How Can The Spread Of Hepatitis C Be Prevented
People who have had hepatitis C should remain aware that their blood is potentially infectious.
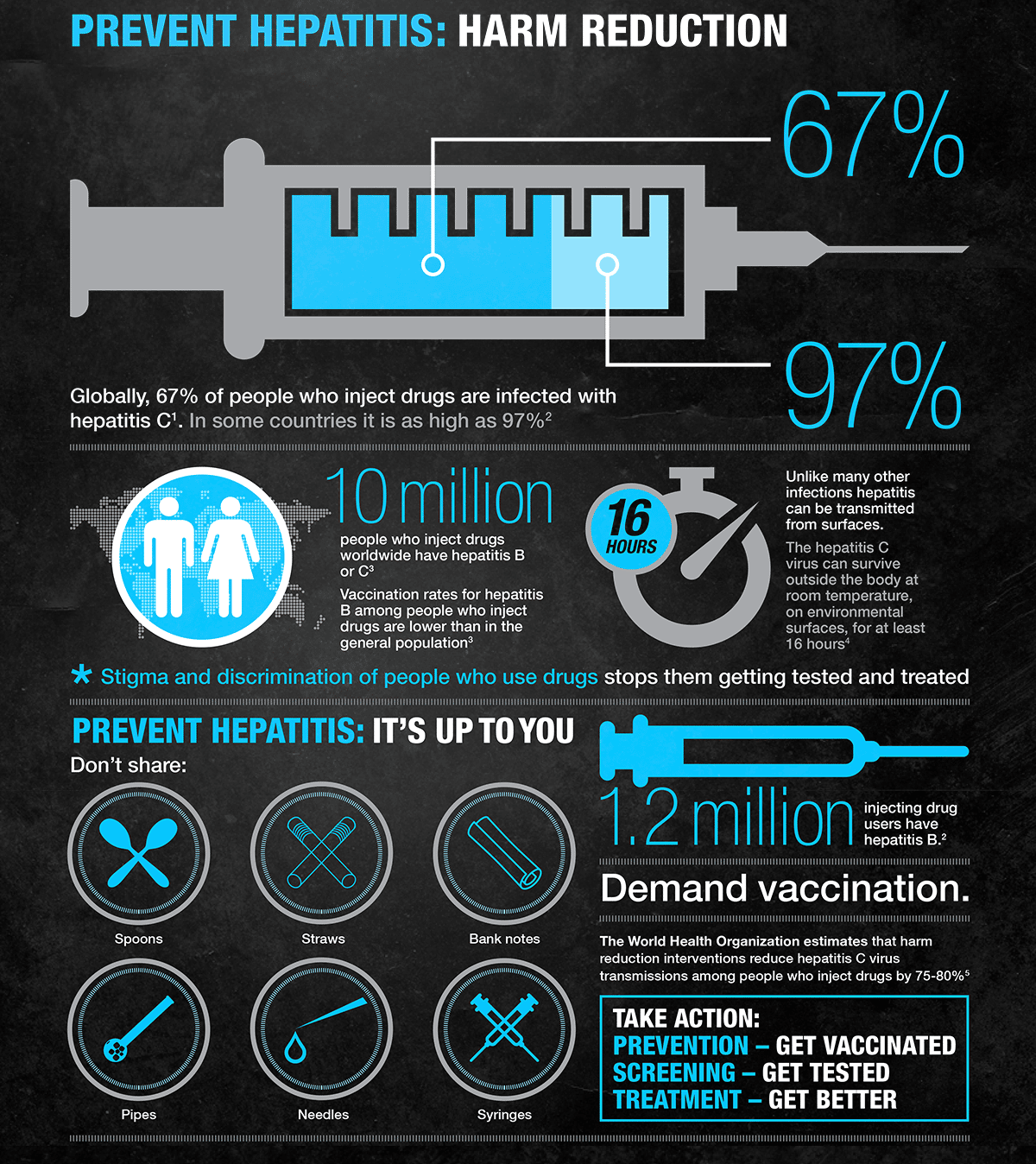
- Do not shoot drugs if you shoot drugs, stop and get into a treatment program if you cant stop, never share needles, syringes, water or works, and get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Do not share personal care items that might have blood on them .
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, always follow routine barrier precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about getting a tattoo or body piercing. You might get infected if the tools have someone elses blood on them or if the artist or piercer does not follow good health practices.
- HCV can be spread by sex, but this is rare. If you are having sex with more than one steady sex partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases. You should also get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- If you are infected with HCV, do not donate blood, organs or tissue.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Pass Hepatitis C
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often does not have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged.
This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition.
Symptoms can include:
- feeling and being sick
The only way to know for certain if these symptoms are caused by hepatitis C is to get tested.
Who Is Most At Risk Of Reinfection
People who continue to inject drugs after theyre cured of hepatitis C are more likely to contract an infection again. Injecting drugs often and sharing equipment like needles and syringes further increases the risk.
Injecting opioids like heroin together with stimulants such as methamphetamine increases the risk for both hepatitis C reinfection and drug overdose, a 2019 study found.
Men who have sex with men without using a condom are also at higher risk of hepatitis C reinfection. Using drugs can lead to sexual practices that can increase the odds of a hepatitis C reinfection
Read Also: Can Hepatitis Cause Kidney Problems
Causes And Risk Factors
THe HCV virus causes hepatitis C.
People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles. The virus is not easy to kill.
The CDC offers advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach might kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning, and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment may reduce the amount of HCV, but it might not stop a person contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so be sure to rinse the syringe thoroughly. Only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
A person cannot contract the virus from casual contact, breathing, kissing, or sharing food. There is no evidence that mosquito bites can transfer the virus.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But itâs important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Recommended Reading: How To Recover From Hepatitis B
Other Steps You Can Take
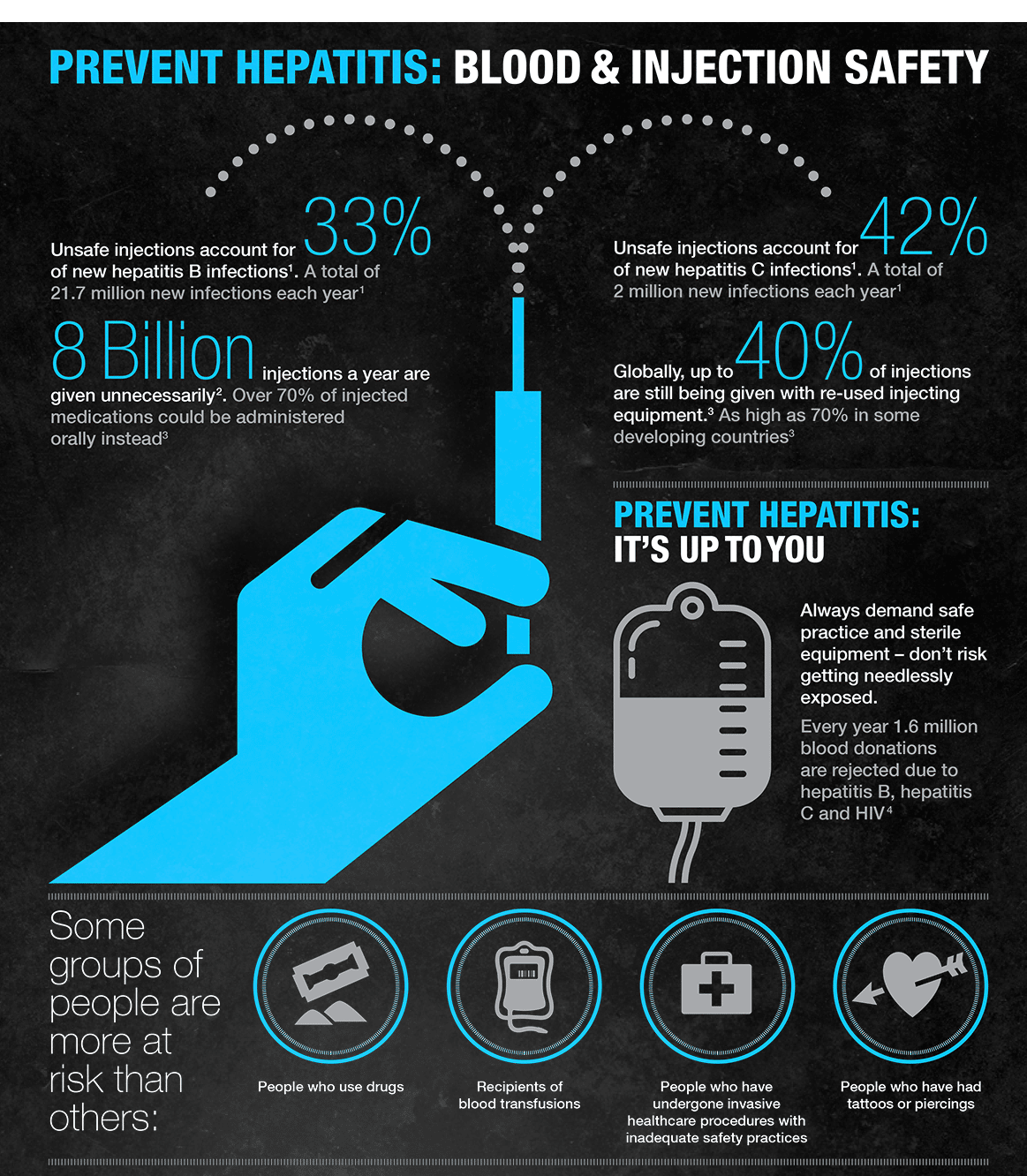
Screening of all donated blood has reduced the chance of getting hepatitis B and C from a blood transfusion. People newly diagnosed with hepatitis B infection should be reported to state health care workers to track the population’s exposure to the virus.
The hepatitis B vaccine, or a hepatitis immune globulin shot, may help prevent infection if it is received within 24 hours of contact with the virus.
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis C
If you are at risk of hepatitis C infection, or think you may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the past, see your doctor for an assessment of your liver health. This will include blood tests and possibly a non-invasive test for liver damage .
There are 2 blood tests used to diagnose hepatitis C. Usually these can be done at the same time but sometimes they will be done separately.
The first test known as a hepatitis C antibody test can tell you whether you have ever been exposed to hepatitis C.
It may take 2 to 3 months from the time of infection until a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis C, so there is a window period during which you cannot tell if you are or have been infected. In this time, take precautions to prevent the potential spread of the virus.
The second test is called hepatitis C PCR, which will be done if the antibody test is positive. This determines if the virus is still present in your blood or liver or if you have already cleared the infection.
If you have cleared the virus or had successful treatment to cure it, the PCR test will be negative.
A liver ultrasound or Fibroscan can also be performed to assess if you have any liver damage.
If your doctor is inexperienced in diagnosing hepatitis C you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Females
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Avoid Sharing Personal Care Items
Razors, cuticle scissors, and nail clippers can sometimes cause minor nicks and cuts. If you or someone else has HCV, infected blood can get on these items and spread the virus when shared between people, notes the Hepatitis C Trust.
Be mindful that the virus might also be spread by direct contact with dried contaminated blood, according to the U.K. National Helath Service . So its important to never share razors, nail clippers, scissors, and other personal care items like toothbrushes that may facilitate blood exposure, warns Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious disease physician and senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security who is based in Pittsburgh.
If personal care items have been contaminated with infected blood, a bleach-based product is a good way to clean these items, continues Dr. Adalja. And once cleaned, store them separately from personal items used by others.
RELATED: 7 Myths About Hepatitis C
You May Like: How Much Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
Drugs are licensed for treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis C. Combination drug therapy, using pegylated interferon and ribavirin, can get rid of the virus in up to five out of ten of persons with genotype 1, the most common genotype in the U.S. and eight out of ten persons with genotype 2 or 3. It is important to know that not everyone will need treatment. The decision to treat hepatitis C is complex and is best made by a physician experienced in treating the disease.
Vaccination For Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B
Vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B are the most effective preventive measures against those viruses. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended these vaccines for all babies as part of routine healthcare since the 1990s.
The vaccine can be administered to people of any age. If you were not vaccinated as a baby, it is fine to be vaccinated now. Vaccination provides long-term protection from infection.
Even if you have recently been exposed to the virus, the vaccine may prevent infection. Ideally, vaccination takes place within 24 hours of a possible exposure.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Our doctors recommend adopting certain behaviorssuch as avoiding shared needles and other risk factorsto prevent infection.
Also Check: Hepatic Wet Food For Cats
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Sexually Transmissible
What Is Hepatitis A
According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, hepatitis A is an infection that affects the liver and is typically transmitted through the fecal-oral route. That means a person ingests contaminated fecal matter from an infected person.
For example, if an infected person doesnt wash their hands properly after using the bathroom, the disease can spread from the persons hands.
A person infected with hepatitis A can remain infectious for a period of two to six weeks, but the majority of people infected with the disease will recover within three to six months and likely wont face life-long health issues.
What Are The Symptoms
Most people have no symptoms when they are first infected with the hepatitis C virus. If you do develop symptoms, they may include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Yellowish eyes and skin . Jaundice usually appears only after other symptoms have started to go away.
Most people go on to develop chronic hepatitis C but still dont have symptoms. This makes it common for people to have hepatitis C for 15 years or longer before it is diagnosed.
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Contagious After Being Cured
You May Like: Hepatitis C Screening Guidelines Cdc
Hepatitis A Outbreak Linked To Strawberries: Signs And Symptoms To Watch Out For
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Contact a qualified medical professional before engaging in any physical activity, or making any changes to your diet, medication or lifestyle.
Canadian health agencies are investigating a hepatitis A outbreak in Alberta and Saskatchewan that was likely caused by imported organic strawberries.
According to the Public Health Agency of Canada , six people in Saskatchewan and four people in Alberta have gotten sick from eating the fruit. While four people have been hospitalized, the PHAC says there have been no reported deaths.
The imported fresh organic strawberries were purchased in early March at Co-op stores in both provinces under the brand name FreshKampo or HEB. Despite the berries no longer being available on Canadian store shelves, health officials are asking people to check their freezers in case they stored the strawberries for later use.
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has also identified the outbreak, reporting 17 cases in three states.
Canadian food-borne illness expert Dr. Michael J. Rieder says its not uncommon for fruit to get contaminated with hepatitis A. However, the professor of paediatrics medicine, physiology and pharmacology at Western University in London, Ont. advises that people should be mindful of what hepatitis A symptoms look like in case a person gets infected with the disease.
Do Not Inject Drugs Or Share Needles
Drug Use
Intravenous drug use, or injecting drugs in any way, is the leading single cause of the spread of HCV. To protect yourself, avoiding the use of used needles is the single best way to stop the spread of HCV.
It is difficult to abruptly stop using addictive drugs. If you are addicted to illegal drugs, a needle exchange program may be available in your area. These programs offer ways to get sterile syringes and many of these programs provide additional services, such as referrals to drug treatment centers, counseling, and primary health care. For more information, check with your local department of public health.
Medical Use
If you use needles for medical care, always use sterile equipment and do not share needles for any reason.
You May Like: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
How Hepatitis C Spreads
The virus spreads from direct contact with infected blood. This means that the blood of an infected person somehow gets inside the body of someone who, up to that point, wasnt infected.
The most common method of hepatitis C transmission is sharing needles or other equipment used to inject drugs. It can also spread in a healthcare setting, such as from an accidental needle stick. A mother can pass it to her baby during childbirth.
Its less common, but you can pick up the virus by sharing razors, toothbrushes, or other personal care items with an infected person.
It can also spread through sexual contact. This is more likely to occur if you:
- have multiple sex partners
- have a sexually transmitted disease
- are infected with HIV
Read Also: How Do Catch Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is usually spread through blood-to-blood contact.
Some ways the infection can be spread include:
- sharing unsterilised needles particularly needles used to inject recreational drugs
- sharing razors or toothbrushes
- from a pregnant woman to her unborn baby
- through unprotected sex although this is very rare
In the UK, most hepatitis C infections happen in people who inject drugs or have injected them in the past.
It’s estimated around half of those who inject drugs have been infected with the virus.
You May Still Have Liver Damage
If you had high levels of liver damage before you started treatment, you may still have an increased risk of liver cancer after the infection has been cured, says Menon.
To assess liver damage, your doctor will perform a biopsy or a scan either before or after treatment. If theres no scarring, you probably wont need long-term follow-up.
If you have cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis , however, you may need to be followed over the long-term, potentially for the rest of your life. The reason: Your doctor will want to be sure your liver is functioning properly and look for signs of liver cancer. Your liver function can deteriorate to the point where you need a transplant, says Menon.
There is some evidence that new treatments may improve scarring but its too early yet to be sure. The drugs are very new, so its hard to say one way or another, says Menon.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B And C Contagious
Wisconsin Hepatitis C Program
The Wisconsin Hepatitis C Program is the lead agency in Wisconsin responsible for coordinating the state’s public health activities focused on the prevention, detection, and treatment of hepatitis C.
COVID-19 impact on people with hepatitis C
Learn how the Hepatitis C Program is impacted by COVID-19.
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C is spread through contact with blood from an infected person. Today, most people become infected with the hepatitis C virus by sharing needles or other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs. For some people, hepatitis C is a short-term illness, but for more than half of people with the hepatitis C virus, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection. People with chronic hepatitis C can often have no symptoms and dont feel sick. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The best way to prevent hepatitis C is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injecting drugs. Getting tested for hepatitis C is important, because treatments can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks..