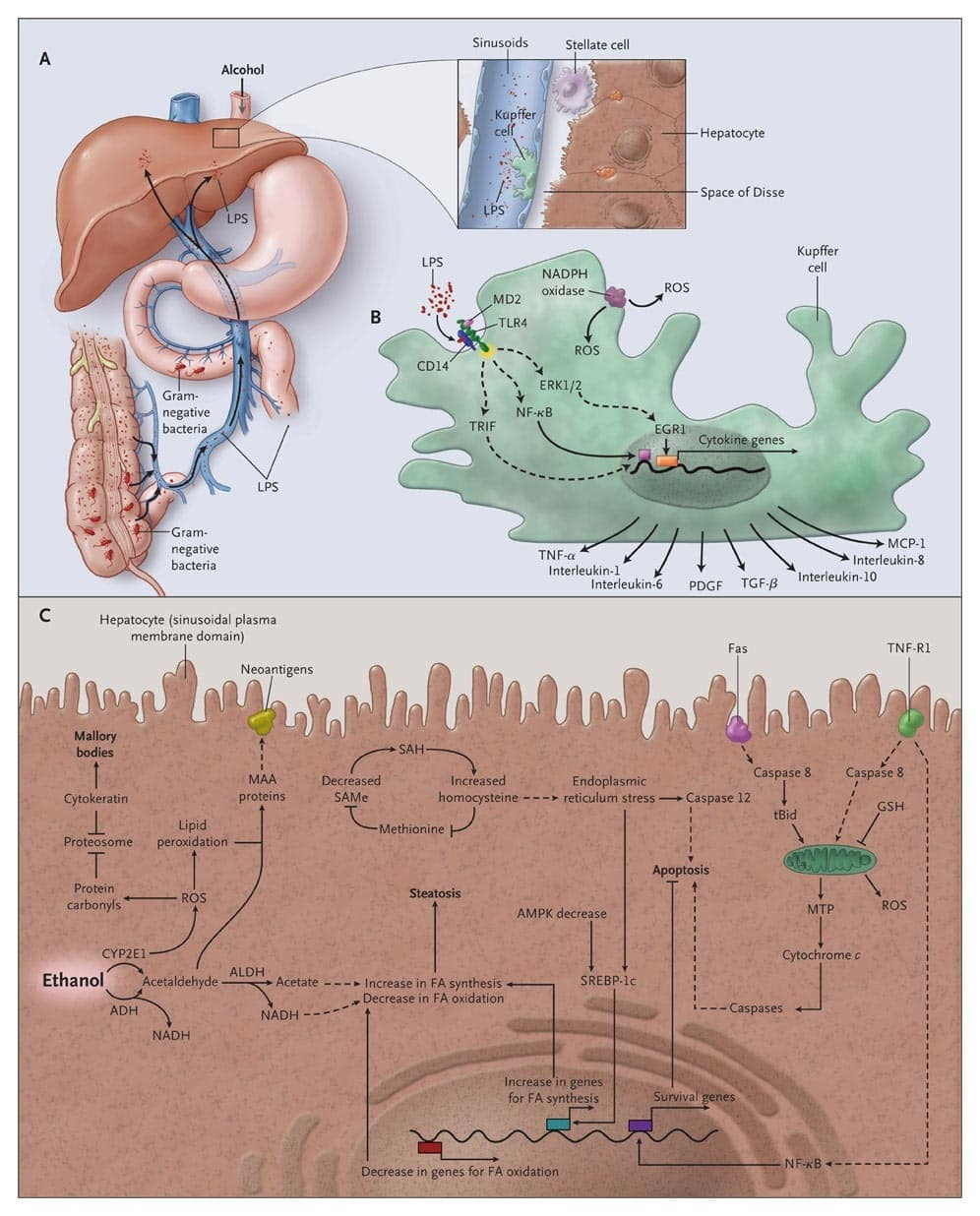
Ethanol and its metabolite, acetaldehyde, have been shown to damage liver cell membranes. Ethanol can alter the fluidity of cell membranes, thereby altering the activity of membrane-bound enzymes and transport proteins. Ethanol damage to mitochondrial membranes may be responsible for the giant mitochondria observed in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Acetaldehyde-modified proteins and lipids on the cell surface may behave as neoantigens and trigger immunologic injury.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Contract Hepatitis C
Is Alcoholic Hepatitis Dangerous
Yes. It may be fatal, especially if you have had previous liver damage.
Those who have had nutritional deficiencies because of heavy drinking may have other ailments. These medical complications may affect almost every system in the body.
It’s important to recognize and treat alcoholic hepatitis early, to help prevent these life-threatening consequences.
Quitting Drinking Abruptly Can Be Dangerous
If you have been drinking heavily for an extended period of time, stopping cold turkey, or all at once, can have serious, even life threatening, health consequences.
Typically, seeking medical guidance to stop drinking gradually under the supervision of a doctor or other healthcare professional can be a safer option and help you prevent complications.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
Race & Genetic Factors
Records also indicate that genetic factors might be part of why some people are more at risk than others, as Blacks and Hispanics seem to be at higher risk. This could be down to the fact that Black and Hispanics have less genetic exposure to alcohol than White people, as alcohol was not part of their diets for as long, although there is a great deal of conversation ongoing as to why exactly race may be a factor.
Can You Drink Alcohol When You Have Hepatitis B Or C
Alcohol is believed to weaken the bodys ability to fight off the hepatitis C virus. The relationship between hepatitis B and alcohol is less well understood, but appears to be similar. With hepatitis B, moderate drinking may be less risky.9 In both cases, however, its best to avoid heavy drinking at all costs.
If you have hepatitis B or C, check with your doctor about what amount of alcohol, if any, is safe. But your safest bet is to avoid drinking altogether.
Recommended Reading: Where Can I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Factors Influencing Ast And Alt
The excessive drinking group had the highest AST when compared with the other groups at any time . However, AST decreased dramatically with time in every group. We found no difference between the moderate drinking and non-drinking groups at 6 months . Excessive drinkers had the highest ALT at any time compared with the other two groups . ALT also progressively decreased after treatment in all group. Throughout, we found no difference between the moderate drinking and non-drinking groups at the 3rd and 6th months .
Figure 1Table 3
Patients Enrollment And Data Acquisition
Medical records of all inpatient subjects diagnosed for the first time with liver cirrhosis in the third affiliated hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China from January 2010 to December 2019 were retrospectively collected from the hospital electronic database of medical record. The identification of the cirrhosis cases was made using ICD-10-CM codes of liver cirrhosis . Patients with Wilson Disease, autoimmune liver disease, congenital biliary atresia, multiple etiologies other than ALD+HBV and ALD+HCV, unknown etiology, and those with incomplete data were excluded. The remaining cases were divided into five groups based on the etiology of cirrhosis: alcohol-induced liver cirrhosis , hepatitis B virus-induced liver cirrhosis , hepatitis C virus-induced liver cirrhosis , coexisting ALD and HBV , and coexisting ALD and HCV . Information such as sex, age at admission, laboratory data, clinical complications and history of antiviral treatment, alcohol consumption and alcohol abstinence were collected. Different liver function assessment scores such as ChildPugh classification, MELD score, GAHS and MDS were calculated. The calculation formulas and criteria for diagnosis of each type of cirrhosis and its complications is detailed in the Additional file .
Read Also: Hepatitis C Virus Is Spread Through The Contact Of
Risk Factors For Alcohol Related Liver Disease
Not everyone who drinks heavily develops ALD. While the amount of alcohol and the length of time as a heavy drinker are the key risk factors, additional forces impact the outcome. They are:
- Obesity/Overweight: Carrying extra weight increases the risk of liver disease because fat builds up in the liver. The fat cells secrete acids which cause a reaction that destroys healthy cells in the liver, leading to scarring. Add alcohol to the mix and the combined effect adds additional liver damage.
- Malnutrition: Often people who drink heavily, eat poorly. They also may have trouble absorbing nutrients because alcohols toxic byproducts make it difficult to break down food. The lack of nutrients contributes to liver cell damage.
- Genetic component: How a body metabolizes alcohol is influenced by genetics. If certain enzymes are missing, that can affect the risk of developing ALD.
- Demographic influencers: Rates of alcohol cirrhosis are higher in African-American and Hispanic males than they are in Caucasian males. Women are more susceptible than men to the impact of alcohol because they become more impaired than men after drinking equal amounts.
- Having viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C: Adding alcohol to a liver already taxed by hepatitis increases the risk of developing liver disease, as well as liver cancer.
Alcoholic Hepatitis Vs Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a permanent scarring of the liver.10 It is not the same condition as hepatitis, but it often develops as a result of it.
While liver damage from hepatitis is sometimes reversible, cirrhosis is not. And the more scar tissue you have in your liver, the harder it becomes for this vital organ to function. This can have many serious consequences for your overall health, and can eventually cause liver failure, which can be fatal. While some milder cases of cirrhosis are manageable, the only treatment for advanced cirrhosis is a liver transplant.
Unfortunately, cirrhosis is on the rise, making it more important than ever to raise awareness of this condition. And since alcoholic hepatitis can lead to cirrhosis, the sooner you catch liver damageand reduce your alcohol consumptionthe better.
