How Is It Diagnosed
First, your doctor will ask you to have some physical examinations and some blood tests.
In addition, he will also ask for ultrasound tests, computed tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging , and angiograms.
You may also need to do a biopsy, in which a piece of liver tissue is removed and studied in the lab.
Reference:
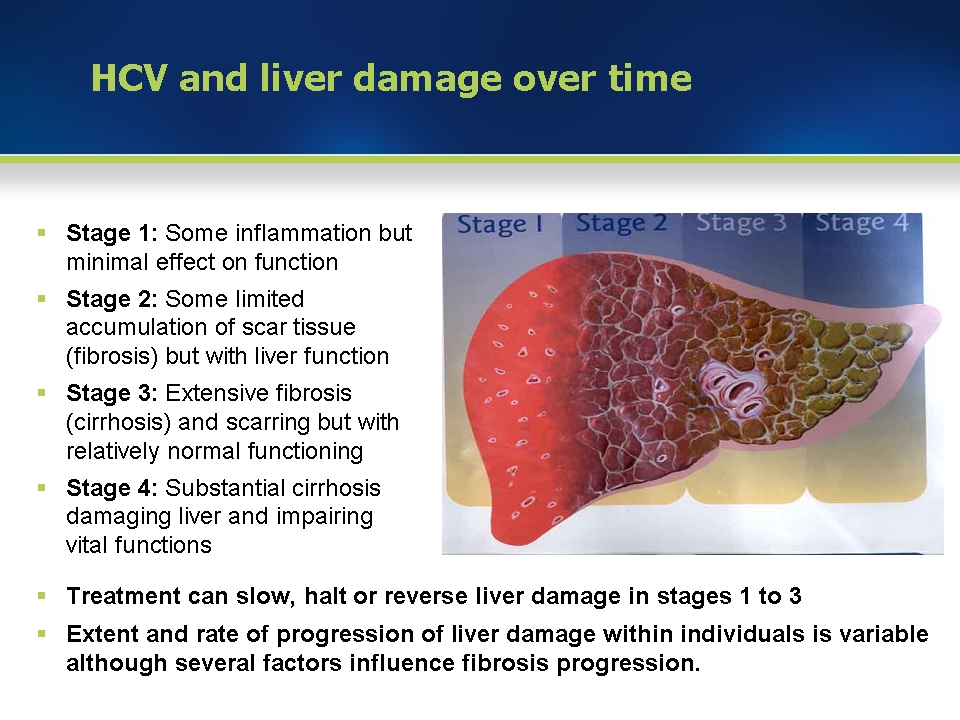
Hepatitis C: Risk Of Liver Cancer
Individuals who are infected with hepatitis B infection or liver disease C virus might establish a chronic infection that can result in cirrhosis. The damage that results increases the risk of liver cancer .
The risk of liver cancer is greater for people who have chronic HBV or HCV infection than for the basic population.
If you have chronic HBV infection:
- You might establish liver cancer even if you do not have cirrhosis. However most people who have HBV and liver cancer also have cirrhosis.
- Getting antiviral therapy to treat chronic HBV infection might reduce your risk for developing liver cancer.
If you have chronic HCV infection:
- The strain of HCV infection does not appear to impact your risk for establishing liver cancer.
- You are not at considerable risk of developing cancer unless you likewise already have cirrhosis.
- You are at significantly increased risk of liver cancer if you have alcohol-related cirrhosis in addition to liver disease.
- Receiving antiviral therapy to treat chronic HCV infection might reduce your risk for establishing liver cancer.
Evaluating with ultrasound of the liver, liver function tests, and blood tests (including alpha-fetoprotein every 6 to 12 months is advised for individuals at risk of liver cancer.
Heres what you have to understand:
What Does The Future Hold
The Canadian Liver Foundation funds research into the causes, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of all forms of liver disease including liver cancer. Scientists are looking for the causes of liver cancer, ways to prevent it and methods to improve treatments. Prevention of new viral hepatitis infections and better treatments for chronic hepatitis could prevent about half of liver cancer cases worldwide. New methods that combine treatments with surgery or other types of treatment are being studied.
Help us help you! If you are not satisfied with the information you just read or any information on our website, please take a moment to send us your comments and suggestions on the type of content you would like to find on liver.ca. Please include the page you are commenting about in the subject line of your
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394424 .Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
2. Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16, 589604 .Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
5. Cancer.net. Liver Cancer: Types of treatment. . 2021. Available from : https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/liver-cancer/types-treatment
You May Like: What Drug Is Used To Treat Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer
If you simply learned you have hepatitis C, your doctor might have informed you that its connected to liver cancer. Its natural to feel worried and have great deals of concerns. You can alleviate your issues. Get the facts and learn how some changes in your life can enhance your chances of remaining healthy.
Are People With Liver Cancer Considered For Liver Transplantation
Most cancers of the liver begin elsewhere in the body and are spread to the liver. These cancers are not curable through liver transplantation. Tumours that start in the liver are usually detected in an advanced stage. They are also rarely cured by a liver transplant. If the primary liver cancer is small and confined to the liver, a liver transplant may be considered.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
HCV spreads by direct contact with an infected person’s blood and other body fluids. This can happen through:
- sharing drug needles and intranasal drug devices
- getting a tattoo or body piercing with unsterilized tools
- sexual contact
- passing of the infection from a pregnant woman to her unborn child
Children who have HCV most often acquired it as newborns from their mothers.
Thanks to blood screening and other health care precautions adopted in the early 1990s, the spread of HCV from hemodialysis, blood transfusions, or organ transplants is now rare.
It’s also rare, but possible, for someone to get HCV by sharing household items that might contain an infected person’s blood, such as razors, toothbrushes, or scissors.
Cirrhosis And Liver Cancer
When people have cirrhosis of the liver, theyre more likely to develop a type of liver cancer called hepatocellular carcinoma. Researchers dont fully understand the link between the two conditions, but one explanation is that the buildup of scar tissue and ongoing inflammation creates an environment where cancerous tumors are more likely to grow. Regardless of exactly why scarring of the liver is linked to cancer, anyone with cirrhosis should be screened regularly for liver cancer, says Dr. Jacobson.
Also Check: What Is The Prognosis For Hepatitis C
Genetic Risk Factors In Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development
Besides the well-known patient-specific risk factors for HCC development in CHB described above, evidence exists for a genetic predisposition due to single-nucleotide polymorphisms . Several SNPs associated with HCC have been reported and expression profiles generated . These polymorphisms alter biological pathways, including inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA repair, cell cycle and growth factors . The association between aflatoxin B1 and CHB is well established, and a concomitant SNP of GTSM1 and GSTT1 is associated with a dramatic increase in HCC risk . This indicates that the HCC risk attributable to specific polymorphisms depends on underlying risk factors and specific SNPs are associated with increased HCC risk in CHB. Such polymorphisms include SNPs of MDM2 and p53 XRCC3 HLA -DQ CTL-4 GLB1 and TGF-1 but no other proinflammatory cytokines or interleukin-10 . Nonetheless, these SNPs were mostly detected in collectives of CHB patients from the Far East or Asia and confirmatory studies in other patient populations are required.
Liver Cancer And Hepatitis C
- Reactions 0 reactions
Liver cancer is a risk for the more than 3 million people in the United States who have chronic hepatitis C. Research shows the impact of liver cancer on Americans is growing, along with the cases of hepatitis C.1
The rate of liver cancer in the United States rose by 20 percent between 2008 and 2017. Some states saw increases of more than 50 percent, with North Dakota topping the list at 107 percent. The rate of liver cancer dropped in only 3 states in the nation.2
The number of deaths from liver cancer in the United States also grew by 18 percent between 2008 and 2017. The American Cancer Society expects deaths from liver cancer to exceed 30,000 by the end of 2020. The deaths are not far behind the count of new liver cancer diagnoses, which will likely total almost 43,000 in 2020.2,3
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention points to 2 likely causes of the increase in liver cancer cases:4,5
- A surge in new HCV infections, which exceeded an estimated 50,000 in 2018
- Improved methods for reporting cases of hepatitis C virus infections
Recommended Reading: Cirrhosis Caused By Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Hepatitis C And Cancer: What To Know
Hepatitis C is one of the leading causes of liver cancer. Its also linked to non-Hodgkins lymphoma, cancer in the bile ducts, and possibly pancreatic and head and neck cancers. And if you already have any other type of cancer, it can cause additional complications. Thats why MD Anderson tests all new patients for hepatitis C.
The good news is that if its found early and treated, hepatitis C can be cured, reducing your risk for cancer and other complications. Thats why hepatitis C screening and treatment is so important.
Unfortunately, an estimated 3.2 million people in the U.S. living with a chronic hepatitis C infection and dont know theyre infected. In many cases, thats because chronic hepatitis C doesnt any symptoms until the liver shows signs of damage.
We talked to Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infection Diseases and founding director of the hepatitis C clinic at MD Anderson, about what you should know about hepatitis C. Heres what he had to say.
Whats the link between hepatitis C and cancer?
There are two types of hepatitis C:
- acute or short-term hepatitis C, which goes away on its own in less than six months
- chronic hepatitis C, which requires treatment
The reason chronic hepatitis C causes multiple types of cancer is complex and not fully understood. The good news is that in most cases, hepatitis C infection can be cured with medication, and treatment can prevent many associated cancers.
Who is at risk for hepatitis C?
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis B Or C
What You Can Do To Help Manage The Symptoms Of Liver Cancer
Symptom management is an important aspect of coping with liver cancer. When symptoms are properly addressed and managed, it can significantly strengthen the capability of your loved one and their overall quality of life. Below are common symptoms experienced by those with liver cancer and suggestions that caregivers can use to help manage these symptoms. Always consult with your healthcare provider before trying any of the following suggestions:
A Role Of Hepatitis C Virus In Promoting A Pro
HCV is classified into seven genotypes and epidemiological studies show that infection with genotypes 1b and 3 is associated with an increased risk of developing HCC . Reports that HCV core gene variants are associated with HCC in patients who have resolved infection suggest that viral factors influence progressive liver disease. CHC is often associated with insulin-resistance , and the core protein has been shown to dysregulate glucose homeostasis, leading to intrahepatic lipid accumulation and steatosis . A recent study highlighted a new role for core to induce mitochondrial damage by impairing mitophagy the resulting oxidative stress is regarded as a key trigger of HCC initiation and development. In vivo studies with HCV core transgenic mice confirmed an imbalance of oxidant/antioxidant state in the liver-induced HCC .
HCC exhibits a high degree of genetic heterogeneity indicative of reduced genomic stability , and HCV induction of ROS is likely to prime DNA damage. Several studies report that HCV core or NS5A proteins increase ROS and promote oxidative stress in both mouse models and in vitro culture systems . Further studies report that HCV infection reduces host cells’ ability to detect and repair damaged DNA via perturbation of ATM kinase . The physiological relevance of these studies is difficult to prove where low-level expression of viral proteins in the infected liver precludes confirmatory studies.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Lower Your Immune System
When Hep C Becomes Chronic
If youre one of the millions of people with ongoing hepatitis C infections, youre in a sort of no mans land, where your immune system keeps beating away at the virus and trying to kill infected liver cells, but it can never quite clear the infection. Over time, that constant assault on your liver causes inflammation, triggered by your bodys immune response. This, combined with the direct action of the virus, damages the organ. You have this smoldering fire in the liver, explains Houghton.
Can Children Get Liver Cancer
Yes, in children the most common liver cancer is called hepatoblastoma. Hepatoblastomas are usually diagnosed within the first three years of life and are rarely found beyond the age of five. Hepatoblastomas are also reported to occur more frequently in males than in females. This cancer is caused by the rapid growth of immature or abnormal cells that no longer have the specialized function of normal liver cells.
You May Like: Best Medication For Hepatitis C
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
How To Reduce Your Risk
Dont share needles or other drug-use equipment. If you use intravenous drugs, take part in a needle exchange program.
Dont share personal care articles, such as razors, scissors, nail clippers or toothbrushes, with an infected person.
If you get a tattoo, body piercing or acupuncture, make sure all equipment is clean and sterile. Needles should always be new, not used, and never homemade.
Wear latex gloves whenever you might come into contact with someone elses blood or body fluids.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis Feel Like
Why Cirrhosis Is Worse For Some People
Close to one in four people will develop cirrhosis of the liver after living with a hep C infection for at least 20 years, according to a large review of clinical studies. Men and older people are more susceptible to the disease. In addition to genetic factors, chronic health conditions, and behaviors like heavy drinking and smoking, the type of viral strain you have can also increase the risk of cirrhosis: Genotype 3 is particularly harmful, accounting for about 20% of infections in the U.S.
Spotting Signs Of Cirrhosis
One of the difficulties with liver disease is that symptoms often dont crop up until advanced stages. If you do notice something, the most common signs include fatigue, nausea, weight loss, easy bleeding or bruising, jaundice, and swollen legs. Luckily, several blood and imaging tests can be used to diagnose the disease. One is called an elastography, which measures how elastic your liver tissue might be by transmitting sound waves through your body. Because scar tissue stiffens the liver, this scan gives clinicians a quick snapshot of the level of damage.
Read Also: Is There Immunization For Hepatitis C
Can Hep C Treatment Lower Liver Cancer Risk
Treatment helps, but its not foolproof. Between 3% and 9% of people treated for hep C with direct acting antivirals still go on to develop hepatocellular carcinoma. That’s because although these drugs work to target the virus, they dont prevent the progression of cancer. So if the early stages of cancer have already been set in motion, the treatment wont help. And if patients receive treatment for hep C after years of infection, they might have accrued enough liver damage to cause the disease, explains Antwi. Early treatment is crucial, he says.
Fact: Rates Of Hepatitis C Are Highest Among Baby Boomerspeople Born From 1945 Through 1965

People in this generation are five times more likely to have hepatitis C than other adults. In fact, three out of every four people with hepatitis C were born between 1945 and 1965. Transmission of the virus was at its peak in the 1960s through the 1980s when there was less known about hepatitis C. It is likely during those decades that most of this population became infected.
There was no screening test for hepatitis C until 1990, Nguyen noted, and the virus wasnt completely eliminated from the U.S. blood supply until 1992 when screening donated blood for hepatitis C became widespread.
Still, many baby boomers dont know how or when they acquired the virus.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Last
Risks Factors Of Hepatitis C
A risk factor is something that increases your chance of getting a disease or condition.
Risk factors that may increase your chance of getting hepatitis C include:
- Receiving a blood transfusion before 1992
- Receiving blood clotting products before 1987
- Having long-term kidney dialysis treatment
- Getting tattoos or body piercings
- Injecting illicit drugs, especially with shared needles
- Having sex with partners who have other sexually transmitted diseases
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epidemiology Risk Factors And Treatment Options
Worldwide, liver cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in men, with 745 000 deaths per year, and the sixth most common cancer, with rising incidence . HCC represents approximately 90% of all primary liver cancer cases, shows a clear gender disparity towards males and is a major cancer in less developed regions, with a correlation to HBV surface antigen prevalence. Chronic HBV and HCV infections represent the leading cause for HCC , with a total incidence of 16/100 000 globally. In most of Africa and Asia, HBV is the single leading risk factor for HCC, whereas in Japan, northern Europe and the USA HCV is the major risk factor . The risk of developing HCC is 10- to 25-fold higher in CHB compared with non-infected controls, and up to 17-fold increased in HCV-associated liver cirrhosis . While HCC in HCV infection rarely occurs without liver cirrhosis, CHB without any obvious liver inflammation per se confers a risk for HCC development. The highest risk for HCC development is associated with co-infection of HBV with HDV, HCV or HIV.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Medicine For Hepatitis B