How Is The Virus Spread
Like hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus is spread when blood of an infected person enters the body of a person who is not infected, such as through sharing needles or “works” when shooting drugs or occupational needle stick injury. The risk of sexual transmission has not been thoroughly studied but appears to be low in long-term, monogamous relationships. There is no evidence that the hepatitis C virus can be transmitted by casual contact such as hugging or shaking hands, through foods, by sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, or by coughing or sneezing. Hepatitis C is not spread by breastmilk.
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
How Can A Person Protect Themselves From Getting Hepatitis C And Other Diseases Spread By Contact With Human Blood
-
Don’t ever shoot drugs. Intranasal is also a risk factor. If you shoot or inhale drugs, stop and get into a treatment program. If you can’t stop, never reuse or share syringes, water, or drug works, and get vaccinated against hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
-
Do not share toothbrushes, razors, or other personal care articles. They might have blood on them.
-
If you are a healthcare worker, always follow routine barrier precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps. Get vaccinated against hepatitis B
-
Consider the health risks if you are thinking about getting a tattoo or body piercing: You can get infected if:
-
the tools that are used have someone else’s blood on them.
-
the artist or piercer doesn’t follow good health practices, such as washing hands and using disposable gloves.
HCV can be spread by sex, but this does not occur very often. If you are having sex, but not with one steady partner:
-
You and your partners can get other diseases spread by having sex .
-
You should use latex condoms correctly and every time. The efficacy of latex condoms in preventing infection with HCV is unknown, but their proper use may reduce transmission.
-
You should get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: What’s In Hepatitis B Vaccine
How Can We Prevent Hepatitis C In The Workplace
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. The risk of hepatitis C can be significantly reduced by implementing infection control guidelines suitable for the specific workplace.
Infection control precautions are the first line of defense to protect workers from hepatitis C and other blood-borne diseases. For this reason, the Public Health Agency of Canada recommends routine practices when there is a risk of exposure to blood or certain body fluids.
Please see the OSH Answers document Routine Practices for more information.
CLOSE ALL
Add a badge to your website or intranet so your workers can quickly find answers to their health and safety questions.
How Is Hepatitis C Spread

Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Don’t Miss: Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis C
The risk of acquiring hepatitis C from the workplace depends on the amount of exposure to human blood or blood products and needlestick injuries. In general, occupational groups with increased risk include workers such as healthcare workers, dentists, and laboratory personnel who are repeatedly exposed to human blood and who are at risk of needlestick injuries.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive Meaning
How To Prevent An Infection
You contract hepatitis C when you come into contact with the blood of a person who has a hepatitis C infection.
The process of screening blood in the United States keeps it from being transmitted during transfusions and organ transplants.
Hepatitis C can be transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth. It can be transmitted from a needle stick in a medical setting too.
Its not common, but hepatitis C can also be transmitted when you share personal items or during sexual contact with a person who has the infection.
Here are some ways to lower your risk of hepatitis infection:
- Do not share needles, syringes, or other injection equipment.
- Do not share razors, toothbrushes, or other personal care items.
- When getting a tattoo or body piercing, use only licensed facilities that prioritize and implement infection-control practices.
- Be very careful when cleaning up blood spills and be sure to wear gloves. The hepatitis C virus can live up to 6 weeks on surfaces.
How Is It Passed On
Hepatitis C is usually transmitted through blood to blood contact. Examples include:
- sharing needles when injecting drugs and through sharing other drug equipment
- use of unsterilized equipment when getting a tattoo/body piercing
- sharing razors or toothbrushes that are contaminated with infected blood.
It can be transmitted through sex, although this is very rare and can be prevented by using a condom.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quant
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
Some groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C, including:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991 or blood products before 1986 in the UK
- UK recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high-risk areas include Africa, the Middle East and central Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners, family members and close contacts of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
- All people born between 1945 and 1965
- Anyone who has ever injected drugs, even if once or many years ago
- People with HIV infection
- People who had a blood transfusion organ transplantation before 1992
- People who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or other injury
- People receiving hemodialysis
- People who have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
Also Check: Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis B
Who Do I Need To Tell That I Have Hepatitis C
It is up to you who you tell that you have hepatitis C.
