How Can Hepatitis D Be Prevented
-
Avoiding hepatitis B infection is the only way to prevent hepatitis D infection. All methods to prevent hepatitis B infection will lead to prevention and reduce the risk of getting hepatitis D.
-
Getting vaccinated: Vaccination is bliss vaccination of hepatitis B is available. All children should be vaccinated. Adults with a high risk of infection are recommended for vaccination. This vaccination is usually an episode of three consecutive injections over six months.
-
Be cautious during tattooing and piercing, inquire about the sterilization of the equipment, and make sure they use sterile needles. Go to a trustworthy place.
-
Stop using drugs, and avoid injectable recreational drugs like heroin and cocaine. Use sterile needles each time in case you are not able to avoid drugs and never share the needle with other people.
-
Always practice safe sex, and use protection such as condoms. Never have unprotected sex with someone who has been infected by any type of hepatitis or any STDs .
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis Ab And C
What Are The Complications Of Chronic Hepatitis D
Chronic hepatitis D may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. People who have chronic hepatitis B and D are more likely to develop these complications than people who have chronic hepatitis B alone.20 Early diagnosis and treatment of chronic hepatitis B and D can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Hepatitis And The Liver
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is important for a range of functions in the body. These include regulating metabolism, making proteins, storing vitamins and iron, removing toxins and producing bile.
If the liver doesnt work properly, it can cause serious illness or sometimes even death.
Hepatitis may be caused by infection, viruses, chemicals, alcohol and other drug use and other factors.
Chronic hepatitis means ongoing inflammation of the liver, irrespective of the underlying cause.
You May Like: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
Read Also: How Did Hepatitis C Start
Causes And Risk Factors Of Hepatitis D
The primary route of transmission for hepatitis D is contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. This can happen through sharing needles or drug materials with an infected person or having unprotected sex with an infected person.
Although it is rare, hepatitis D can be passed from mother to child during birth.
People cant get hepatitis D through everyday close contact that doesnt involve blood or bodily fluids.
Does Medicare Cover Hep C Testing

Medicare typically does cover Hepatitis C testing one time if you have risk factors that put you at a high risk for getting Hepatitis C.
Medicare Advantage plans may also cover Hep C testing that meets eligible criteria and is ordered by a doctor. Many Medicare Advantage plans also cover prescriptions drugs, which Original Medicare doesnt cover.
Also Check: How Do They Treat Hepatitis C
Diagnostic And Clinical Features
Active HDV infection is diagnosed by the finding in serum or liver of the HDV RNA or of the HDAg. Viremia can be detected with genetic probes that hybridize with complementary HDV RNA transcription polymerase chain reaction can detect in serum 10 to 100 copies of the viral genome.
The clinical course of acute HBV/HDV coinfections varies according to the degree of HBV and HDV expression and the interplay between the two viruses, ranging from icteric hepatitis, with full but transient expression of both viruses, to milder anicteric forms associated with diminished HDV expression. Early repression of HBV can inhibit HBsAg synthesis to the extent that this marker is not detectable in serum.
Acute hepatitis D is clinically and histologically indistinguishable from ordinary hepatitis B distinction requires specific serologic testing. The markers of HBV infection are the HBsAg and IgM anti-HBc finding the latter is required for diagnosing HBV/HDV coinfection as opposed to superinfection. Coinfection hepatitis is diagnosed from the increase of IgM anti-HD the IgG antibody also increases but is usually elevated after a delay of several weeks, compared to the IgM antibody.
Severe forms of the illness are accompanied by the full battery of HDV markers, including early HD antigenemia. HDV RNA can be detected in serum very soon during the course of infection and disappears with resolution of disease.
Quirino Lai, … Jan P. Lerut, in, 2014
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis B
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis B is to control the virus and keep it from damaging the liver. This begins with regular monitoring for signs of liver disease. Antiviral medications may help, but not everyone can take them or needs to be on medication. Be sure to discuss the risks and benefits of antiviral therapy with your doctor.
You May Like: Is There Any Cure For Hepatitis C
Immunisation For Hepatitis B
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. A course of vaccination is recommended for all babies and people in high-risk groups.
Immunisation can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine. To be immunised, contact your doctor or local council.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule. In Victoria, immunisation against hepatitis B is free for:
- Babies at birth immunisation against hepatitis B alone as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months combination immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 9 years of age.
- People aged less than 20 years having a catch-up immunisation.
- Refugees and humanitarian entrants aged 20 years and above.
In Victoria, free hepatitis B vaccine is provided for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
Immunisation is also recommended, but not necessarily free, for people who are at increased risk of infection, including:
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Information Sheet
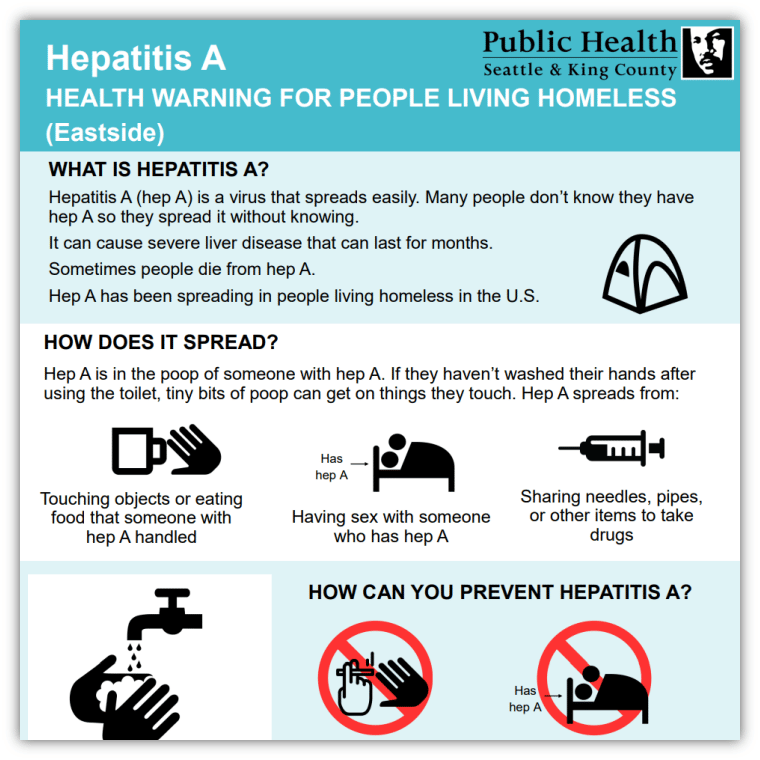
How Is Hepatitis A Infection Prevented
Vaccination
- The hepatitis A vaccine offers excellent protection against HAV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 2 doses of vaccine spaced 6-12 months apart. Protection starts 1-2 weeks after the first dose of vaccine, and lasts for 20 years to life after 2 doses.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis A vaccine starting at 1 year of age .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccine for all persons traveling to countries where HAV is common . For infants that will be traveling internationally, an early dose of Hepatitis A vaccine can be given at age 6-11 months.
Natural Immunity
- People who have hepatitis A infection become immune to HAV for the rest of their lives once they recover. They cannot get hepatitis A twice.
- The blood test for immunity to hepatitis A is called the Hepatitis A Total Antibody test. People who have had hepatitis A and those who have received hepatitis A vaccine show positive antibodies to hepatitis A on this test for the rest of their life.
Healthy Habits
- Good personal hygiene and proper sanitation help prevent the spread of the HAV virus. Always wash your hands with soap and water after using the bathroom, changing a diaper, and before preparing, serving, or eating food.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers do not kill the hepatitis A virus
After Exposure to HAV
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis
Treatment And Medication Options For Hepatitis D
Medications are not effective against acute hepatitis D, but fortunately, the acute infection tends to subside on its own.
As for chronic hepatitis D, appropriate treatment depends on the phase of the disease and how severe the infection is.
If a persons liver is severely damaged, a liver transplant may become necessary.
While treatment options for hepatitis D are limited, new medications are being studied.
The 5 Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Viral infections of the liver that are classified as hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. A different virus is responsible for each type of virally transmitted hepatitis.
Hepatitis A is always an acute, short-term disease, while hepatitis B, C, and D are most likely to become ongoing and chronic. Hepatitis E is usually acute but can be particularly dangerous in pregnant women.
You May Like: How Often Should You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDCâs travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
What Does The Test Measure
An acute viral hepatitis panel includes several tests that measure antigens and antibodies. Antigens are foreign substances such as proteins of the virus itself, while antibodies are substances produced by the immune system in response to the viral infection.
An acute viral hepatitis panel tests for antigens and/or antibodies of hepatitis A, B, and C:
Dont Miss: Does Hepatitis A Cause Diarrhea
Also Check: Common Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Whos At Risk For Hepatitis C
You might be more likely to get it if you:
- Inject or have injected street drugs
- Were born between 1945 and 1965
- Got clotting factor concentrates made before 1987
- Received a blood transfusion or solid organ transplants before July 1992
- Got blood or organs from a donor who tested positive for hepatitis C
- Are on dialysis
Enteric Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
The Hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses are both transmitted by enteric, that is digestive or by fecal, routes. This is also known as the fecal-oral route. To be exposed to these viruses, you must ingest fecal matter that is infected with the virus. While there are several ways in which this fecal-oral route can be established, poor hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in some countries lead to higher rates of infection of these viruses.
As a result, some areas of the world, like India, Bangladesh, and Central and South America, are particularly prone to the hepatitis E virus. About one-third of people in the United States have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus.
It is believed that the hepatitis F virus may also be spread by enteric routes.
Read Also: What Is Viral Hepatitis C
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus, meaning that a person must come into contact with blood that contains the virus to contract it.
Most new cases of hepatitis C in the U.S. are due to injecting recreational drugs. Transmission can happen when a person with the virus shares needles or contaminated drugs with others.
The hepatitis C virus is very difficult to kill, and even tiny spots of blood that are invisible to the human eye can contain the virus.
People can also contract the virus in healthcare settings through exposure to blood that contains the virus, such as through accidental needlesticks.
According to the , the most common ways for hepatitis C to spread include:
- using injectable drugs
- receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992, which is before regular blood screens took place
- being accidentally poked with a used syringe, which can occur in healthcare settings
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can also spread through the following actions, though these are less common:
- sharing personal items that may contain blood, such as toothbrushes or razors
- getting a tattoo or piercing from an unregulated provider
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms. This means that a person can contract hepatitis C without knowing it. This makes it easier for them to transmit it to others.
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Chronic hepatitis D can lead to cirrhosis, which is when the liver slowly breaks down. Scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, which blocks the flow of blood. Gradually, the liver is able to function less and less.
If cirrhosis is diagnosed early and the underlying cause is treated, the damage can be halted and in some rare cases, reversed.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative
Home Remedies And Lifestyle
Healthcare and sanitation workers who have a higher chance of exposure to needle pricks should take additional precautions to prevent the accidental spread of infection. If you use injection drugs or live with someone who does, seek help immediately to reduce your exposure to long-term consequences.
Getting a hepatitis B vaccination can protect you against contracting hepatitis D, so talk to your doctor if you believe youre at risk.
Abstaining from alcohol will minimize strain on your liver. If you choose to drink, its essential to drink responsibly. Health authorities define responsible drinking as no more than one drink per day for women and no more than two drinks per day for men.
Binge drinking is harmful, especially when your liver function is already compromised from hepatitis.
Following safe sex practices will keep you from contracting additional infections and help keep your partner from getting hepatitis D. Safe sex to prevent the spread of hepatitis D is particularly important for men who have sex with other men.
How To Protect Yourself Against Hepatitis B
Dr. Fried emphasizes that hepatitis B infection can be prevented by avoiding risky behaviors involving sex and drugs and by getting vaccinated. The hepatitis B vaccination is required for infants at birth, and subsequent vaccinations for adults are also important. There are separate vaccines for hepatitis A and B, but there is also a combination A and B vaccine so you can take care of both types at once. In North Carolina, newborn vaccinations have been required since 1994. Anyone born before this year should talk to their health care provider about being vaccinated for hepatitis B.
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive
What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
What Is Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can spread from person to person.
The hepatitis D virus is unusual because it can only infect you when you also have a hepatitis B virus infection. In this way, hepatitis D is a double infection. You can protect yourself from hepatitis D by protecting yourself from hepatitis B by getting the hepatitis B vaccine.
Hepatitis D spreads the same way that hepatitis B spreads, through contact with an infected persons blood or other body fluids.
The hepatitis D virus can cause an acute or chronic infection, or both.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Common Cause Of Hepatitis
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Read Also: Do You Die From Hepatitis C