Read More: Early Signs of Liver Damage From Drinking
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Test Done
Who Can Get Alcohol
You’re more at risk if you use alcohol heavily over many years. But not everyone who gets alcohol-induced hepatitis fits this profile. Some people are more sensitive to alcohol, and their livers react to even moderate use. Others may be able to drink more without inducing hepatitis.
Genetic differences may partially explain this. You may be more at risk if you have a family history of alcohol use disorder or liver disease. Sex differences also play a part. In general, people who were assigned male at birth can tolerate more alcohol than those who were assigned female at birth.
However, everyone is different, and medically we cant say what a safe amount of alcohol is. Some people develop alcohol-associated hepatitis and cirrhosis from seemingly insignificant quantities of alcohol.
Reasons To Head To The Doctor
Alcoholic hepatitis is a very serious disease, with 30 to 40 percent of people with severe alcoholic hepatitis facing death within just one month. Here are some reasons to make an appointment with your doctor right away.
- You display signs or symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis .
- You cant control your drinking.
- You want to cut back on your drinking.
Recommended Reading: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Symptoms Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis are often mild and mistaken for symptoms of other common health conditions. For individuals who consume alcohol on a regular basis, it is essential to know these symptoms to be more aware of their actual cause.
Symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis commonly include:
- fever, which is often low-grade
- nausea and vomiting
- changes in, or loss of, appetite
- fatigue and weakness
Symptoms that typically occur in more severe cases of alcoholic hepatitis include:
- changes in mental state, such as confusion due to toxin build up
- fluid accumulation in the abdomen
- kidney and liver failure
If someone develops one or more of these symptoms, they should contact their doctor to receive a proper diagnosis.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
This article discusses hepatitis, which is a complex disease and requires an interprofessional approach from healthcare providers to tackle it. The article discusses strategies to prevent hepatitis through patient education and vaccination and the importance of closer monitoring for disease progression and complications. These strategies require significant interprofessional communication and care coordination by physicians, including primary care physicians and specialists, nurses, pharmacists, and other health professionals, to enhance patient-centered care. Nursing needs to work closely with the patient to ensure they understand their disease, are compliant with medications and vaccines, and note progress or lack thereof. Pharmacists are crucial to ensuring the proper medications at the correct dose are in the therapy regimen, and that there are no interactions. Any issues noted by any member of the interprofessional healthcare team need to be shared and charted, so everyone operates from the same data. These measures can help improve the outcomes and aid to patient safety and can also help enhance team performance.
You May Like: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Hepatitis C Fast
Can Hepatitis C And Alcoholic Hepatitis Coexist
Hepatitis due to both HCV and alcohol abuse can coexist. According to a 2018 article, it is common for the two conditions to occur simultaneously.
Excessive alcohol consumption can accelerate and multiply the damage due to HCV, worsening liver cirrhosis. However, even small amounts of alcohol can exacerbate HCV. It may also interfere with HCV treatment by causing the virus to become resistant to medication.
Although both conditions are responsible for liver inflammation, there are differences in the symptoms of HCV and alcoholic hepatitis.
According to the World Health Organization , around of people with HCV show no symptoms after contracting the initial infection. They may not realize they have the virus until later if it becomes chronic and causes liver damage.
Individuals who do experience hepatitis C symptoms may develop:
- tenderness in the liver
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome, which involves fever, fast heart rate, and fast breathing
It is important to note that HCV is contagious. If a person is unsure if they have contracted the infection, they should take safety precautions to prevent others from coming into contact with their blood.
Its Not Too Late To Get Help
The good news is that if acted upon early enough, alcohol hepatitis can be reversed. The liver has an incredible ability to repair itself, in fact, after part of it has been surgically removed the liver can regenerate itself in only a matter of months. However, continued alcohol damage can destroy this capability so it is imperative that those with this condition immediately cease alcohol consumption. Time is of the essence to get your drinking habit under control but quitting cold turkey is never recommended. Alcohol rehab facilities like the Freedom Center can help safely mitigate alcohol withdrawal symptoms and ultimately, help you achieve life-saving abstinence.
by The Freedom Center | Last updated Aug 16, 2022 | Published on Aug 25, 2022 | Alcohol, Mental Health
If you’re taking an antidepressant, it’s important to understand the risks of combining alcohol with this medication. Alcohol is a depressant, so mixing it with antidepressants can make you feel worse. You may have more side effects from your antidepressants when…
by The Freedom Center | Last updated Aug 16, 2022 | Published on Aug 16, 2022 | Addiction Treatment, Alcohol
If you’re struggling with alcoholism or just want to cut back on alcohol consumption, there are two main options: cold turkey and tapering off. Both involve quitting drinking, but tapering off involves slowly reducing the alcohol consumed over time until you’re no…
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Hepatitis B Test