The Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis C
Antiviral drugs
The basis of current, interferon-free treatment is a combination of directly acting antiviral drugs with high antiviral efficacy, resistance barriers, and different sites of attack.
In the multicenter German Acute HCV IV trial, six weeks of treatment with sofosbuvir/ledipasvir resulted in a sustained viral eradication rate of 100% in patients acutely infected with HCV genotype 1 . It should be noted, however, that the combination of sofosbuvir and ledipasvir is available in Germany only in packages of 28 tablets, so that taking a single tablet per day for six weeks is unreasonable in terms of drug economics. Until further data are available, patients with acute hepatitis C should be treated for eight weeks, analogously to the recommendations for previously untreated patients with acute hepatitis C. As the rate of HCV transmission to health care workers via needle stick injury is very low, no post-exposure prophylaxis is recommended in this situation .
Polymerase inhibitors
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors are categorized as either nucleotide inhibitors or non-nucleoside inhibitors . The generic names of all HCV polymerase inhibitors end in -buvir.
Persons With Advanced Liver Disease
For persons with advanced liver disease , the risk of developing complications of liver disease, such as hepatic decompensation or HCC, is substantial and may occur in a relatively short timeframe. A large prospective study of patients with cirrhosis resulting from HCV infection examined the risk of decompensationincluding HCC, ascites, jaundice, bleeding, and encephalopathyand found that the overall annual incidence rate was 3.9% . The National Institutes of Health -sponsored HALTC study included a group of 220 patients with HCV-related cirrhosis who were observed for approximately 8 years. A primary outcome of death, hepatic decompensation, HCC, or an increase in CTP score 2 occurred at a rate of 7.5% per year . Patients with a CTP score of 7 experienced a death rate of 10% per year.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that hepatitis C therapy and the achievement of SVR in this population results in dramatic decreases in hepatic decompensation events, HCC, and liver-related mortality . In the HALT-C study, patients with advanced fibrosis secondary to HCV infection who achieved SVR, compared with patients with similarly advanced liver fibrosis who did not achieve SVR, had a decreased need for liver transplantation , decreased development of liver-related morbidity and mortality , and decreased HCC . Importantly, persons with advanced liver disease also require long-term follow-up and HCC surveillance regardless of treatment outcome .
What Does It Mean To Have A Successful Treatment What Is A Sustained Virologic Response
In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases. The amount of virus in the blood is measured by aviral load.
Treatment is successful when the viral load drops toundetectablelevels, which means the virus cannot be detected in the bloodstream at all. The viral load becomes undetectable during treatment and remains undetected after treatment has ended. If there is still no detectable virus in the blood 12 weeks after the end of the treatment, the treatment was successful. This is called a Sustained Virologic Response .
A patient who has achieved an SVR is considered to be cured of the hepatitis C virus.
Also Check: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
Herbal Remedies To Avoid
Some herbal supplements are dangerous for people with hepatitis C because they cause liver damage. These include:
- Artemesia
Show Sources
Advances in Nutrition: “Effect of citrus flavonoids, naringin and naringenin, on metabolic syndrome and their mechanisms of action.”
American Liver Foundation: “Treating Hepatitis C.”
Annals of Gastroenterology: “25-Vitamin D levels in chronic hepatitis C infection: Association with cirrhosis and sustained virologic response.”
Antiviral Therapy: “Complementary and alternative medicine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and C: A review.”
BioMed Research International: “Effects and tolerance of silymarin in chronic hepatitis C virus infection patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.”
CATIE: “Hepatitis C: An In-Depth Guide.”
: “Curcumin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication via suppressing the Akt-SREBP-1 pathway.”
Harvard: “Grapefruit compound may help combat hepatitis C infection.”
Hepatology: “Hepatoprotective and antiviral functions of silymarin components in HCV infection.”
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition: “Zinc supplementation improves the outcome of chronic hepatitis C and liver cirrhosis.”
Mayo Clinic: “Zinc.”
Persons With Extrahepatic Manifestations Of Chronic Hcv Infection
Cryoglobulinemia
Chronic hepatitis C is associated with a syndrome of cryoglobulinemia, an immune complex and lymphoproliferative disorder that leads to arthralgia, fatigue, palpable purpura, renal disease , neurologic disease , and reduced complement levels . Glomerular disease results from deposition of HCV-related immune complexes in the glomeruli . Because patients with chronic hepatitis C frequently have laboratory evidence of cryoglobulins , antiviral treatment is imperative for those with the syndrome of cryoglobulinemia and symptoms or objective evidence of end-organ manifestations. Limited data with DAA therapy in the setting of vasculitis end-organ disease related to cyroglobulinemia have demonstrated responses in 20% to 90% of patients . Despite this, patients with severe end-organ disease may still require treatment with plasmapheresis or rituximab .
Diabetes
Fatigue
A recent analysis of 413 patients from the NEUTRINO and FUSION trials who were treated with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen and achieved SVR12 demonstrated improvement in patient fatigue from the pretreatment level . After achieving SVR12, participants had marked improvements in fatigue over their pretreatment scores, measured by 3 separate validated questionnaires. Additional studies support and extend these findings beyond fatigue, with improvements in overall health-related quality of life and work productivity observed following successful HCV therapy .
Dermatologic Manifestations
Read Also: The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Molecular Targeting Of Antiviral Drugs Used Against Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Mohammad Irshad1 Priyanka Gupta1 Khushboo Irshad2
1Clinical Biochemistry Division, Department of Laboratory Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi 110029, India.
2Department of Biochemistry, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi 110029, India.
Received: First Decision: Revised: Accepted: Science Editor: Copy Editor: Production Editor:
© The Author 2018. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Persons Who Inject Drugs
Injection drug use is the most common risk factor for HCV infection in the United States and Europe, with an HCV seroprevalence rate of 10% to 70% . IDU also accounts for the majority of new HCV infections and is the key driving force in the perpetuation of the epidemic. Given these facts and the absence of an effective vaccine against HCV, testing and linkage to care combined with treatment of HCV infection with potent DAAs has the potential to dramatically decrease HCV incidence and prevalence . However, treatment-based strategies to prevent HCV transmission have yet to be studied, including how to integrate hepatitis C treatment with other risk-reduction strategies .
In studies of interferon-based treatments in persons who inject drugs, adherence and efficacy rates are comparable to those of patients who do not use injected drugs. A meta-analysis of treatment with peginterferon, with or without ribavirin, in active or recent injection drug users showed SVR rates of 37% and 67% for genotype 1 or 4, and 2 or 3, respectively . With the introduction of shorter, better-tolerated, and more efficacious interferon-free therapies, these SVR rates are expected to improve. Importantly, the rate of reinfection in this population is lower than that of incident infection in the general population of injection drug users , although reinfection increases with active or ongoing IDU and available data on follow-up duration are limited .
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Sustained Viral Response: A Patient
The molecular demonstration of the absence of HCV-RNA twelve weeks after the end of a course of antiviral treatment confirms the sustained eradication of the virus. The likelihood of a late recurrence is well under 1% , and most such events are actually not recurrences but reinfections . The eradication of HCV does not generate protective immunity .
A meta-analysis of 129 studies involving a total of 34 563 patients who had undergone interferon-based treatment revealed that a sustained virological response was associated with a 62% to 84% reduction of mortality, a 68% to 79% reduction of the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma , and a 90% reduction of the risk of needing liver transplantation . As interferon-based treatment was contraindicated in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, these data are uninformative with respect to any potential clinical benefit, for these patients, of sustained viral eradication with direct antiviral agents . Initial studies have yielded clinical and laboratory evidence of improvement mainly for patients with a MELD score below 1618 points . In large-scale cohort studies, sustained viral eradication was associated both with lower liver-associated mortality and with substantially lower extrahepatic mortality . Sustained viral eradication eliminates the risk of individual transmission and is associated with a better quality of life .
HCV genotypes
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Read Also: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C
Antiviral Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus Reduces Risk Of Post
In a new cohort study of patients with hepatitis C virus -related hepatocellular carcinoma , a disease with a high recurrence rate, researchers at the Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine reported that after receiving cancer treatment, the oral administration of direct-acting antivirals reduces the risk of tumor progression following recurrence of the liver disease. The findings were published in the Journal of Viral Hepatitis.
Led by Norifumi Kawada, professor of the Department of Hepatology, the study investigated the effect eliminating HCV had on tumor progression of early-stage HCC. “DAA therapy is effective at eradicating the hepatitis C virus, a major risk factor for HCC” says Professor Kawada. “While it is deemed low or inconclusive whether DAA therapy helps prevent HCC recurrence, little is known about how the antiviral therapy affects progression of the liver disease after cancer treatment.”