Your health information is confidential. If you dont want to, you do not have to tell your employer, landlord, school, family or friends.
You may want to tell certain friends or family members that you have hepatitis C so they can help or support you if you need it.
When deciding who to tell about your hepatitis C, take your time. Ask yourself these questions:
- Who will try to understand?
- Who will respect my privacy?
- Who will listen to my feelings?
- Who will give me emotional support?
You may also want to think about these questions before you tell someone:
- Where would you feel safe telling them?
- What questions would you feel comfortable answering?
- Do you want someone with you when you tell others, for example, a friend, doctor, nurse, or other healthcare worker?
Remember, there is no rush to tell people you have hepatitis C.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
What About Sex And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be spread through sexual intercourse, but the risk is considered to be low. It is extremely rare among monogamous couples, meaning couples who only have sex with one another. The risk increases if you:
- Have multiple sex partners
- Have a sexually transmitted disease
- Are infected with HIV
There is no evidence that Hepatitis C is spread by oral sex.
To reduce the chance of getting or giving Hepatitis C through sexual contact, follow these guidelines:
- Use latex condoms every time you have sex, particularly if you have:
- More than one partner
- Rough sex that might make one of you bleed
- Sex during your or your partners menstrual period
- Sex when you or your partner has an open sore on either of your genitals
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis B And C Contagious
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis C testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with their insurance company. In addition to the cost of testing, there may be other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance, or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
At-home hepatitis C testing starts around $49. Some at-home kits test for multiple types of viral hepatitis at once, with the cost of these panels starting around $80.
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Positive Means
How Is It Spread
The hepatitis C virus is spread by direct contact with blood of an infected person. This can happen through:
- Sharing equipment used to inject drugs
- Blood transfusions and organ transplants prior to 1992 when widespread screening of the blood supply began
- Pregnant women infected with the virus passing it to their babies at birth.
- Sharing personal items, such as a toothbrushes, nail clippers, or razors that have blood on it
- Getting tattoos or body piercings in informal settings or with non-sterile equipment
- Poor infection control in health care facilities and residential care facilities
- Sexual transmission is possible, although rare. Things that increase sexual transmission of hepatitis C include: having a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection, sex with multiple partners, or rough sex
- The hepatitis C virus is NOT spread by casual contact, such as hugging, or through sneezing, coughing, or sharing food and drinks.
Other Risks Can Include:
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- Inoculation practices involving multiple use needles or immunization air guns
- Exposure of broken skin to HCV infected blood
- HIV infected persons
People with current or past risk behaviors should consider HCV testing and consult with a physician. HCV testing is currently not available at most public health clinics in Missouri. For information about HCV testing that is available, call the HCV Program Coordinator at 573-751-6439.
Read Also: Does Hepatitis C Cause Fatigue
What Are The Symptoms And Consequences Of Infection
Approximately 20 percent of persons exposed to the virus develop symptoms which may include jaundice , fatigue, dark-colored urine, stomach pain, loss of appetite and nausea. After the initial infection, 15-25 percent will recover and 75-85 percent will become chronically infected . Approximately 70 percent of persons chronically infected may develop liver disease, sometimes decades after initial infection.
Where Can You Get More Information
Your doctor, nurse, or health care clinic listed in the telephone directory can provide you with more information.
Persons who inject drugs can substantially reduce their risk of getting and transmitting HIV, viral hepatitis and other blood borne infections by using a sterile needle and syringe for every injection. The Massachusetts Department of Public Health supports programs where persons who inject drugs can access sterile needles and syringes through syringe services programs . Through these programs you can get sterile needles and syringes free of cost, dispose of used needles and syringes, and get connected to other services such as testing for hepatitis C, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, overdose education, and narcan . To find an MDPH-supported SSP program near you, please click here.
Hepatitis C and Related Resources in Massachusetts This provides information about MDPH-supported programs including testing for hepatitis C, linkage to treatment for individuals with hepatitis C infection, and other resources such as overdose prevention programs.
Additional information about substance use disorder treatment programs may be obtained from the MDPH.
Viral Hepatitis Information from the CDC. The CDC provides resources on a variety of topics, including general information regarding transmission and prevention, statistics about HCV, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C.
You May Like: Can Autoimmune Hepatitis Be Cured
Possible Complications Of Hepatitis C
Theres one main complication of acute hepatitis C: It could become chronic.
If you go on to develop chronic hepatitis C, you could eventually experience a number of health complications, including:
- Cirrhosis. With cirrhosis, scar tissue gradually replaces healthy tissue in your liver, blocking blood flow and disrupting liver function. Cirrhosis can eventually lead to liver failure.
- Liver cancer. Having chronic hepatitis C raises your risk for eventually developing liver cancer. If you develop cirrhosis or your liver is very damaged before treatment, youll still have a higher risk for cancer after getting treated.
- Liver failure. It takes a long time for your liver to fail. Liver failure, or end-stage liver disease, happens slowly over months, often years. When your liver becomes unable to function properly, youll need a transplant.
If you believe you contracted the hepatitis C virus, a good next step involves reaching out to a healthcare professional. Getting timely treatment can lower your risk for experiencing serious complications.
The sooner you get a diagnosis, the sooner your healthcare professional can start a treatment plan.
research continues.
Currently, the best way to protect yourself from the hepatitis C virus is to avoid using any items that may have come into contact with someone elses blood.
You can do this by:
You May Like: Which Test For Hepatitis B
Its Different Than Hepatitis A And B
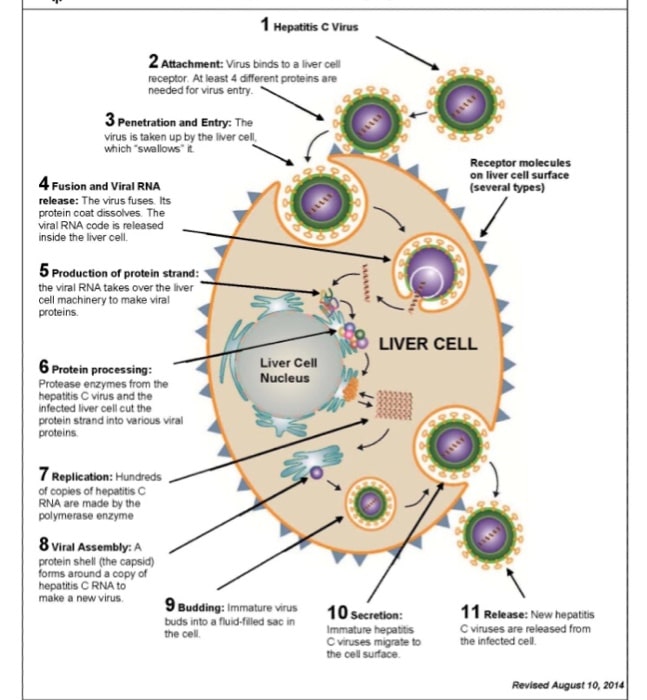
Each form of hepatitis has its own specific virus that spreads and is treated differently. Hepatitis simply means inflammation of the liver, or that the virus has an affinity for hurting the liver, Reau says.
- Hepatitis A is an acute, short-term infection that often does not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B hides deep in the body and, like hepatitis C, is treated in a variety of ways, from antiviral medications to liver transplants.
The viruses are different, but all of them should be taken very seriously since they can lead to significant liver disease and even death, she adds.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis B Or C Contagious
Who Is At Risk Of Hepatitis C
Anyone can get hepatitis C. It is important for peopleat high risk of infection to be tested and treated forhepatitis C. In the U.S., you are at a higher risk if you:
- Have ever used a needle to inject drugs, even if once and long ago
- Had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Are a health care worker who had blood exposure to mucous membranes or to non-intact skin, or a needlestick injury
- Have ever been on kidney dialysis
- Were born of a mother who had hepatitis C at the time
- Are a Vietnam-era Veteran
- Had contact with hepatitis-C-positive blood to nonintact skin or to mucous membranes
- Received tattoos or body piercings in non-regulated settings
- Have ever snorted drugs or shared drug equipment
- Have liver disease
- Have a history of alcohol abuse
- Have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- Have had a sexual partner with hepatitis C, now or in the past
- Have had 10 or more lifetime sexual partners
- Have HIV infection
The only way to know if you haveHepatitis C is to be tested. VA offershepatitis C testing and treatment toenrolled Veterans.
Read Also: Is Viral Hepatitis C Contagious