Should All Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Be On Treatment
Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B need to be on treatment. The decision to treat HBV is based on several factors including blood tests results, the patient’s age, and the risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer. Sometimes a liver biopsy is needed to see if there is significant liver damage to make a decision.
Hepatitis B medications are recommended for patients with detected HBV virus on a blood test and evidence of liver damage. Liver damage can be detected with a liver enzyme known as ALT. People with cirrhosis should be considered for treatment even if the liver enzymes appear normal.
Chronic hepatitis B may change over time. Patients can go through different phases with low amounts of virus and normal level of ALT followed by high viral loads and ALT levels. These bursts of virus activity usually don’t cause any symptoms but may cause liver damage overtime. It is important that people with chronic hepatitis B have blood tests on a regular basis to see if treatment is needed.
There are some medications which can cause hepatitis B “reactivation” which can lead to life threatening liver failure. These medications are used to treat some cancers, inflammatory conditions and hepatitis C. Reactivation reactions can be prevented and it is important to let your provider know you have HBV before you start any new medications.
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Because their immune systems arent fully developed, infants and young children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B, so its important to limit their exposure to the virus. All expecting women should be screened for hepatitis B. If a high viral load is detected through testing, your doctor will initiate treatment during your third trimester to reduce the likelihood that your baby will contract the disease during delivery.
Additionally, the infants of mothers with hepatitis B should receive the hepatitis B vaccination series and immune globulins at birth so they do not develop hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis Curable Or Treatable
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. If you have acute hepatitis B, you may be asymptomatic or have symptoms and develop icteric hepatitis. It can transition into chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesnt naturally go away after 6 months.
- Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least 6 months. If you have this type of hepatitis, you may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of your life. Its possible to have chronic hepatitis B that started as acute, but many people dont have acute hepatitis B first.
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the infection. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Your risk of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on when you first received your diagnosis of the virus. Children who receive a diagnosis of hepatitis B, especially those under the age of 5 years old, have a higher risk of the infection becoming chronic. Adults are less likely to develop chronic hepatitis B. Around 90 percent of adults who develop it will fully recover.
Keep in mind that hepatitis B can be present for years before you start to show any symptoms.
World Health Organization Recommendations
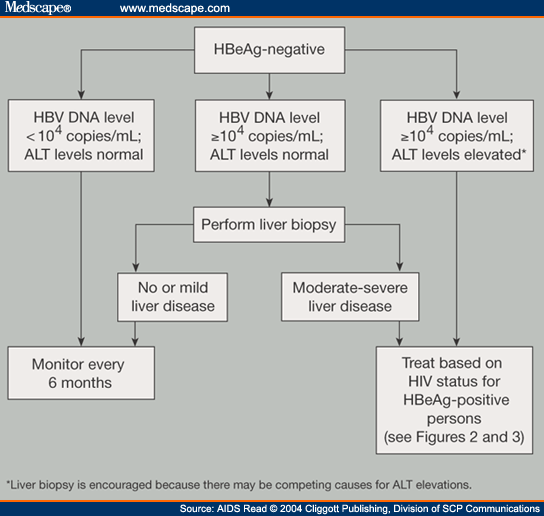
The 2015 WHO guidelines for the prevention, care, and treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis B infection indicate treatment priority for individuals of all ages who have chronic hepatitis B infection and clinical evidence of compensated/decompensated cirrhosis , regardless of their levels of ALT or HBV DNA, or their HBeAg status.
Treatment is recommended for adults with chronic hepatitis B infection without clinical evidence of cirrhosis , but who have all of the following features , and regardless of HBeAg status :
- Are older than 30 years
- Have persistently abnormal ALT levels
- Have evidence of high-level HBV replication .
Recommended Reading: Best Vitamins For Hepatitis B
What If I Am Pregnant
It’s recommended that all pregnant women have a blood test for hepatitis B in early pregnancy.
If you have hepatitis B and are pregnant, treatments can reduce the risk of transmission of hepatitis B to the baby.
If you have hepatitis B, it is important to protect others from infection.
Important ways to prevent the spread of hepatitis B include:
- vaccination of all your close contacts
- practise safe sex until your sexual contacts are fully vaccinated and immune
- do not donate blood, organs or body tissue
- do not allow your blood to contact another person
- inform healthcare workers
- if your work involves potential for your blood or other body fluid to spread to other people, discuss your situation with your doctor
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective in protecting against hepatitis B infection, providing protection in 95 in 100 vaccinated people.
In Australia, hepatitis B vaccination is part of the standard immunisation schedule for all newborn babies and infants. It’s also recommended for adults who are at high risk of exposure, people who are immunosuppressed or have other liver disease. People in these risk groups should be vaccinated against hepatitis B. Talk to your doctor about your level of risk and whether hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for you.
If you werent vaccinated against hepatitis B as a child, or if youre not sure whether you are vaccinated, talk to your doctor about whether you need a catch-up vaccine.
Unlikely Sources Of Infection
Trace levels of HBV can also be found in saliva, tears, urine, and feces but in amounts that are highly unlikely to cause infection.
While vaccination remains the cornerstone of HBV prevention, there are ways to further reduce the risk of transmission, especially if you or someone in your household has hepatitis B:
- Wash your hands with soap and water if exposed to blood.
- Avoid sharing razors or toothbrushes.
- Use condoms during sex.
Recommended Reading: If My Husband Has Hepatitis C Will I Get It
Efficacy And Safety Of Available Treatments
Currently, two types of treatment, IFNs and NAs, are approved for chronic HBV infection. The virologic responses to these therapies are summarized in Table Table11.13, 24, 25 Pegylated IFNs have a more convenient dosing schedule and improved efficacy. Among the NAs, entecavir , TDF, and tenofovir alafenamide are preferred because of their potent antiviral activity and high barrier to antiviral resistance. A 1year course of pegylated IFN results in higher rates of HBeAg seroconversion and HBsAg loss than the same duration of ETV, TDF, or TAF therapy in patients who are HBeAgpositive despite lower rates of undetectable HBV DNA . Similarly, in patients who are HBeAgnegative, a 1year course of pegylated IFN results in a higher rate of HBsAg loss than the same duration of ETV, TDF, or TAF therapy despite a lower rate of undetectable HBV DNA . Response to IFN is more durable, and rates of HBeAg and HBsAg loss continue to increase after cessation of treatment, whereas viral relapse is universal when NA is discontinued after 1 year of therapy.
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Donât Miss: How Do You Get Hiv And Hepatitis
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Oral Sex
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Many people with hepatitis B won’t experience any symptoms and may fight off the virus without realising they had it.
If symptoms do develop, they tend to occur 2 or 3 months after exposure to the hepatitis B virus.
Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- flu-like symptoms, including tiredness, a fever, and general aches and pains
- loss of appetite
Read more about treatments for hepatitis B and complications of hepatitis B.
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. The virus is found in the blood and bodily fluids of an infected person.
Many people with hepatitis B have few symptoms and may not know they’re infected. They may spread the infection without realising it.
Hepatitis B is most often caught in parts of the world where the infection is more common, although certain groups of people are at risk of picking up the infection in the UK.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Genotype 2b Treatment
What Is The Price Of The Treatment In India
The vaccinations are the best forms of treatment from hepatitis B, and these can cost around INR 1,000 per shot. The treatment cost and the antiviral medicines can be extremely costly with each antiviral injection costing up to INR 4000. Also, these have to be taken for a long term, and the post-treatment medications can be additional.
Is Hepatitis B Preventable
Chronic hepatitis B infection affects at least 250 million people worldwide, causing over 880,000 deaths annually. It is also the major cause of liver cancer, the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States.
Unlike its cousin hepatitis C, hepatitis B can be prevented with vaccines. If you are accidentally exposed to the virus, there are also drug therapies you can takeâcalled postexposure prophylaxisâto avert the infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Test Results 0.1
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can get hepatitis B, but the risk is higher in:
- Infants born to mothers who have hepatitis B
- People who inject drugs or share needles, syringes, and other types of drug equipment
- Sex partners of people with hepatitis B, especially if they are not using latex or polyurethane condoms during sex
- Men who have sex with men
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B, especially if they use the same razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- Health care and public-safety workers who are exposed to blood on the job
- Yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you may not have symptoms until complications develop. This could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis B screening is important, even if you have no symptoms. Screening means that you are tested for a disease even though you don’t have symptoms. If you are at high risk, your health care provider may suggest screening.
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis and other drug use.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Don’t Miss: How Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria Diagnosed
Is Surgery A Treatment For Hepatitis B
There is no surgical therapy for hepatitis B.
If liver damage is so severe that the liver starts to fail, liver transplant may be recommended:
- Liver transplant is a major process and surgery with an extended recovery period.
- It also depends on the availability of a matching donor liver.
- If liver transplant becomes a possibility for an individual, a health care practitioner will discuss the risks and benefits with them.
How Hepatitis B Is Spread
Hepatitis B can be spread by:
- a mother to their newborn baby, particularly in countries where the infection is common all pregnant women in the UK are offered screening for hepatitis B babies of infected mothers are vaccinated immediately after birth to help prevent infection
- injecting drugs and sharing needles and other drug equipment, such as spoons and filters
- having sex with an infected person without using a condom
- having a tattoo, body piercing, or medical or dental treatment in an unhygienic environment with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country where blood isn’t tested for hepatitis B all blood donations in the UK are now tested for the infection
- sharing toothbrushes or razors contaminated with infected blood
- the skin being accidentally punctured by a used needle this is mainly a risk for healthcare workers
- the blood of someone with hepatitis B getting into an open wound, cut, or scratch in rare cases, being bitten by someone with hepatitis B can also spread the infection
Hepatitis B isn’t spread by kissing, holding hands, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or sharing crockery and utensils.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Test For Hepatitis
How Long Does It Take To Recover
The recovery period depends on how much the virus has affected your liver and how far your body has cooperated with the antiviral drugs. For some, the results of the treatment can be immediate, but for others, it can be long term. The antiviral drugs may also not work across for some sections of people. Consult with your doctor about these implications and the recovery period.
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
You May Like: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Is There A Hepatitis B Vaccine
There is a vaccine against the hepatitis B virus . It is safe and works well to prevent the disease. A total of 3 doses of the vaccine are given over several months. Hepatitis B vaccine is also produced as a combination product which includes other common childhood vaccinations. This can reduce the number of shots that a child needs at a single visit.
The following groups should be vaccinated for hepatitis B:
- All children younger than 19 years, including all newborns – especially those born to mothers who are infected with HBV
- All health care and public safety workers who may be exposed to blood
- People who have hemophilia or other blood clotting disorders and receive transfusions of human clotting factors
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâs unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Also Check: What Is Treatment For Hepatitis A