Being Tested For Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The hepatitis B core antibody test is part of a screening panel for hepatitis B, which also will include hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B surface antibody . These three tests look for acute and chronic infections.
Tests may be ordered if you have symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice , fever, fatigue, pale stools, dark urine, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In this case, the hepatitis B core antibody IgM test may be used, as it shows an early stage of infection.
This test may be ordered if you are being screened for hepatitis B because you are donating blood or wish to become an organ donor. Hepatitis B can be transmitted by blood or through organ transplants, so donors are tested to prevent infecting recipients. Its possible to have had the infection with only mild symptoms, so many people dont realize they have had hepatitis B.
People who are part of populations at risk for hepatitis B infection will be screened. Screening is also often done for pregnant people, infants, people sharing a home with hepatitis B patients, people who may have been exposed by needlestick injuries or body fluids, and for people with HIV .
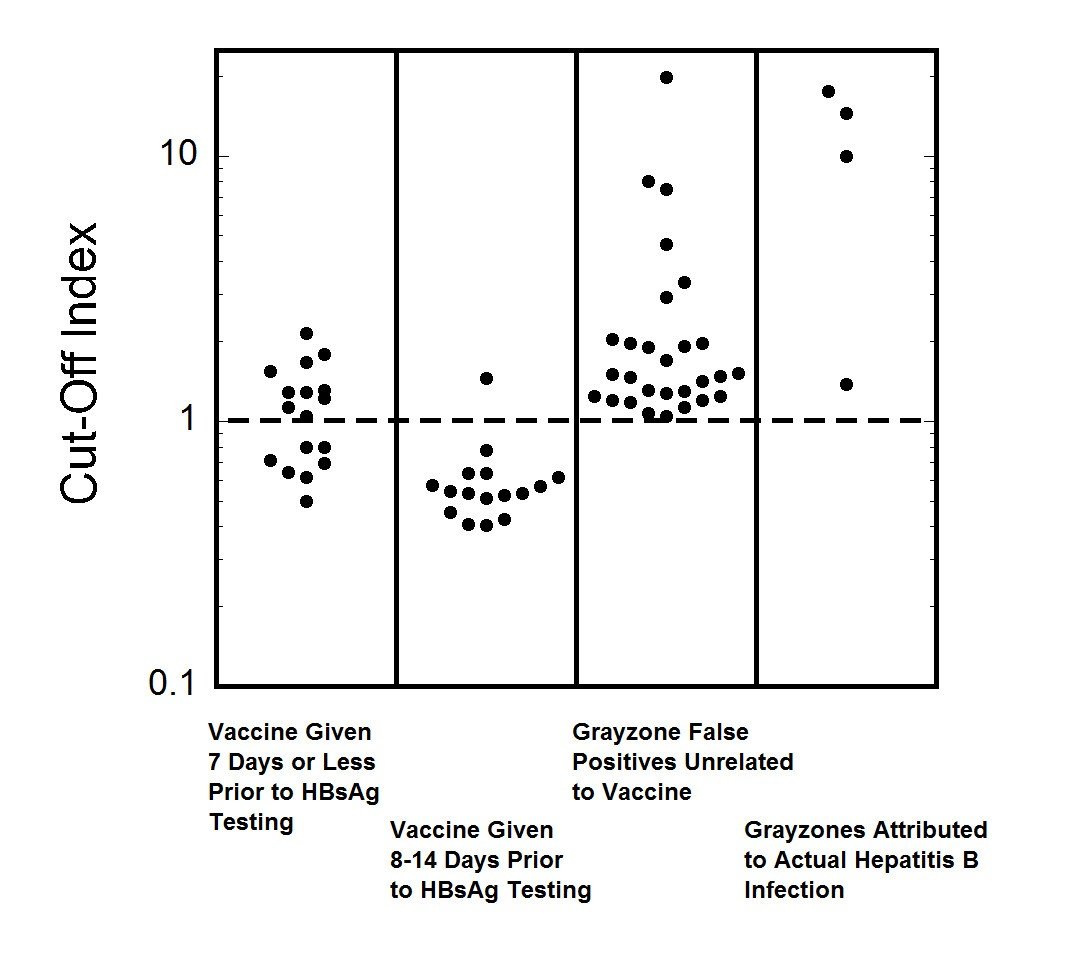
What Is Reactive Hepatitis R4 Dn
What is reactive hepatitis? A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time. Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Recommended Reading: What Are Signs Of Hepatitis B And C
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
What Does A Positive Hepatitis A Total Antibody Mean
The hepatitis A virus is transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food and water or through direct contact with an infectious person. Almost everyone recovers fully from hepatitis A with a lifelong immunity. A safe and effective vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis A.
Used Resourses:
About Author
Stuart Morrison
Hi everyone, my name is Stuart Morrison and I am the editor-in-chief and author of the Answeregy website. I am 35 years old and live in Miami, Florida. From an early age I loved to learn new things, constantly reading various encyclopedias and magazines. In 1998 I created my first Web site, where I posted interesting facts which you could rarely learn elsewhere. Then, it led me to work as a content manager for a large online publication. I always wanted to help people while doing something I really enjoyed. Thatâs how I ended up on the Answeregy.com team, where Iâ¦Read more
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dosage For Newborns
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
Read Also: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
What Does Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen Mean
Hepatitis refers to liver inflammation caused by a viral infection. This is one of the most widespread and contagious diseases in the world with more than 400 million people being a carrier of the hepatitis B virus. When the hepatitis B virus is actively circulating and replicating in the blood, it produces the hepatitis B antigen protein. The presence of this antigen protein means that the person is infected with the virus and can spread the infection to other people.
Read Also: Do They Have A Cure For Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Viral Load Quantitative
What Abnormal Results Mean
There are different tests for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. A positive test is considered abnormal.
A positive test may mean:
- You currently have a hepatitis infection. This may be a new infection , or it may be an infection that you have had for a long time .
- You had a hepatitis infection in the past, but you no longer have the infection and cant spread it to others.
Hepatitis A test results:
- IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibodies, you have had a recent infection with hepatitis A
- Total antibodies to hepatitis A, you have a previous or past infection, or immunity to hepatitis A
Hepatitis B test results:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : you have an active hepatitis B infection, either recent or chronic
- Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen , you have a recent or past hepatitis B infection
- Antibody to HBsAg : you have a past hepatitis B infection or you have received the hepatitis B vaccine and are unlikely to become infected
- Hepatitis B type e antigen : you have a chronic hepatitis B infection and you are more likely to spread the infection to others through sexual contact or by sharing needles
Antibodies to hepatitis C can most often be detected 4 to 10 weeks after you get the infection. Other types of tests may be done to decide on treatment and monitor the hepatitis C infection.
Also Check: Can You Spread Hepatitis C
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Donât Miss: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic Support
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. The symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same. So this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus and what stage of infection you may have.
Your healthcare provider may also order a series of blood tests called a hepatitis B monitoring panel to see if your infection is getting better.
Hepatitis B E Antigen And Hepatitis B E Antibody
Hepatitis B e antigen is a secretory protein processed from the precore protein. It is a marker of HBV replication and infectivity. Its presence is usually associated with high levels of HBV DNA. During acute HBV infection, HBeAg appears shortly after the appearance of HBsAg. In persons who recover from HBV infection, HBeAg to hepatitis B e antibody seroconversion precedes that of HBsAg to anti-HBs seroconversion. Anti-HBe may persist for many years after the resolution of acute HBV infection. In persons with chronic infection, HBeAg may persist for years to decades. Seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe is usually associated with a marked decrease in serum HBV DNA levels and remission of liver disease, but some patients with anti-HBe continue to have high serum HBV DNA levels and associated active liver disease. The latter patients often have precore or core promoter HBV variants that prevent or decrease the production of HBeAg.37,38
Henry Lik-Yuen Chan, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, in, 2012
Also Check: What Is The Cure For Hepatitis B
False Reactive Test Results
What if I have a false reactive test result?
Every donation given to Canadian Blood Services is tested for infectious diseases caused by the hepatitis viruses B and C, HIV, syphilis and another uncommon virus called HTLV .
A false reactive test result means your initial screening test was reactivein other words, suggested the presence of something that would prevent you from donating bloodand a more precise follow-up test was negative. Almost all false reactive results occur because of interference with a test and are not necessarily due to testing positive for an infection.
FAQS
How does Canadian Blood Services test blood?
We follow a two-stage testing method that is used in laboratories worldwide. In the first stage, a sensitive screening test looks for the possible presence of infection. If the screening test shows no reaction, the blood is considered free of infection and no further testing is done. However, if the screening test is reactive, further testing is done to sort out whether the reactive result was due to an infection in the blood or interference with the test. The second test identifies markers in the blood that are found only when infection is present.
Do I need to go to my doctor for repeat testing?
Yes. Repeat testing should be discussed with your doctor because he/she is in the best position to offer you personal medical advice.
Do my partner, children, or friends need to worry if Ive had a false reactive result?
We Implement Proven Measures To Keep Your Data Safe

At HealthMatters, were committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. Weve put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
Popular search
Read Also: How Do You Contact Hepatitis A
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
Explainer: Lab Results And Their Interpretation
Before posting your lab results, please read through and abide by the best practices thread first
We all know that its important to have blood tests to know your current Hep B status or to know if youre protected against it. There are a lot of different tests in a panel for Hep B and these can be confusing. Here are short explanations for some of the common ones:
Use this thread to get help if you dont understand your results.
Hi Everich,
You need to be a bit more specific about what the exact test was. What is all the information you have about the test? We cannot answer your question without that information.
Thomas
Hi Everich, there are basically 3 blood tests that are required for a new vs. a chronic hepatitis B infection. Below is a simple summary of these tests. If you could let us know which blood test was indeterminate that would be very helpful.
Hepatitis B surface antigen – If or means the hep b virus is present. This could mean a new infection or a chronic infection . If this test is or , then the hep b virus is not present in the blood.
Hepatitis B surface antibody – this tests for a protective antibody against the hep b virus. This can occur through getting the hep b vaccine or recovery from an exposure to the virus. If or , then it means a person has been protected against the hep b virus either through vaccination or recovery from an infection. Generally, the above test will be or .
Her report says HBV VIRAL LOAD < 34. IU/ml
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis Be Transmitted Through Saliva
Interpretation Of Diagnostic Tests
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first marker of HBV detectable in serum in acute infection. By the time clinical and biochemical hepatitis is present after an incubation period of up to 140 days, other serologic markers of HBV infection appearâincluding antibody to HBV core antigen . Hepatitis B core antigen, a marker of viral replication found in infected hepatocytes, does not circulate in serum. However, its corresponding antibody does. Documented HBsAg positivity in serum for 6 or more months suggests chronic HBV with a low likelihood of subsequent spontaneous resolution. Chronic HBV is diagnosed by the absence of IgM anti-HBc antibody. IgM anti-HBc antibody is a marker of acute or recent acute hepatitis B and is detectable for 6 months after infection, whereas IgG anti-HBc is lifelong. If acute HBV resolves, neutralizing antibody against HBsAg develops. If HBV infection becomes chronic, other HBV markersâincluding HBV viremia and hepatitis e antigen âshould be sought. Both of these markers imply viral replication and thus greater infectivity, although any patient who is HBsAg positive is potentially infectious.
Rima Fawaz, Maureen M. Jonas, in, 2021
Dont Miss: Hepatitis B Shot Side Effects
Additional Specimen Collection Information
Collect blood in a lithium heparin, green-top, EDTA purple-topor red-top tube. PST and SST are acceptable. Serum orplasma should be separated from contact with the cells within 2hours of collection. Specimens not centrifuged within 4 hours ofcollection may be rejected. Refrigerate the specimen if unable toassay within 8 hours of collection. Samples with > 1+ lipemiamust be cleared prior to analysis.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
Surrogate Outcome For Nucleoside Analogs
Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion is much less durable for nucleoside analogs than peginterferon therapy, particularly among Asian patients for whom the infection has persisted since early childhood. Up to 50% of patients may experience hepatitis relapse after HBeAg seroconversion within 3 years posttreatment.92 Therefore HBeAg seroconversion is not an ideal surrogate marker of response for nucleoside analogs, particularly if the posttreatment follow-up is not long enough. As HBsAg clearance is rarely observed with nucleotide analogs, evaluation of predictors for HBsAg clearance may be difficult and less clinically useful.
Milan J. Sonneveld, Suzanne van Meer, in, 2021
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc