What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
“Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment,” says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Chronic Hepatitis B Treatment
For hepatitis B, treatment is aimed at controlling the virus and preventing damage to the liver. Antiviral medications are available that will benefit most people, but the medications need to be chosen carefully, and the treatment needs to be monitored in order to assure successful treatment and to prevent or treat medication-related side effects. For some individuals, the risks of treatment may not be justified.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Infection
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the bodys reaction to the viral infection or the bodys reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Dont Miss: Where Does The Hepatitis C Virus Come From
Preparation And Use Of Drugs

Washing hands and using sterile water to prepare and use drugs lower the risk of catching hepatitis A. The use of new paraphernalia for the preparation, injection and inhalation of drugs lowers the risk of catching hepatitis B and C through blood.
Never share drug paraphernalia. To know the location of distribution points for drug injecting material, call Info-Santé 811.
Dont Miss: Is Hepatitis C A Blood Borne Pathogen
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis Of The Liver
There Is A Test For Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C antibody test determines if a person has been infected with the virus. A positive, or reactive result, means antibodies were found and you were infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time. Additional tests are required to confirm if you have active infection at present.
Hiv And Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Coinfection
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are liver infections caused by a virus. Because these infections can be spread in the same ways as HIV, people with HIV in the United States are often also affected by chronic viral hepatitis.
Viral hepatitis progresses faster and causes more liver-related health problems among people with HIV than among those who do not have HIV. Liver disease, much of which is related to HBV or HCV, is a major cause of non-AIDS-related deaths among people with HIV.
Given the risks of hepatitis B or hepatitis C coinfection to the health of people living with HIV, it is important to understand these risks, take steps to prevent infection, know your status, and, if necessary, get medical care from someone who is experienced in treating people who are coinfected with HIV and HBV, or HIV and HCV.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Kidney Failure
Testing Treating And Reducing Risk Of Hepatitis
If you think youre at risk for hepatitis infection, talk to your healthcare provider about getting tested. A blood test is usually done to see if you have been exposed to the virus. Women who are pregnant or trying to become pregnant should get tested for hepatitis.
Get treated for hepatitis infection
There are treatments for hepatitis. Treating long-lasting hepatitis B or C infection can reduce the amount of the virus in a person, which may lower the risk of liver cancer.
Dont Miss: Symptoms Of Acute Hepatic Porphyria
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic
Recommended Reading: Which Hepatitis Causes Liver Cancer
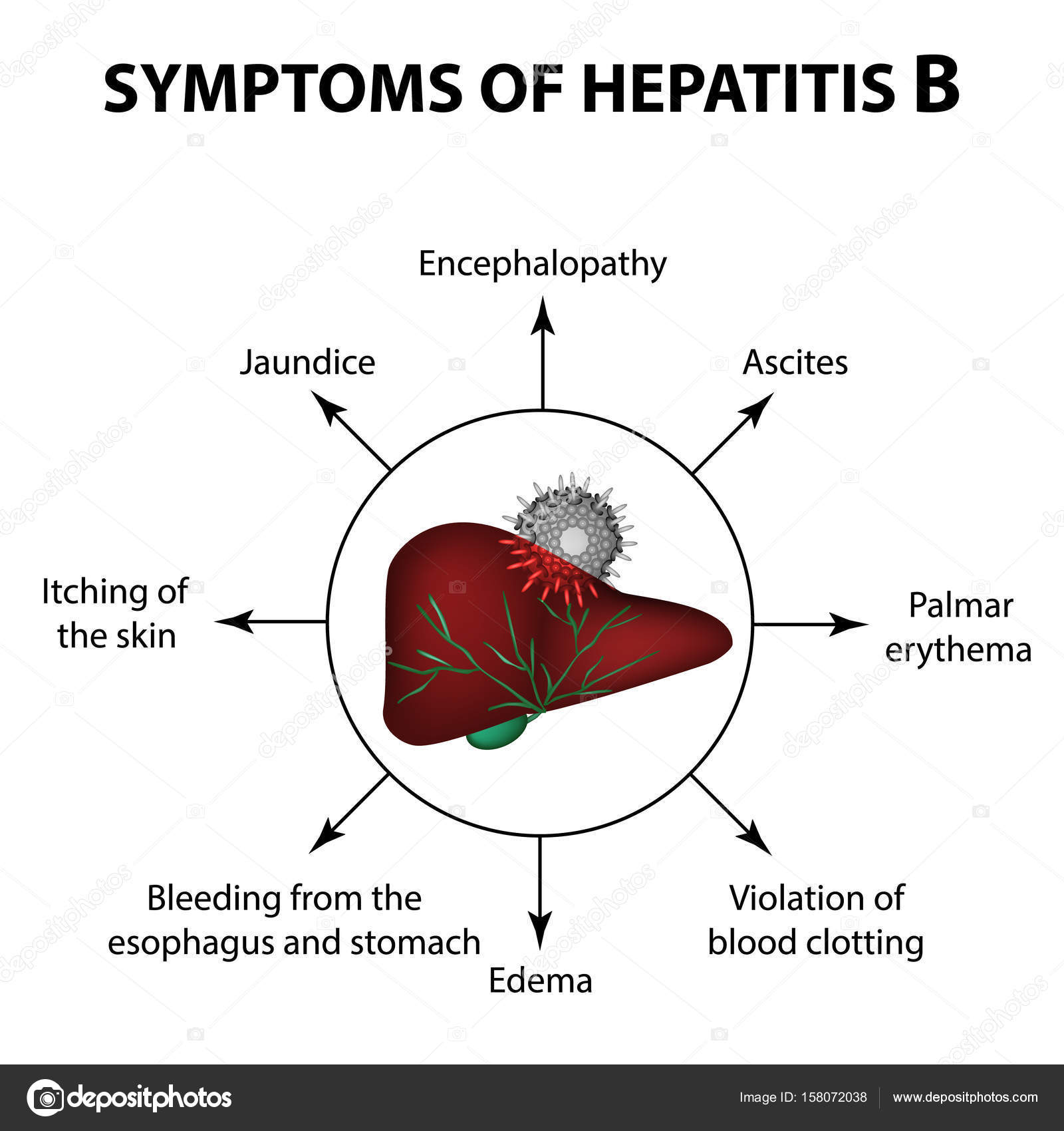
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by a virus that infects the liver. It is one of the most common vaccine-preventable diseases affecting travellers and can cause either acute or chronic infection.
About 90 to 95 percent of adults with acute hepatitis B infection will clear the virus on their own within six months, and develop lifelong protection against it.
Some people are unable to clear the virus, and develop chronic hepatitis B. Untreated chronic hepatitis B can later develop into serious health problems. Children under four years old are at particular risk of chronic hepatitis B, because only up to 10% will clear the virus.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Just like hepatitis B, you can get this type by sharing needles or having contact with infected blood. You can also catch it by having sex with somebody who’s infected, but that’s less common.
If you had a blood transfusion before new screening rules were put in place in 1992, you are at risk for hepatitis C. If not, the blood used in transfusions today is safe. It gets checked beforehand to make sure it’s free of the virus that causes hepatitis B and C.
It’s rare, but if you’re pregnant and have the disease, it’s possible to pass it to your newborn.
There are some myths out there about how you get hepatitis C, so let’s set the record straight. It’s not spread by food and water . And you canât spread it by doing any of these things:
See your doctor as soon as possible if you have any of these symptoms.
Sometimes, people have no symptoms. To be sure you have hepatitis, youâll need to get tested.
You May Like: Is Fasting Required For Hepatitis C Test
Is Hepatitis B Worse Than Hepatitis C
Michael says, At the end of the day, its not which ones worsetheyre both bad. He points out that both can lead to liver cancer if left untreated.
Together, hepatitis B and C account for more than 80% of all liver cancers in the world. However, hepatitis B does seem to be more dangerous in some ways than hepatitis C for several reasons:
- Hepatitis B is certainly more virulent and contagious than hepatitis C.
- Hepatitis B is prevalent around the world and it causes more liver cancer than hepatitis C.
- People with hepatitis B are more likely to die from complications to their liver than people with any of the other hepatitis infections.
When comparing hepatitis B and C, we should note that these viruses attack our cells in completely different ways. Hepatitis C operates in the standard virus way, by invading our cells and reproducing copy after copy of itself until it overwhelms the healthy cells. Hepatitis B, however, goes beyond cloning itself to reproduce and instead inserts itself into the healthy cells DNA. This is a more ominous process because it is much harder to destroy the hepatitis B cell when it takes root at the DNA level.
Additionally, hepatitis C typically causes cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver that interferes with its function, leading to liver cancer. However, in some cases, hepatitis B can cause liver cancer without any signs of cirrhosis. That can make liver cancer itself difficult to diagnose.
Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C has evolved, rendering many earlier drugs obsolete. The drugs currently used include pegylated interferon, ribavirin, elbasvir, grazoprevir, ledipasvir, sofosbuvir, paritaprevir, ritonavir, ombitasvir, dasabuvir, simeprevir, daclatasvir. These are always used in various combinations, never alone. Interferon is given by injection while the other medications are pills. Studies have shown that combinations of these drugs can cure all but a small proportion of patients however, serious side effects of treatment can occur.
Treatment options need to be discussed with a knowledgeable physician, as the appropriate combination is dependent upon multiple factors. These include genotype , prior treatment and results, drug intolerances, presence of compensated liver disease or uncompensated cirrhosis, presence of HIV co-infection, other complicating conditions and liver transplantation.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Important Questions And Needs For Future Research
How does HBV establish productive infection in vivo and what is the host response early during the infection? Despite well-described information on the clinical manifestations and natural history of acute HBV infection, detailed knowledge of the virus-host interaction during this stage remains poorly defined. Advances in this area would offer a better understanding of the pathogenesis of HBV infection and its associated disease.
What is the immunologic basis of chronic infection and hepatocellular injury? There have been great strides in understanding the virology and immune response of HBV infection, but the molecular mechanisms whereby the host fails to clear the virus and develops chronic infection remain largely unknown. In addition, the adaptive evolution of virus under host immune pressure remains to be elucidated. Finally, the pathogenesis of various extra-hepatic manifestations associated with HBV infection is poorly understood. Further research in these areas is crucial not only in better understanding the natural history and disease progression but also in improving treatment for chronic hepatitis B.
You May Like: How To Treat Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis A: What Happens
Hepatitis A is highly contagious and can spread from person to person in many different settings. It typically causes only a mild illness, and many people who are infected may never realize they’re sick at all. The virus almost always goes away on its own and does not cause long-term liver damage.
Can Hbv Infection Be Prevented
Yes. The best way to prevent HBV is to get the hepatitis B vaccine.
CDC recommends that people with HIV and people who are at risk for HIV get the HBV vaccine . The housemates and sexual partners of people with HBV should get the HBV vaccine, too.
People, including people with HIV, can also take the following steps to reduce their risk of HBV infection:
- Use condoms during sex to reduce the risk of HBV infection and infection with other sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea and syphilis.
- Do not inject drugs. But if you do, do not share needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
- If you get a tattoo or body piercing, make sure the instruments used are sterile.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis C Non Reactive Mean
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
People who have injected illegal drugs at any time, even one time, many years ago, could be walking around with chronic hepatitis C. Because there are often no symptoms, many former drug users may not realize they have the infection. People who received a blood transfusion before 1992 also have a higher risk. Before that year, donated blood was not screened for the hepatitis C virus.
Blood Tests To Diagnose Hepatitis B
Blood tests are done to help diagnose hepatitis B. They include:
- Hepatitis B antigens and antibodies. These help tell if you are or were infected with the virus. They also can show if you have been immunized and if you have long-term infection. You also may get tested for the viruss genetic material . For more information, see Hepatitis B Virus Tests.
- Tests to see if the hepatitis A, hepatitis C, or Epstein-Barr viruses are causing your hepatitis.
- Tests to see if you are infected with hepatitis D along with hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis B and C: Should I Be Tested?
Read Also: New Medicine For Hepatitis B
Also Check: Is There An Immunization For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread
It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
Also Check: How To Check For Hepatitis
The A B Cs Of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus causes acute inflammation of the liver that almost always gets better on its own, although it can be more serious if you get it when you are older or if you already have liver disease. It is easily spread from person to person, in food and water, and can infect many people at once. For example, if a food handler at a restaurant is infected with hepatitis A, those who eat food prepared by that handler may be infected. Hepatitis A can be prevented by getting vaccinated.
Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus can be both acute and chronic and is spread through blood or other body fluids in various ways. Hepatitis B is very common in Asia and Africa and those who were born or lived in these areas should be checked for hepatitis B. Like hepatitis A, a vaccine is available to prevent HBV infection as long as you have not been previously exposed. Although chronic HBV cannot be cured, there are oral medications available to treat and control the virus.
Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is almost always chronic and spreads mostly by direct blood to blood contact. Although hepatitis A and B can be prevented by vaccination, hepatitis C cannot. However, there are currently oral medications available that are able to cure Hepatitis C in 95% of all cases regardless of prior treatment history.