What Are The Treatment Options For Hcv
Currently, the standard of care for the treatment of HCV is pegylated interferon in combination with ribavirin. This combination therapy is typically a 24-week or 48-week course. Research has shown that combination therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin can result in undetectable levels of HCV in 40-50 percent of people with genotype 1 and 70-80 percent of people with genotypes 2 and 3.11,12,13,14
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
To check for hepatitis, doctors do a blood test called a hepatic function panel to see how well the liver is working. If the test shows signs of liver inflammation, they might do more blood tests to look for a cause . Signs of liver inflammation are common in a mild viral illness, so doctors might monitor a person’s liver function with repeat blood tests until the inflammation clears up.
Sometimes a doctor might ask for an imaging test, like an ultrasound scan of the belly. They might also do a liver biopsy, where they use a needle take a small sample of the liver and look at it under a microscope.
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Sexuality Activity
How We Care For Hepatitis C
The Center for Childhood Liver Disease at Boston Children’s Hospital is one of the leading centers in the world for the care of children with hepatitis C. The centers director, Maureen Jonas, MD, is a national leader in the care, diagnosis, and treatment for children with viral hepatitis. Dr. Jonas, along with her team, wrote the clinical guidelines that shape the way pediatric GI specialists and pediatricians around the country treat hepatitis C.
In addition to the standard treatments, our team of certified pediatric hepatologists is also at the forefront of treatment research, treating adolescents with newly approved treatments for adults and conducting clinical trials to help make them available to children as young as 3 years of age.
How Can Hepatitis C Affect My Child In The Long Term
Children with hepatitis C can lead completely normal lives, attend school, and play sports without any special arrangements.
If left untreated or if treatment fails, chronic hepatitis C can last for decades. During that time, it can progressively damage the liver and lead to such complications as cirrhosis and liver cancer. When they become older, children with hepatitis C should avoid drinking alcohol, as it can make the disease progress more quickly.
If the liver begins to fail because of the hepatitis and its complications, your child may need a liver transplant. While hepatitis C is one of the most common reasons for an adult to receive a liver transplant, it is not a common reason among children.
You May Like: Antiviral Treatment For Hepatitis C
Where Can One Find More Information About Hcv
For more information about HCV, please visit www.HepCFight.com where people with HCV, their family and friends will find various online resources.
1 Centers for Disease Control. “Hepatitis C FAQs for the Public,” available online at. Last accessed March 7, 2010.
2 University of Maryland Medical Center. “Liver Disease,” available online at . Last accessed April 1, 2010.
3 National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. “Chronic Hepatitis C: Current Disease Management,” available online at . Last accessed February 16, 2010.
4 Colvin, HM, Mitchell, AE. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C. . Accessed March 7, 2010.
5 Rodriguez-Torres M. “Peginterferon Alfa-2a and Ribavirin in Latino and Non-Latino Whites with Hepatitis C.” The New England Journal of Medicine. 2009 360:257-267.
6 Center for Disease Control and Prevention. “Hepatitis C Information for Health Professionals,” available online at . Last accessed on February 16, 2010.
7 New York Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. “Hepatitis C.” . Last accessed on April 2, 2010.
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Certain foreign substances that enter your body trigger your immune system to make antibodies. Antibodies are specifically programmed to only target the foreign substance they were made to fight.
If youve ever had a hepatitis C infection, your body will make hepatitis C antibodies as part of its immune response.
Your body only makes these antibodies if you have hepatitis C or had it in the past. So the hepatitis C antibody test can confirm whether you have the virus by testing for these specific antibodies.
It may take 2 to 3 months after exposure for the test to detect antibodies. If needed, your healthcare professional may order an HCV RNA test, which can detect the virus after just 1 or 2 weeks.
If the antibody test is positive, an HCV RNA test can show whether the infection is current.
While people of any gender experience the same hepatitis C symptoms, 2014 research suggested some effects of the virus may differ, depending on the sex you were assigned at birth.
Researchers noted that:
- women have a higher chance of clearing the virus without treatment
- liver disease may progress more rapidly in men
- men have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis
Read Also: How Many People Have Hepatitis C
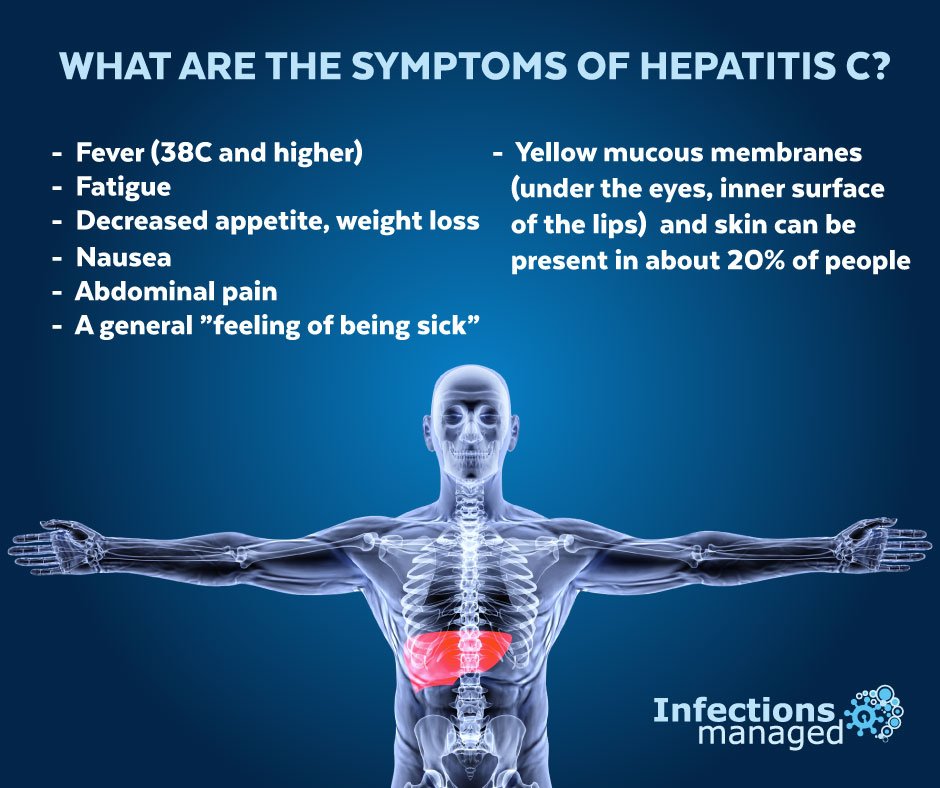
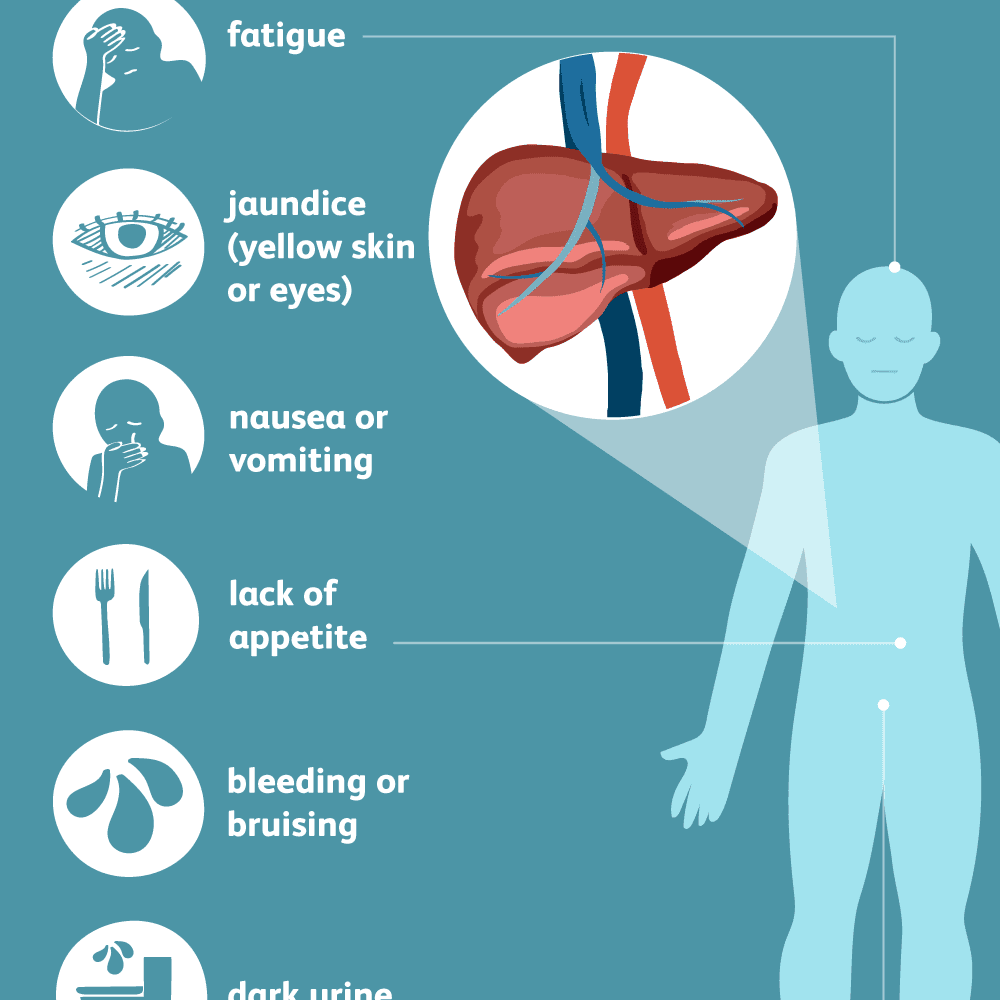
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But it’s important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Read Also: How Did I Get Hepatitis B
Optimizing The Response Rate To Hcv Treatment
Establishing trust is critical to completing treatment programsâIn a 2019 study led by researchers at the Edith Nourse Rogers VA Medical Center in Bedford, Massachusetts, a team sought to understand factors that led to successful completion of the new hepatitis C treatment regimens from the perspectives of both Veteran patients and providers.
The team interviewed 38 Veterans from three New England VA medical centers and their health care providers. They found many patients were concerned about side effects of the treatment. Full explanations by providers of the new treatmentâs side effect profile helped get patients to begin and continue with their treatment programs. Establishing trust between patients and providers also led patients to believe the new treatment could provide a cure, which increased the likelihood they would begin treatment and stay with the treatment until it was completed.
Hepatocellular carcinoma calculator developedâHCC is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults, and the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis of the liver. The disease is closely linked to hepatitis B or C and exposure to toxins such as alcohol. Getting rid of the HCV through treatment significantly reduces the risk of developing HCC, although it does not entirely eliminate that risk.
The 2018 study describing the model can be found here, and the model itself is available to clinicians at www.hcrisk.com.
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Also Check: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C Virus
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Vaccines For Adults
About Jaundice And Jaundice Hepatitis Difference
Jaundice is a condition in which the below organs turn yellow:
- Mucous membranes.
This yellow color is caused by a high level of bilirubin which is a yellow-orange bile pigment. Liver secretes a fluid called bile.
Jaundice has many causes. These may include hepatitis, gallstones and tumors. The difference between jaundice and hepatitis therefore lies in the fact that jaundice can be caused by hepatitis.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis
What If You Test Positive For Hepatitis
If testing discloses that you have viral hepatitis there are steps to prevent your passing the viruses to family and friends. Washing the hands helps prevent transmission of hepatitis A. Not sharing needles, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes also will reduce transmission of viral hepatitis. Everyone should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Can Cause Hepatitis B
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Caused By A Virus Or Bacteria
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Don’t Miss: What Is Acute Hepatic Porphyria
Is Hepatitis Testing Recommended For People With Hiv
Yes. Everyone living with HIV should be tested for HBV and HCV when they are first diagnosed with HIV and begin treatment. People living with HIV who have ongoing risk factors for getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C should be tested annually.
In addition, new HCV screening recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention call for:
- One-time screening for all adults 18 years and older
- Screening of all pregnant women during every pregnancy
- Testing for all persons with risk factors, with testing continued periodic testing those with ongoing risk.
- People can be sick for a few weeks to a few months
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage
- Although very rare, death can occur
- 15%25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer
- More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection
- 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 1020 years
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Also Check: Need For Hepatitis C Screening Test
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
There are some very effective options for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. They are listed on the Medicare PBS , which makes them available at a much lower cost.
Newer treatments differ from those available previously:
- they cure more than 95% of people
- their side effects are minimal
- treatments last just 8 to 12 weeks
- they involve just a few pills each day, with no injections required
Curing hepatitis C means clearing the virus from the body. It helps reduce liver inflammation and can also help reverse scarring and cirrhosis. You can be re-treated if your treatment doesnt work the first time.
You should check with your doctor before taking any other medication or supplements, and whether you need vaccinations against hepatitis A and hepatitis B. You should also avoid alcohol if you have hepatitis. If you have liver damage, you may also need to see a liver specialist
For more information on how to get treatment, contact the National Hepatitis Info Line on 1800 437 222.
What Causes Hepatitis C Infection
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus. It is spread by contact with an infected person’s blood.
You can get hepatitis C if:
- You share needles and other equipment used to inject illegal drugs. This is the most common way to get hepatitis C in the United States.
- You had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992. As of 1992 in the United States, all donated blood and organs are screened for hepatitis C.
- You get a shot with a needle that has infected blood on it. This happens in some developing countries where they use needles more than once when giving shots.
- You get a tattoo or a piercing with a needle that has infected blood on it. This can happen if equipment isn’t cleaned properly after it is used.
In rare cases, a mother with hepatitis C spreads the virus to her baby at birth, or a health care worker is accidentally exposed to blood that is infected with hepatitis C.
The risk of getting hepatitis C through sexual contact is very small. The risk is higher if you have many sex partners.
If you live with someone who has hepatitis C or you know someone who has hepatitis C, you generally don’t need to worry about getting the disease from that person. You can help protect yourself by not sharing anything that may have blood on it, such as razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
What Are The Treatment Options For Hepatic Steatosis
Currently, no medications have been approved to treat fatty liver disease.
- Usually, the first line of treatment is to lose weight. It helps reduce fat, inflammation, and scarring in your liver. Losing just three to five percent of your body weight can cut down a significant amount of fat in your liver. Weight loss surgery is an option if you have a lot to lose.
- More research is needed to develop and test medications to treat this condition.
In many cases, lifestyle changes can help reverse most stages of fatty liver disease. For example, your doctor might advise you to:
- Limit or avoid alcohol.
- Take steps to lose weight.
- Make changes to your diet.
- Avoid medications and supplements that are hard on your liver.
If you have alcoholic fatty liver disease, your doctor will instruct you to completely abstain from alcohol. They may recommend a detoxification program and counseling if you have alcohol use disorder.
Several viral infections can damage the liver. To protect your liver health, your doctor may advise you to receive vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. Depending on your situation, they may also recommend regular screenings for hepatitis C.
If you have complications due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis such as cirrhosis or liver failure, you may need to have a liver transplant. In general, people with NASH who get a liver transplant do very well.
Other lifestyle changes for hepatic steatosis include: