What Is Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
Hepatitis A and B are serious diseases caused by virus. Hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
The hepatitis A and B vaccine is used to help prevent these diseases in adults. The vaccine works by exposing you to a small dose of the virus, which causes the body to develop immunity to the disease. This vaccine will not treat an active infection that has already developed in the body.
This vaccine is recommended for adults with risk factors for getting hepatitis A or B, including:
-
having chronic liver problems, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis C, or needing a liver transplant
-
using intravenous drugs
-
living with a person who has either hepatitis A or B infection
-
having sexual contact with an infected person
-
having a blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia
-
being on dialysis or receiving blood transfusions
-
living in a correctional institution
-
being in the military or traveling to high-risk areas and
-
working in healthcare or public safety and being exposed to infected blood or body fluids.
Like any vaccine, the hepatitis A and B vaccine may not provide protection from disease in every person.
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Read Also: How Can I Catch Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
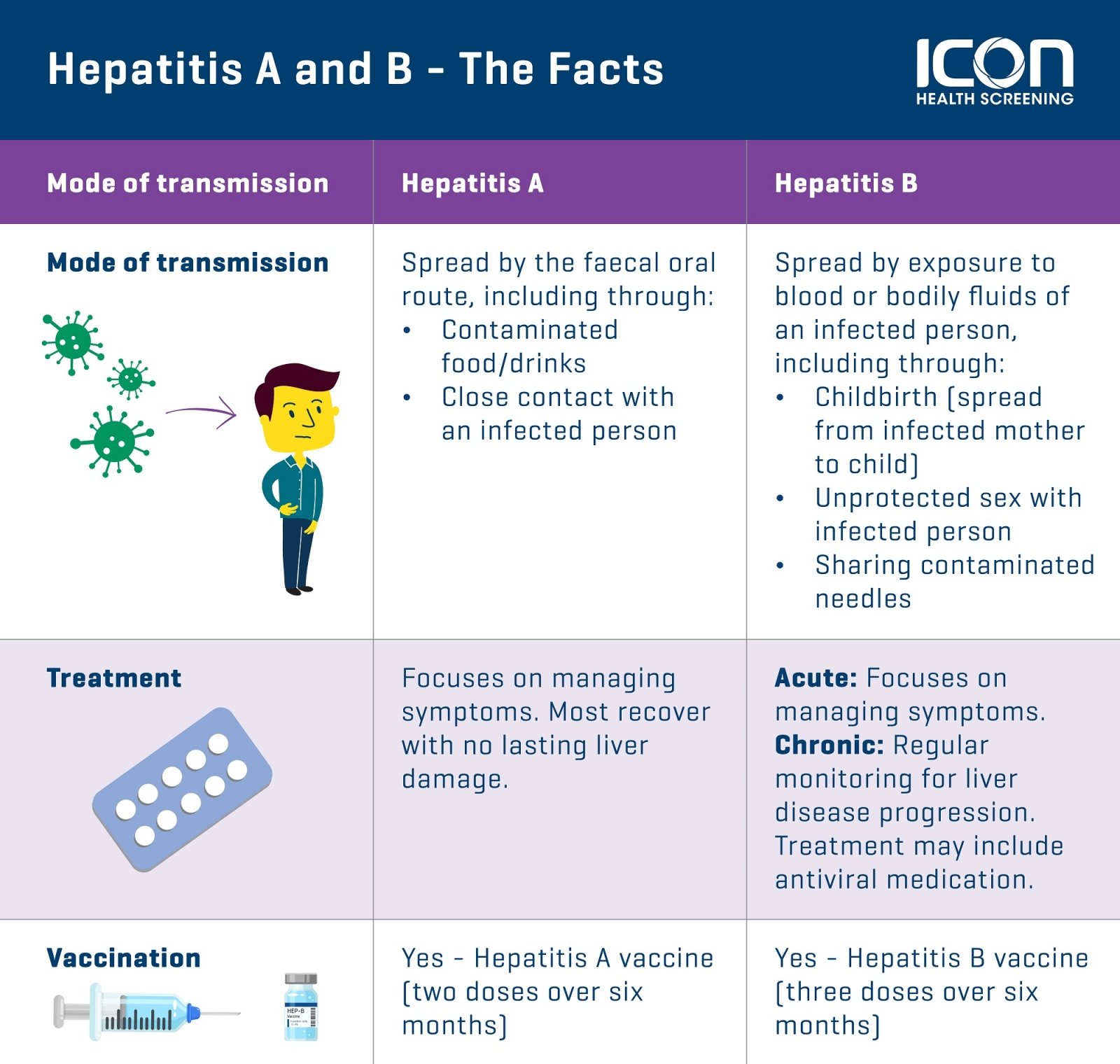
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
Don’t Miss: Hiv And Hepatitis B Coinfection Treatment
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Because clinical manifestations of hepatitis B are indistinguishable from other causes of viral hepatitis, a definitive diagnosis requires serological testing . This testing uses different serologic markers to identify different phases of HBV infection and to conclude whether a person has acute or chronic HBV infection, or is immune to HBV as a result of prior HBV infection or vaccination, or is susceptible to infection . In Table 1 an interpretation of hepatitis B serologic test results is given.
Immunogenicity In Hemodialysis Patients:
Hemodialysis patients given hepatitis B vaccines respond with lower titers,12 which remain at protective levels for shorter durations than in normal subjects. In a study in which patients on chronic hemodialysis received 40 mcg of the plasma-derived vaccine at months 0, 1, and 6, approximately 50% of patients achieved antibody titers 10 mIU/mL.12 Since a fourth dose of ENGERIX-B given to healthy adults at month 12 following the 0-, 1-, and 2-month schedule resulted in a substantial increase in the GMT , a 4-dose regimen was studied in hemodialysis patients. In a clinical trial of adults who had been on hemodialysis for a mean of 56 months , 67% of patients were seroprotected 2 months after the last dose of 40 mcg of ENGERIX-B given on a 0-, 1-, 2-, and 6-month schedule the GMT among seroconverters was 93 mIU/mL.
Recommended Reading: How Does One Contract Hepatitis
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
How Is A Hepatitis B Vaccine Given
A health care provider gives the hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine is given as a shot injected into a muscle, usually in the arm for adults and children older than 1 year and in the thigh for infants and children younger than 1 year. Vaccination with a hepatitis B vaccine is usually given as a series of injections over a period of time, depending on the specific brand of the vaccine. Read any printed information that your health care provider gives you about the hepatitis B vaccine.
Read Also: Hepatitis B E Antibody Reactive Means
Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Side Effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives difficult breathing swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Keep track of any and all side effects you have after receiving this vaccine. When you receive a booster dose, you will need to tell the doctor if the previous shot caused any side effects.
You should not receive a booster vaccine if you had a life-threatening allergic reaction after the first shot.
You may feel faint after receiving this vaccine. Some people have had seizure like reactions after receiving this vaccine. Your doctor may want you to remain under observation during the first 15 minutes after the injection.
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have:
-
numbness, pain, tingling, weakness, burning or prickly feeling, vision or hearing problems, trouble breathing
-
red or blistering skin rash or
-
easy bruising or bleeding .
Common side effects of hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine may include:
-
redness or tenderness where the shot was given
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report vaccine side effects to the US Department of Health and Human Services at 1-800-822-7967.
What Is The Morphology Of Hbv
HBV is an oncogenic DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. The discovery of the etiologic agent of hepatitis B remains a remarkable scientific achievement. It was discovered in 1965 by Dr Blumberg, who won the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his discovery in 1976 . HBV virus, initially called the Dane particle, is a 42-nm virus . HBV is composed of a nucleocapsid core, surrounded by an outer lipoprotein coat . The virus contains 3 primary structural antigens: surface , core , and e . HBsAg is produced in excess amounts and found in the blood of infected individuals in the form of spherical and tubular particles . These immunogenic, but noninfectious, subviral particles lack genomic DNA and paved the way to develop hepatitis B vaccines . HBV is divided into 4 major phenotypic subtypes based on antigenic epitopes presented on its envelope proteins, and comprises 10 major genotypes that differ at the nucleotide level across full-length genotypes by> 8% . The HBV genotypes have distinct virological characteristics and geographical distributions however, the licensed HBV vaccines are effective against all genotypes .
A, Electron micrograph of hepatitis B virus : Dane particles and spherical and tubular surface antigen particles . Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. As a work of the U.S. federal government. B, A simplified figure of the HBV particle and surface antigens.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A How Do You Get It
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The infection can range in severity from mild to acute. It may last just a few weeks or become a serious, chronic, and potentially fatal health condition.
The best way to prevent this infection is to get the hepatitis B vaccine. Heres what you need to know.
Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Titer Blood Test
Interchangeability With Other Hepatitis B Vaccines:
Recombinant DNA vaccines are produced in yeast by expression of a hepatitis B virus gene sequence that codes for the hepatitis B surface antigen. Like plasma-derived vaccine, the yeast-derived vaccines are protein particles visible by electron microscopy and have hepatitis B surface antigen epitopes as determined by monoclonal antibody analyses. Yeast-derived vaccines have been shown by in vitro analyses to induce antibodies which are immunologically comparable by epitope specificity and binding affinity to antibodies induced by plasma-derived vaccine.13 In cross-absorption studies, no differences were detected in the spectra of antibodies induced in man to plasma-derived or to yeast-derived hepatitis B vaccines.13
Additionally, patients immunized approximately 3 years previously with plasma-derived vaccine and whose antibody titers were < 100 mIU/mL were given a 20-mcg dose of ENGERIX-B. All patients, including 2 who had not responded to the plasma-derived vaccine, showed a response to ENGERIX-B . There have been no clinical studies in which a 3-dose vaccine series was initiated with a plasma-derived hepatitis B vaccine and completed with ENGERIX-B, or vice versa. However, because the in vitro and in vivo studies described above indicate the comparability of the antibody produced in response to plasma-derived vaccine and ENGERIX-B, it should be possible to interchange the use of ENGERIX-B and plasma-derived vaccines .
What Are The Uses For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is used to prevent hepatitis B, a serious infection that affects the liver.
Most children are given their first shot at birth, followed by a 2nd shot at 1-2 months of age, and a 3rd shot at 6-18 months of age. Also, anyone who is 18 years of age or younger and hasn’t received the vaccine should be vaccinated.
Additionally, all unvaccinated adults at risk for hepatitis B infection should be vaccinated. This includes:
- Partners or people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject street drugs
- People with more than one sex partner
- People with chronic liver or kidney disease
- People under the age of 60 who have type 1 or 2 diabetes
- People with jobs that expose them to human blood or other body fluids
- People who live with a family member infected with hepatitis B
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Most babies now get the HBV vaccine from their doctor as a regular part of their checkups.
Hepatitis B is really contagious. You can easily get it through unprotected sex or contact with infected blood or urine. So if youve never had the vaccine, its a good idea to talk to your doctor about getting it.
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected don’t know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Hepatitis C From Another Person
Hepatitis B Vaccine Market 2022 Key Product Segments Application Analysis And Industry Growth Forecast By 2028
The MarketWatch News Department was not involved in the creation of this content.
Sep 28, 2022 —Number of Tables and Figures :125 | The global “Hepatitis B Vaccine Market“size is projected to reach Multimillion USD by 2028, In comparison to 2021, at unexpected CAGR during 2022-2028 and generated magnificent revenue. The market is segmented on the basis of End-user Industry , By Type , and Geography .
Hepatitis B Vaccine Market Research Report is spread across 89 Pages and provides exclusive data, information, vital statistics, trends, and competitive landscape details in this niche sector.
Recombinant hepatitis b vaccine is the second generation of hepatitis b vaccine developed by genetic engineering technology.
10mcg/0.5ml accounting for % of the Hepatitis B Vaccine global market in 2021, is projected to value USD million by 2028, growing at a revised % CAGR from 2022 to 2028. While Newborn segment is altered to an % CAGR throughout this forecast period and will hold a share about % in 2028.
The global major manufacturers of Hepatitis B Vaccine include GSK, Merck, Sanofi Pasteur, Dynavax Technologies, LG Life Sciences, KM Biologics, Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products and Serum Institute, etc. In terms of revenue, the global 3 largest players have a % market share of Hepatitis B Vaccine in 2021.
Global Hepatitis B Vaccine Market: Segment Analysis
Get a Sample PDF of report –
COVID-19 IMPACT ON MARKET