Disease Burden And Epidemiology
Many patients with chronic HCV infection are asymptomatic and it is estimated that 45%-85% are unaware they are even infected. Large population studies testing for positivity of anti-HCV antibody in non-institutionalized population in the United States have shown the prevalence to be approximately 1.8% in the general population. In these studies, the strongest risk factors predicting a positive HCV infection were illegal drug use, blood transfusions prior to 1992 and high risk sexual behavior with high number of lifetime sexual partners. Other risk factors associated with a positive HCV infection included poverty, having less than twelve years of education and having been divorced or separated. Surprisingly the study also showed that 15%-30% of infected patients reported no risk factors for the transmission of HCV infection. Additional studies examining the burden of HCV infection in the United States, show that by 2007, HCV had superseded human immunodeficiency virus as a cause of death in the United States. Several additional United States studies have also predicted a two-fold increase in HCV related deaths with direct medical expenditure exceeding $6.7 billion USD between 2010 and 2019 and without intervention, suggest that morbidity and mortality from HCV will peak between 2030 and 2035 forecasting for 38600 incident cases of end-stage liver disease, 3200 referrals per year for liver transplant and 36100 deaths.
Relation Between Hepatitis C And Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma accounts for 85 to 90% of the cases of primary liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis constitute the major preneoplastic conditions in the majority of HCC. The risk of developing HCC for a patient with HCV-related cirrhosis is approximately 2-6% per year. HCC risk increases to 17-fold in HCV-infected patients compared to HCV-negative subjects. In general, HCC develops only after two or more decades of HCV infection and the increased risk is restricted largely to patients with cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis.
Multiple steps are required in the induction of all cancers it would be mandatory for hepatocarcinogenesis that genetic mutations accumulate in the hepatocytes. In HCV infection, however, some of these steps might be skipped in the development of HCC, in presence of the core protein. The overall effects achieved by the expression of the core protein would be the induction of HCC, even in the absence of a complete set of genetic aberrations, required for carcinogenesis. By considering such a non-Vogelstein type process for the induction of HCC, a plausible explanation might be given for many unusual events happening in HCV carriers.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Also Check: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B
How We Care For Hepatitis C
The Center for Childhood Liver Disease at Boston Children’s Hospital is one of the leading centers in the world for the care of children with hepatitis C. The centerâs director, Maureen Jonas, MD is a national leader in the care, diagnosis and treatment for children with viral hepatitis. Dr. Jonas, along with her team, wrote the clinical guidelines that shape the way pediatric GI specialists and pediatricians around the country treat hepatitis C.
In addition to the standard treatments, our team of certified pediatric hepatologists is also at the forefront of treatment research, treating adolescents with newly approved treatments for adults and conducting clinical trials to help make them available to children as young as 3 years of age.
How Can I Prevent Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Food and drink issues:
- Dont abuse alcohol. If you do drink alcohol, limit how much you drink and how often. If you drink more than two drinks a day if you are a man or more than one if you are a woman, you are increasing your risk. A drink is a glass of wine or a 12-ounce can of beer or a 1.5 ounce serving of hard liquor. If you have liver disease, you should not drink alcohol at all.
- Eat a well-balanced, low-fat diet, such as the Mediterranean diet. A well-balanced healthy diet consists of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains.
- Dont eat raw seafood, especially oysters and clams. These foods can contain a bacteria that can cause serious illness.
- Cut back on the amount of salt in your diet. Use other seasonings to flavor your foods.
Healthy body habits:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess body fat can damage your liver. Ask your healthcare provider for a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
- Exercise regularly.
- See your healthcare provider regularly for check-ups. Follow medical recommendations to control obesity, diabetes, hypertension and cholesterol and high triglycerides.
- Quit smoking if you smoke.
Healthy liver practices:
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Swollen Feet
New Perspective On Treatments For Patients With Hcv Infection And Cirrhosis
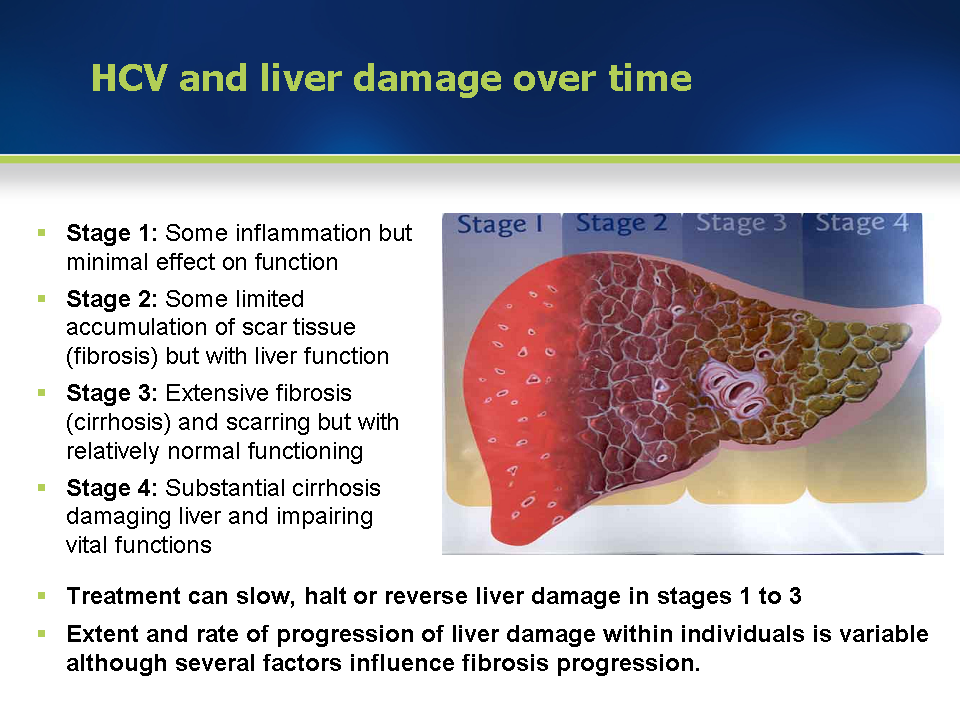
The goal of treatment for HCV infection early in the disease process is to reduce all-cause mortality and prevent development of liver complications. Immediate benefits of treatment include decrease in liver inflammation as reflected by improvement in aminotransferase levels and reduction in the rate of liver fibrosis. Long-term benefits include a more than 70% reduction in the risk of HCC and a 90% reduction in the risk of liver related mortality and need for liver transplantation. Achievement of virologic cure is determined by achieving undetectable HCV RNA levels defined as sustained virologic response at 12 wk or more following treatment completion. SVR has been shown in multiple studies to be a good marker for cure of chronic HCV infection in patients followed for greater than five years and corresponds with presence of anti-HCV antibodies but without detectable HCV RNA in the serum, in liver tissue and mononuclear cells. SVR at 12 wk has generally been accepted as primary efficacy end-point and a marker for virologic cure. Although previously SVR at 24 wk was used as a marker for virologic cure, multiple new studies show high concordance rate between SVR24 and SVR12 hence allowing for its use in multiple studies for effectiveness of treatment.
What Is Hepatitis C Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, and hepatitis C is liver inflammation caused by the hepatitis C virus .
Journal of Clinical MicrobiologyJournal of Infectious Diseases
Though these genotypes appear to affect people similarly, they respond differently to treatments, and its possible to be infected with more than one HCV genotype at the same time.
Whatever the genotype, hepatitis C is considered either acute or chronic .
Dont Miss: How To Reduce Hepatitis B Viral Load Naturally
You May Like: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis
What Exactly Is Liver Cirrhosis
This is a late-stage liver disease thats very serious and develops over a long period of time. In fact, its possible to have liver cirrhosis for several years without experiencing any symptoms. This is related to how serious your condition is.
The first stages of the liver disease result in something called fatty liver. This involves extra fat in the vital organ. However, over time this condition can develop into more serious stages. The most serious stage is known as live cirrhosis.
Its important to get treatment for the liver condition to help prevent the symptoms from getting worse. Here are some symptoms of liver cirrhosis early stages:
| Hair loss |
- Black stools
- Uncontrollable shaking.
Liver cirrhosis is often linked to alcoholism. However, there are also non-alcoholic causes of liver disease/cirrhosis. When a person experiences cirrhosis their liver isnt functioning properly. The liver has several functions including producing enzymes for food digestion, removing toxins from the blood, and battling infections.
The liver can normally repair itself and make strong scar tissue. However, when theres a scar tissue buildup the organ is unable to work properly. This results in liver cirrhosis.
Its important to know the main causes of liver cirrhosis. They include obesity, hepatitis B/C infections, and heavy drinking of alcoholic beverages. There are also other conditions that might boost your risk of cirrhosis. They include:
- Iron buildup
- Digestion problems
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis A
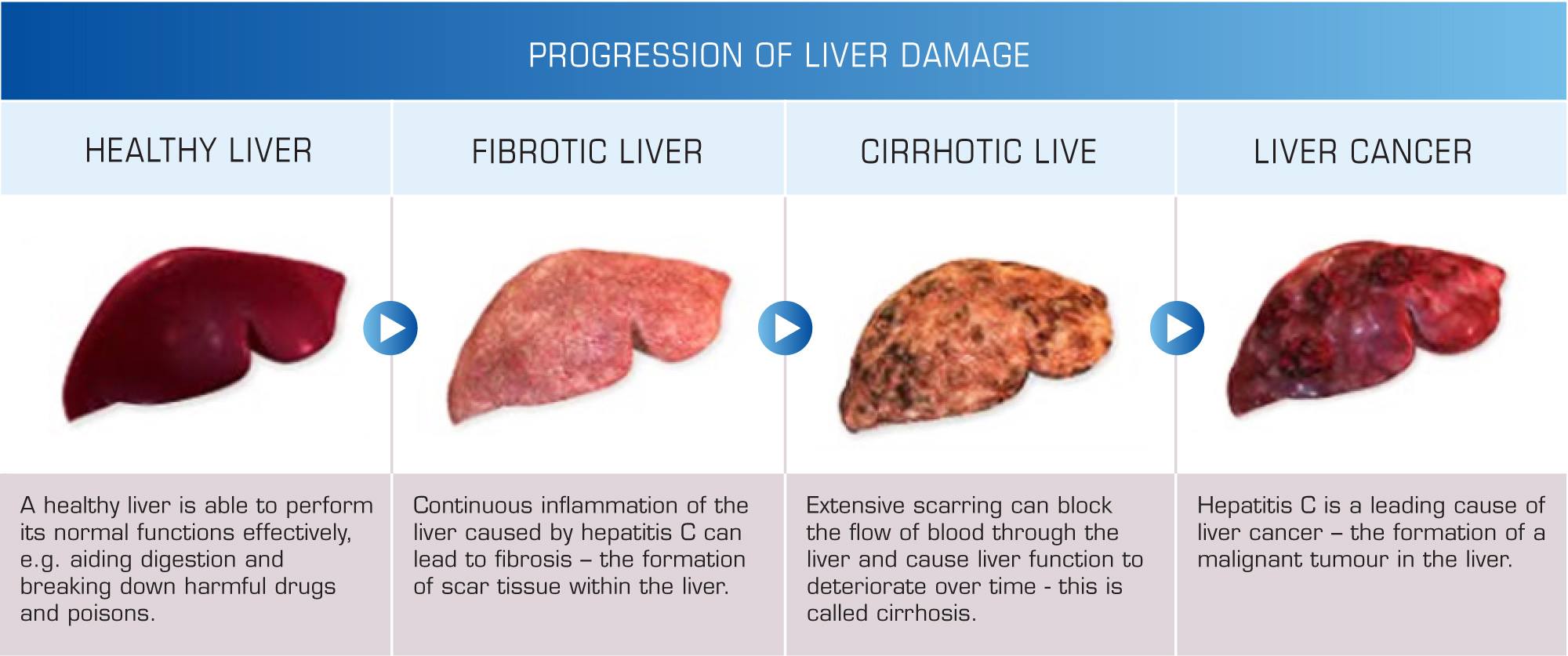
Liver Cirrhosis Caused By Hepatitis C Is Reversible
Every day someone asks me what needs to be done to restore the livers health after clearing Hepatitis C. What they are really asking is how to remove liver fibrosis or liver cirrhosis
One piece of information that everyone who has, or has had, Hepatitis C should know is that the liver damage caused by a chronic Hepatitis C infection is reversible. But first, let me explain what liver cirrhosis is.
Making The Diagnosis Of Compensated Vs Decompensated Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis can be diagnosed with clinical, laboratory, radiologic, elastographic, or biopsy findings
- The diagnosis of compensated cirrhosis is more challenging since patients may lack clinical, laboratory, and radiologic findings and may require biopsy for diagnosis
- The diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis is easier as the patient history, physical exam, and laboratory findings are usually more evident
Child-Turcotte-Pugh score
- TheChild-Turcotte-Pugh score is used as a prognostic scoring system in cirrhosis based on 2 clinical and 3 laboratory parameters:
- Ascites: none diuretic-sensitive or mild/moderate diuretic-refractory or tense
- Encephalopathy: none episodic or overt grade 2 recurrent/chronic or grade 3-4
- Albumin in g/dL:> 3.5 3.4-2.8 < 2.8
- Bilirubin in mg/dL:< 2 2-3 > 3
- INR:< 1.7 1.7-2.3 > 2.3
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Shot For
When Do Symptoms Develop
Many patients experience no symptoms and, for those who do, symptoms may not show up for years or even decades. Chronic liver disease in HCV-infected people usually progresses slowly without detection. Many times, HCV infection is not recognized until it is identified when people are screened for blood donations or through routine examinations.6 HCV is not routinely screened for in regular examination, so it’s important that someone who may have been exposed talk to a doctor. When left undiagnosed, HCV can lead to serious liver problems, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, and is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the United States.1
How Common Is Hepatitis C
An estimated 4 million people in the United States have HCV infection. Often dubbed the “silent disease,” HCV infects approximately 17,000 people each year, and many are asymptomatic for years after initial infection. Every year, the disease causes an estimated 8,000 to 10,000 deaths in the United States.1,4 Chronic viral hepatitis infections are three to five times more frequent than HIV infection in the United States.4
The rate of HCV infection is higher among African Americans.4 The HCV-related mortality rate among Latinos is nearly twice the rate among non-Latino whites. HCV in Latinos causes more aggressive inflammatory activity and fibrosis, greater disease progression and greater risk of cirrhosis than in non-Latino whites or African-Americans.5
Don’t Miss: Herbal Cure For Hepatitis B
What Causes Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is caused by chronic liver diseases that damage liver tissue. It can take many years for liver damage to lead to cirrhosis.
Chronic AlcoholismChronic alcoholism is one of the leading causes of cirrhosis in the United States. Drinking too much alcohol can cause the liver to swell, which over time can lead to cirrhosis. The amount of alcohol that causes cirrhosis is different for each person.
Chronic Viral HepatitisChronic hepatitis C is the another leading cause of cirrhosis in the United States. Hepatitis C causes the liver to swell, which over time can lead to cirrhosis. About one in four people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis. Chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis D also can cause cirrhosis.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis Fat build up in the liver that is not caused by alcohol use, is called Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease , which can lead to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis . NASH can cause the liver to swell and can lead to cirrhosis. People with NASH often have other health issues including diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol, coronary artery disease and poor eating habits.
Bile Duct DiseaseBile duct disease limits or stops bile from flowing to the small intestine. The bile backs up in the liver causing the liver to swell and can lead to cirrhosis. Two common bile duct diseases are primary sclerosing cholangitis and primary biliary cirrhosis.
How Is Hcv Spread
HCV is spread primarily through contact with infected blood. Common routes of infection include:3,6,7
- Receiving blood, blood products and organs before June 1992
- The use of shared or unsterilized needles and injection equipment
- Birth to an HCV-infected mother
- Hemodialysis for kidney failure
- Accidental exposure to a needle contaminated with infected blood
- Sexual contact with an HCV-infected person
- Intranasal cocaine use through shared paraphernalia
- Use of unsterilized and infected needles or ink for tattooing and piercing
- Sharing infected personal items and other household items that may have blood on them
You May Like: What To Do If I Have Hepatitis B
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood.
Hepatitis C can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Although no vaccine for hepatitis C is available, you can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about treatment. Medicines can cure most cases of hepatitis C.
Distinguishing Compensated And Decompensated Cirrhosis
One important step in treating HCV in persons with cirrhosis is to determine whether the cirrhosis is compensated or decompensated. The Child-Turcotte-Pugh score is an important component of determining the status of the cirrhosis and predicts morbidity and mortality. The treatment approach and goals are divergent based on the classification of compensated versus decompensated cirrhosis. In particular, HCV protease inhibitor-based regimens are not recommended for use in persons with decompensated cirrhosis due to the risk of hepatotoxicity with some medications and lack of data with the others.
You May Like: Do They Have A Cure For Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Virus