“Usually, cancer cells grow over long periods of time before they can be detected as a tumor,” states first author Hiroko Ikenaga. “Our study showed that eliminating the hepatitis C virus with DAA suppresses tumor progression, which we suggest contributes to overall patient survival.”
Explore further
Current Antiviral Treatment Strategies
The introduction of DAA revolutionized the field of antiviral therapy for patients chronically infected with HCV. Antiviral therapy usually consists of at least two antiviral substances from different drug classes with different modes of action . Treatment decisions are based on genotype , presence of cirrhosis and response to prior treatments . Typical treatment regimens for patients with and without compensated cirrhosis are depicted in Tables 1 and 2. All different recommended regimens achieve SVR rates of more than 95% if administered correctly .
Table 1.
Treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C without cirrhosis
Table 2.
Treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C with compensated cirrhosis
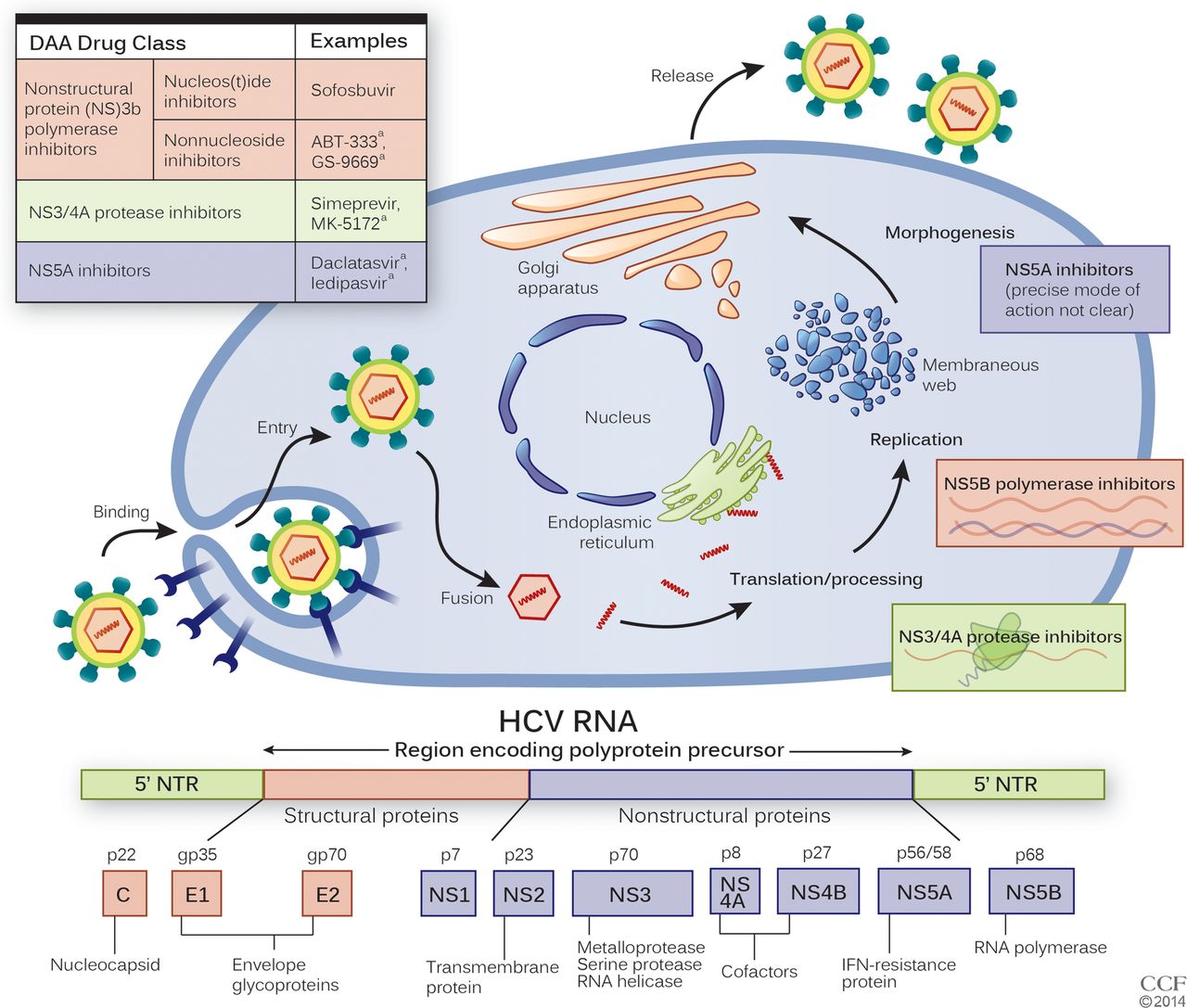
Fig. 1.
The replication cycle of the hepatitis C virus and modes of action of direct-acting antivirals are displayed .
The pangenotypic drug combinations sofosbuvir/velpatasvir and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir show high antiviral efficacy against all HCV genotypes. Treatment duration differs from 8 weeks for glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in noncirrhotic treatment-naive patients to 12 weeks for patients with liver cirrhosis or 16 weeks for GT 3 patients with liver cirrhosis and/or prior treatment failure. Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir has to be administered for 12 weeks independently of fibrosis level . Treatment with grazoprevir/elbasvir is possible in patients with GT 1 or 4 infection and has to be administered for 1216 weeks depending on GT, fibrosis stage and viral load .
Also Check: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
Direct Acting Antiviral Agents
This is the class of drugs acting against viral and host proteins involved in HCV life cycle. The major inhibitors of NS3 viral protein are telaprevir and boceprevir. Telaprevir was approved and recommended for use with PegIFN- and ribavirin in genotype-1 patients. This was classified as triple therapy. Since telaprevir treatment is reported to be effective against the resistant mutants in the short term duration, it was decided to use it for long-term and subsequently approved for the treatment. It is important to note here that the long term use of these drugs often leads to drug resistance including T54A/S, R155K/T, V36A/M, V55A, and A156/S/T/V, etc. Simeprevir is another NS3 protease inhibitor classified as second generation drug. This drug is a reversible inhibitor of NS3/4A protease. Danoprevir and faldaprevir are also second-generation HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors and used in patients infected HCV genotype-1. In addition to these drugs, there are various other NS3 protease inhibitors like Vaniprevir , Narlaprevir , Asunaprevir , VX 985, and MK-5172 which are used for treatment of HCV infection. There is every possibility that these drugs may be approved for therapeutic use against HCV infection.
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis B And C Be Transmitted
Does Hcv Clearance With Daas Lead To Significant Improvement Of Glycometabolic Control In Patients With Dm If So Is This Control Maintained Over The Long Term
A recent review with a meta-analysis demonstrated and quantified the improvement of glycometabolic control in diabetic patients with CHC achieving SVR after treatment with DAAs. Eleven publications were considered and discussed by the review but only five met the inclusion requirements for the meta-analysis. Regarding the variation of HbA1c levels, an average decrease of 0.45% was found with strong heterogeneity between the studies . Glycemic values were evaluated by three studies : A significant reduction of 22 mg/dL was observed, with wide heterogeneity among the studies . According to the reported data, the number of published studies that agreed with the glycometabolic amelioration induced by SVR was higher than the number of studies that disagreed with this hypothesis.
Actually, several studies show significant improvement in glycemic levels and HbA1C at the end of DAA therapy, compared to a few that did not show any significant change in glycometabolic control.
Recommendation For When And In Whom To Initiate Treatment
RECOMMENDED RATING Treatment is recommended for all patients with acute or chronic HCV infection, except those with a short life expectancy that cannot be remediated by HCV therapy, liver transplantation, or another directed therapy. Patients with a short life expectancy owing to liver disease should be managed in consultation with an expert. I, A
Also Check: Diet For Dogs With Chronic Hepatitis
Ombitasvir Paritaprevir And Ritonavir Tablets Co
This is a relatively new group of medicines that treat genotype 1 hepatitis.
Facts about the drug pack include:
- Treatment time is 12 or 24 weeks.
- Dosage is a pack of tablets containing 12.5 mg of ombitasvir, 75 mg of paritaprevir, and 50 mg ritonavir, taken once daily in the morning, and one 250 mg tablet of dasabuvir taken twice daily with a meal.
- Common side effects of this group of drugs include nausea, itching, and trouble sleeping. If the person also takes ribavirin, side effects include tiredness, nausea, fatigue, and skin reactions.
The following medications may be effective for genotype 2:
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Read Also: New Drug To Cure Hepatitis C
Prior Antiviral Treatment And Mortality Among Patients With Hepatitis C Virus
-
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing original draft
¶ DHS and DK contributed equally to this work as co-first authors.
Affiliation Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea
-
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing original draft
¶ DHS and DK contributed equally to this work as co-first authors.
Affiliations Department of Clinical Research Design and Evaluation, SAIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, Center for Clinical Epidemiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea