Clinical Significance Of Hepatitis C Genotypes
Genotype generally has not been found in epidemiological studies to play a large rolein liver disease progression due to HCV. Rather, genotype is of clinical importanceprincipally as a factor in selecting the appropriate HCV medications for treatment. Please see the HCV Treatment Considerations for more information.
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis B
In most of the adult cases of hepatitis B , the virus is completely cleared from the body upon treatment. However, the remaining 5% can go on to develop chronic forms of the disease. It has been observed that within 6 months of the treatment, most people not only clear the virus but also become immune to the same. In general, there are 3 distinct types of hepatitis B infections seen:Healthy Chronic Carriers These people carry the virus but dont develop any symptoms. They are not infectious to others but have a higher risk of developing hepatic conditions such as cirrhosis. However, if the immune system in such individuals gets suppressed owing to an infection or treatment via immunosuppressant drugs, there are chances that they may develop hepatitis B infection. Chronic Infectious Carriers They are the contagious carriers of the disease as they have virus replicating in their systems. They show signs of hepatitis such as damaged liver that progresses into liver cirrhosis. Only 5% of the cases can show remission of the virus.Chronic Mutant The chronic mutant form is a result of a mutated strain of the virus that causes permanent alteration to the hepatitis B viruss genetic makeup. Those with it have the risk of being infectious to others and it is observed to be more resistant to treatment than other forms of hepatitis B.
Also Check: How Often For Hepatitis B Vaccine
What’s The Difference Between Hepatitis A B And C
So, what are the main differences between hepatitis A, B, and C? Let’s summarise …
- Hepatitis A and B can be passed on via bodily fluids, whereas hepatitis C usually only spreads through blood-to-blood contact with an infected person.
- Unlike hepatitis A and B, it can take years for symptoms to present themselves in hepatitis C.
- A vaccine for hepatitis B is typically offered to babies to reduce their risk of contracting the virus.
- Hepatitis C has no immunity, and it is possible to get it again, whereas the risk of becoming infected again is lower with hepatitis A and B.
You May Like: How To Tell If You Have Hepatitis
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the bodyâs reaction to the viral infection or the bodyâs reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Read Also: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis
Different Types Of Hepatitis And Their Symptoms
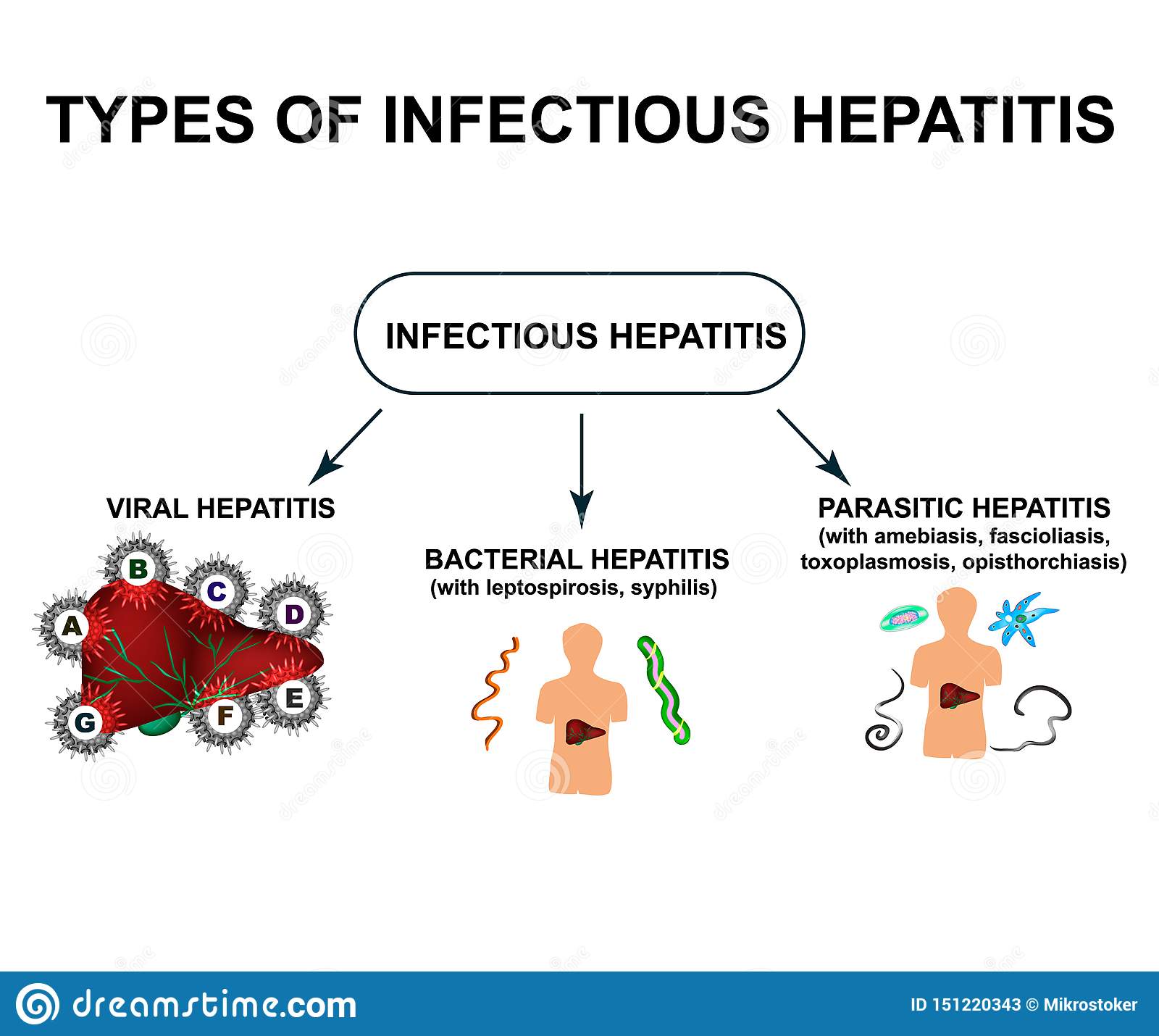
In this article:
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis B and C can lead to chronic liver disease, whereas hepatitis C accounts for a larger proportion of disease in the United States, with approximately 2.4 million adults being infected with hepatitis C compared to 1.59 million infected with hepatitis B.
The incidence of cirrhosis in the affected groups is comparable. The risk of liver cancer is also similar in patients with chronic hepatitis B and C with cirrhosis.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
What You Should Do
- Get the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines series.
- Wear gloves if you have any chance of touching blood or other body fluids.
- Dont share or re-use needles or works.
- Dont share personal-care items, such as toothbrushes, razors, nail files, combs, or washcloths. There may be contaminated blood on these items that you cannot see.
- Use a condom every time you have sex.
- If you are a healthcare worker or first responder, always follow universal precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps.
- Wash your hands after going to the bathroom or changing a diaper on a young child or an adult.
- Wash your hands before preparing food.
Hepatitis And The Liver
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is important for a range of functions in the body. These include regulating metabolism, making proteins, storing vitamins and iron, removing toxins and producing bile.
If the liver doesnt work properly, it can cause serious illness or sometimes even death.
Hepatitis may be caused by infection, viruses, chemicals, alcohol and other drug use and other factors.
Chronic hepatitis means ongoing inflammation of the liver, irrespective of the underlying cause.
Read Also: Best Food For Hepatitis B
Is There A Cure For Hepatitis A
Though a Hepatitis A infection can pass within a few months, it can sometimes be life-threatening. No specific treatment can be provided for this type of Hepatitis aside from medication that may help relieve symptoms such as pain, itching and feeling sick.
You should get vaccinated against Hepatitis A if you are planning travel to a region where there is a high prevalence of the virus. This includes areas such as Africa, Central and South America, Eastern Europe, the Far East or the Indian subcontinent.
How Is Hepatitis A Diagnosed
Some people have only a few symptoms and no signs of jaundice. Without visible signs of jaundice, its hard to diagnose any form of hepatitis through a physical examination. When symptoms are minimal, hepatitis A can remain undiagnosed.
After you discuss your symptoms with your doctor, they may order a blood test to check for the presence of a viral or bacterial infection. A blood test will reveal the presence of the hepatitis A virus.
Complications due to a lack of diagnosis are rare.
Also Check: Will Hepatitis C Kill You
Passing On Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is rarely passed on during sex like hepatitis A and B are, but is usually spread through blood-to-blood contact, which can include sharing needles.
There is no immunity to hepatitis C, and it is possible to get it again, even if previous infections have cleared. If left untreated, hepatitis C can be fatal. Hepatitis C can also be chronic, meaning it leaves long-term effects. In very serious cases, it can lead to liver failure or liver cancer.
If you have concerns about possible hepatitis, you should consult your GP or a sexual health professional.
You can also find advice below, with websites linking to support groups in various areas:
How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
Like hepatitis A, medical treatment for acute hepatitis B is focused on getting plenty of rest and fluids and eating a healthy diet, although sometimes antiviral drugs are recommended for severe cases to help prevent liver failure. Patients with chronic hepatitis B may be given an oral antiviral drug to control the viral infection and minimize liver damage. These drugs are effective, but they rarely cure chronic hepatitis B. Therefore, these medications often have to be taken for life.
Also Check: What Is The Meaning Of Hepatitis B
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Govind explains that a lot of people who contract hepatitis B do not notice any symptoms, or the symptoms can be mild and, therefore, easy to miss.
But, after weeks or months, hepatitis B can lead to:
These symptoms can also last for several weeks and take months to recover from, but 95% of adults do recover fully from hepatitis B and symptoms tend to be mild1.
What Is The Prognosis Of Viral Hepatitis
The prognosis of viral hepatitis for most patients is good however, this prognosis varies somewhat depending on the infecting virus. For example, those patients who develop chronic hepatitis have a worse prognosis because of the potential to develop cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer , and occasionally death.
Symptoms of viral hepatitis such as fatigue, poor appetite, nausea, and jaundice usually subside in several weeks to months, without any specific treatment. Virtually all patients with acute infection with HAV and most adults with acute HBV recover completely.
Complete recovery from viral hepatitis means that:
- the hepatitis virus has been eliminated from the liver by the body’s immune system,
- the inflammation in the liver subsides,
- the patient develops immunity to future infection with the same virus, and
- the patient cannot transmit the infection to others.
Unfortunately, not all patients with viral hepatitis recover completely. Five to 10 percent of patients with acute HBV infection and about 75% to 80% of patients with acute HCV infection develop chronic hepatitis. Patients that develop fulminant hepatitis have about an 80% fatality rate. Chronic HCV infections are the leading cause of liver transplants.
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
Also Check: How Did I Get Hepatitis B
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
- All people born between 1945 and 1965
- Anyone who has ever injected drugs, even if once or many years ago
- People with HIV infection
- People who had a blood transfusion organ transplantation before 1992
- People who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or other injury
- People receiving hemodialysis
- People who have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
You May Like: Blood Work For Hepatitis B
Killed Or Inactivated Vaccines
One alternative to attenuated vaccines is a killed or inactivated vaccine. Vaccines of this type are created by inactivating a pathogen, typically using heat or chemicals such as formaldehyde or formalin. This destroys the pathogens ability to replicate, but keeps it intact so that the immune system can still recognize it.
Because killed or inactivated pathogens cant replicate at all, they cant revert to a more virulent form capable of causing disease . However, they tend to provide a shorter length of protection than live vaccines, and are more likely to require boosters to create long-term immunity. Killed or inactivated vaccines on the U.S. Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule include the inactivated polio vaccine and the seasonal influenza vaccine .
Dont Miss: What Is Hepatitis C Ab
What Is The Treatment For Viral Hepatitis
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis and chronic viral hepatitis are different. Treatment of acute viral hepatitis involves resting, relieving symptoms, and maintaining an adequate intake of fluids. Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis involves medications to eradicate the virus and taking measures to prevent further liver damage.
Acute hepatitis
In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain . Careful attention should be given to medications or compounds, which can have adverse effects in patients with abnormal liver function . Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally, and drugs may accumulate in the blood and reach toxic levels. Moreover, sedatives and tranquilizers are avoided because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma. The patient must abstain from drinking alcohol since alcohol is toxic to the liver. It occasionally is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Chronic hepatitis
Medications for chronic hepatitis C infection include:
- oral daclatasvir
Also Check: How Hepatitis C Virus Spread
If You Think You Have Been Exposed To Viral Hepatitis
- Contact your healthcare provider or go to a to get a blood test. If you think you were exposed to hepatitis A or B, call your healthcare provider to get a hepatitis A or B blood test.
- Ask your healthcare provider if you or other people who live with you need Immune Globulin or hepatitis B Immune Globulin . IG may be recommended for people who live with or have close contact with someone who has hepatitis. HBIG may be recommended for someone who was exposed to hepatitis B.
Do You Need Vaccinations Before Traveling Abroad
The CDC divides travel vaccinations into three categories: 1) routine, 2) recommended, and 3) required. The only vaccine classified as required by International Health Regulations is the yellow fever vaccination for travel to certain countries in sub-Saharan Africa and tropical South America.
Routine vaccinations are those that are normally administered, usually during childhood, in the United States. These include immunizations against:
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B Cause Urinary Tract Infection
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Types Of Hepatitis: Hepatitis D
The hepatitis delta virus , which is a satellite , causes this disease. Thus, to spread, the patient or host has to be infected with the hepatitis B virus.
Transmission can occur through blood or sexual contact. Also, an infected mother can transmit it to her child in the womb. Fortunately, the hepatitis B vaccine is effective in preventing the delta particle as well.
Experts dont know much about this delta agent. In some cases, the hepatitis B symptoms worsen due to the coinfection, while it went unnoticed in others.
You May Like: How Do You Contact Hepatitis C
How Is Viral Hepatitis Spread
Hepatitis A and hepatitis E usually spread through contact with food or water that was contaminated with an infected personâs stool. You can also get hepatitis E by eating undercooked pork, deer, or shellfish.
Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hepatitis D spread through contact with the blood of someone who has the disease. Hepatitis B and D may also spread through contact with other body fluids. This can happen in many ways, such as sharing drug needles or having unprotected sex.
What Is Reactive Hepatitis
Looking for an answer to the question: What is reactive hepatitis? On this page, we have gathered for you the most accurate and comprehensive information that will fully answer the question: What is reactive hepatitis?
For the hepatitisBcore antibody test,a reactiveor positive resultcan meaneither that a person is currently infected with hepatitisBvirus or have been some time in the test. A reactiveresultfor this testcan also be a false positive,meaningthat the person has never been infected with the virus.
anti-HBs or HBsAb â A âpositiveâ or âreactiveâ anti-HBs test result indicates that a person is protected against the hepatitis B virus. This protection can be the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine or successfully recovering from a past hepatitis B infection.
A âreactiveâ HCV antibody test could mean you were exposed to the HCV virus at some point in the past . However, there is a significant chance this was a false positive test. Additionally, about 20% of patients who are indeed exposed will clear the virus with their own immune response in the acute phase of infection.
A âreactiveâ result from your finger prick test indicates that HIV antibodies may be present. However,this is NOT definite and reactive results can occur and a subsequent negative HIV result be determined. If the test result is âreactiveâ additional laboratory testing is required before a definitive HIV result can be confirmed.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Reactive What Does It Mean
What Is A Ccg Or Ics
CCGs were established as part of the Health and Social Care Act in 2012. They are groups of general practices, which come together in each area to commission the best services for their patients and population.
ICS are new partnerships between the organisations that meet health and care needs across an area, to coordinate services and to plan in a way that improves population health and reduces inequalities between different groups. ICS will replace Clinical Commissioning Groups by April 2022 and cover a wider geographic area than CCGs.
Devolved nations health is primarily a devolved matter across the four nations which make up the UK. Among these variations are differing regional structures, Scotland and Wales have Health Boards, England have CCGs and Northern Ireland has Health and Social Care Trusts.