Reducing The Risk Of Hepatitis B
Simple steps that everyone can take to protect themselves against hepatitis B include:
- Making sure you and your children are immunised this is the best protection.
- Using condoms every time you have anal or vaginal sex with new partners until you both get a check-up .
- Avoiding oral sex if you or your partner have herpes, ulcers or bleeding gums it is unlikely that you will contract hepatitis through oral sex unless blood is present.
- Choosing to have any body piercing or tattooing done by an experienced practitioner who follows good sterilisation and hygiene practices, and who works at premises registered by the local council.
- Wearing single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or need to clean up blood or body fluids.
- Never sharing needles and syringes or other equipment , if you inject drugs. Always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. Always wash your hands before and after injecting.
If you have hepatitis B:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment in some instances, which greatly reduces the risk of you becoming infected with hepatitis B.
How Can I Pay For My Medication
Private health insurance or drug plansIf you have private health insurance or a drug plan at work, you may be able to have the medication paid through your plan. Please consult your private health insurance or drug plan provider to see if your drug is covered.
Publicly funded drug plansEach province and territory has their own rules. Some provincial drug plans provide coverage for individuals 65 and older, or those on social assistance. Some provinces provide special support to low-income individuals. Please call your Provincial Ministry or Department of Health to get more information about the terms of the publicly funded drug plan in your province.
Quebec public drug programIn Quebec, everyone must be covered by prescription drug insurance either through private or publicly funded plans.
Each provincial and territorial government offers a drug benefit plan for eligible groups. Some are income-based universal programs. Most have specific programs for population groups that may require more enhanced coverage for high drug costs. These groups include seniors, recipients of social assistance, and individuals with diseases or conditions that are associated with high drug costs. For more details, please contact your provincial or territorial health care ministry, or click on the appropriate link below.
Yukon
Available Patient Assistance Program for Hepatitis B treatment VEMLIDY
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis Look Like
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
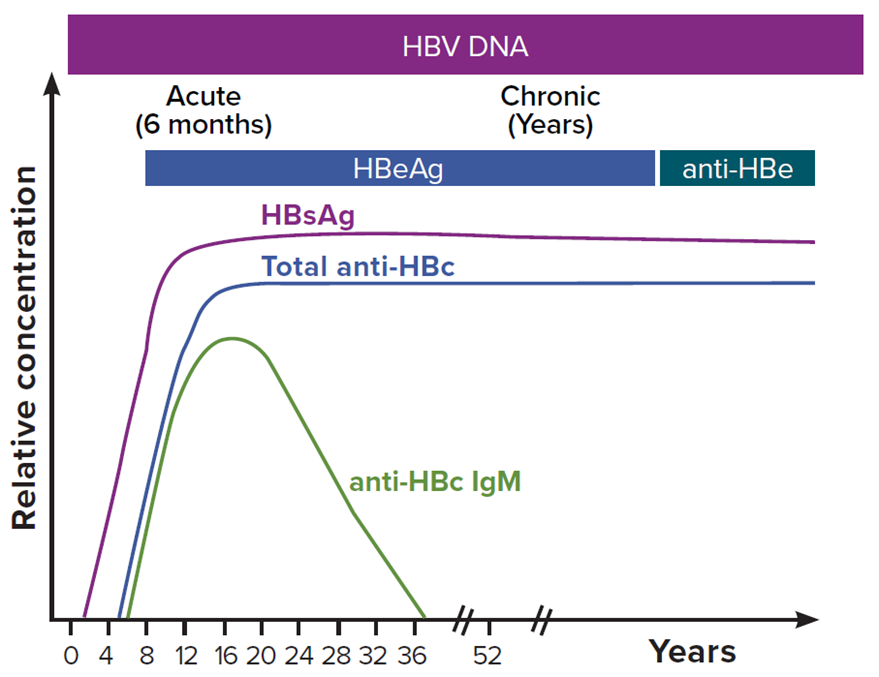
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
Screening Healthy People For Hepatitis B
Doctors sometimes test certain healthy people for hepatitis B infection because the virus can damage the liver before causing signs and symptoms. Talk to your doctor about screening for hepatitis B infection if you:
- Are pregnant
- Live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Have had many sexual partners
- Have had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Have a history of a sexually transmitted illness
- Have HIV or hepatitis C
- Have a liver enzyme test with unexplained abnormal results
- Receive kidney dialysis
- Take medications that suppress the immune system, such as those used to prevent rejection after an organ transplant
- Use illegal injected drugs
- Are in prison
- Were born in a country where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe
- Have parents or adopted children from places where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
Most people diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B infection need treatment for the rest of their lives. Treatment helps reduce the risk of liver disease and prevents you from passing the infection to others. Treatment for chronic hepatitis B may include:
- Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medications including entecavir , tenofovir , lamivudine , adefovir and telbivudine can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth. Talk to your doctor about which medication might be right for you.
- Interferon injections. Interferon alfa-2b is a man-made version of a substance produced by the body to fight infection. It’s used mainly for young people with hepatitis B who wish to avoid long-term treatment or women who might want to get pregnant within a few years, after completing a finite course of therapy. Interferon should not be used during pregnancy. Side effects may include nausea, vomiting, difficulty breathing and depression.
- Liver transplant. If your liver has been severely damaged, a liver transplant may be an option. During a liver transplant, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. Most transplanted livers come from deceased donors, though a small number come from living donors who donate a portion of their livers.
Other drugs to treat hepatitis B are being developed.
Also Check: Daa Drugs For Hepatitis C
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Who Is At Risk Of Hepatitis B
Anyone can get hepatitis B if not vaccinated. However, in the U.S., you may be at a higher risk if you:
- Have sex partners that have hepatitis B
- Have HIV or another STD
- Inject drugs or share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Are undergoing dialysis
- Have diabetes
- Travel to areas that have moderate to high rates of hepatitis B
- Work in health care or public safety and are exposed to blood or body fluids on the job
- Are an infant born to an infected mother
Don’t Miss: If You Have Hepatitis B Do You Have Hiv
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
From Person To Person
Blood and other bodily fluids, such as semen and vaginal secretions, contain the virus in infected people. The main ways in which people in the UK become infected include the following:
- Having unprotected sex with an infected person. Even having oral sex can transmit hepatitis B.
- From infected blood. You only need a tiny amount of infected blood to come into contact with a cut or wound on your body to allow the virus to enter your bloodstream, multiply and cause infection. For example:
- Sharing needles and/or any injecting equipment to inject drugs. Even a tiny amount of blood left on a needle from an infected person is enough to cause spread to others.
- Some people who had a blood transfusion or another blood product several years ago were infected with hepatitis B. Now, all blood donated in the UK is checked for the hepatitis B virus . So, the risk of getting hepatitis B from a blood transfusion in the UK is now very small.
- From ‘needlestick’ accidents where the needle was used on an infected person.
- There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors and other such items which may be contaminated with blood. The virus can actually live outside the body for more than one week.
- From using equipment which is not sterile for dental work, medical procedures, tattooing, body piercing, etc.
- A bite from an infected person, or if their blood spills on to a wound on your skin, or on to your eyes or into your mouth.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
How Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Series Work
The vaccine protects you from the hepatitis B virus by getting your body’s immune system to make antibodies. Those antibodies protect you by fighting off the virus if it ever gets into your body.
Usually, the vaccine is spaced out into three different shots called a hepatitis B vaccine schedule. One month after your first shot, you get the second shot. Six months after your first shot, you get the third shot. If you miss your second or third dose, get it as soon as you remember.
The hepatitis vaccine is super effective. Its worked really well to lower the number of people who get hepatitis B every year.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis From Donating Plasma
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
What Makes Hepatitis B Such A Difficult And Lethal Virus
Hepatitis B is a highly infectious virus, more so than hepatitis C and even HIV. In some parts of the world, the prevalence rates are very high up to 20%. For Korean people, the prevalence rates have been markedly reduced by nationwide vaccination programs, but those who already have the infection remain at risk.
Even with vaccination, there are instances where, for those at high risk such as babies born to mothers who have hepatitis B vaccination may not be enough to prevent infection. Also, in some cases, one course of hepatitis B vaccine might not be adequate and further vaccination courses may be needed. It is safest for people to have a doctor check their blood tests looking for protective antibody levels to ensure that they are not in this group.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Titer Blood Test
Treatment For The Short
No treatment can clear the germ from the body. If you develop symptoms when first infected, treatment aims to help ease symptoms until they go – for example, drinking plenty of water to avoid lack of fluid in the body . Rarely, a severe hepatitis develops which may need hospital care. No treatment can prevent acute hepatitis B from becoming persistent .