Explainer: Lab Results And Their Interpretation
Before posting your lab results, please read through and abide by the best practices thread first
We all know that its important to have blood tests to know your current Hep B status or to know if youre protected against it. There are a lot of different tests in a panel for Hep B and these can be confusing. Here are short explanations for some of the common ones:
Use this thread to get help if you dont understand your results.
Hi Everich,
You need to be a bit more specific about what the exact test was. What is all the information you have about the test? We cannot answer your question without that information.
Thomas
Hi Everich, there are basically 3 blood tests that are required for a new vs. a chronic hepatitis B infection. Below is a simple summary of these tests. If you could let us know which blood test was indeterminate that would be very helpful.
Hepatitis B surface antigen â If or means the hep b virus is present. This could mean a new infection or a chronic infection . If this test is or , then the hep b virus is not present in the blood.
Hepatitis B surface antibody â this tests for a protective antibody against the hep b virus. This can occur through getting the hep b vaccine or recovery from an exposure to the virus. If or , then it means a person has been protected against the hep b virus either through vaccination or recovery from an infection. Generally, the above test will be or .
Her report says HBV VIRAL LOAD < 34. IU/ml
Additional Specimen Collection Information
Collect blood in a lithium heparin, green-top, EDTA purple-topor red-top tube. PST and SST are acceptable. Serum orplasma should be separated from contact with the cells within 2hours of collection. Specimens not centrifuged within 4 hours ofcollection may be rejected. Refrigerate the specimen if unable toassay within 8 hours of collection. Samples with > 1+ lipemiamust be cleared prior to analysis.
False Reactive Test Results
What if I have a false reactive test result?
Every donation given to Canadian Blood Services is tested for infectious diseases caused by the hepatitis viruses B and C, HIV, syphilis and another uncommon virus called HTLV .
A false reactive test result means your initial screening test was reactivein other words, suggested the presence of something that would prevent you from donating bloodand a more precise follow-up test was negative. Almost all false reactive results occur because of interference with a test and are not necessarily due to testing positive for an infection.
FAQS
How does Canadian Blood Services test blood?
We follow a two-stage testing method that is used in laboratories worldwide. In the first stage, a sensitive screening test looks for the possible presence of infection. If the screening test shows no reaction, the blood is considered free of infection and no further testing is done. However, if the screening test is reactive, further testing is done to sort out whether the reactive result was due to an infection in the blood or interference with the test. The second test identifies markers in the blood that are found only when infection is present.
Do I need to go to my doctor for repeat testing?
Yes. Repeat testing should be discussed with your doctor because he/she is in the best position to offer you personal medical advice.
Do my partner, children, or friends need to worry if Ive had a false reactive result?
Recommended Reading: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?
Identifying Patterns Of Risky Behavior
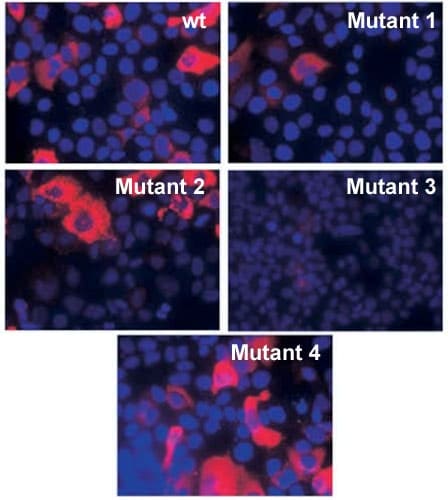
Screening is an opportunity to draw attention to the clients behaviors that put him or her at risk for contracting :
- Ask for the clients perception of his or her risk for having contracted : How likely do you think it is that the test will be positive?
- Listen for and identify behaviors that put the client at risk for contracting , B, and C and HIV, especially unprotected sex and sharing injection drug paraphernalia.
- Assess the clients alcohol consumption.
Read Also: How Do I Get Tested For Hepatitis
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
HBsAg is the first serologic marker to appear and may be detected within 1 to 2 weeks after exposure. It precedes the development of symptoms by an average of 4 weeks.106 The presence of HBsAg indicates ongoing infection. Qualitative but not quantitative methods are used by most clinical laboratories because the amount of antigen does not correlate with disease activity or with the presence of an acute or chronic infection.28 Some symptomatic patients may have self-limited, acute HBV infection without detectable HBsAg. These patients, up to 9% in some studies, have other detectable markers of infection.106 HBeAg appears virtually simultaneously, peaks, and then declines in parallel with HBsAg. It usually disappears before HBsAg does. Adult patients who remain persistently positive for HBeAg for more than 10 weeks are likely to become chronically infected. HBeAg indicates a high level of viral replication and infectivity. Most patients with nondetectable HBeAg have resolving, minimal, or no active liver disease.28 Precore mutants of HBV do not express HBeAg they may be responsible for a more severe course and, in some cases, fulminant disease. Serum aminotransferase levels become elevated but are nonspecific. They begin to increase just before the development of symptoms and then peak with the development of jaundice.
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Recommended Reading: What Are Signs Of Hepatitis B And C
Also Check: Hepatitis A Virus Ab Positive
Definition Of Hcc Occurrence Cirrhosis And Significant Fibrosis
HCC was diagnosed according to the guidelines of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. The presence of cirrhosis was reviewed according to imaging findings of cirrhotic hepatic change and/or clinical criteria indicating portal hypertension, such as the presence of ascites, esophageal or gastric varix, or splenomegaly with thrombocytopenia.
Hepatic fibrosis was defined using a noninvasive prediction model Fibrosis-4 index. The equation for FIB-4 index is as follows
FIB-4=age x AST / x 1/2)
Subjects with FIB-4> 1.45 were regarded as those who have high probability of advanced fibrosis,.
Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen And Antibody
- Hepatitis B e Ag and Ab by EIA
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen and Antibody
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis B virus e antigen and Hepatitis B virus e antibody in human sera by the FDA approved LIASON® IgG Assay.
The presence of HBeAg in serum is associated with presence of Dane particles and Hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase enzyme. These markers suggest active HBV replication. Hepatitis B Surface antigen positive and HBeAg positive persons are much more likely to transmit infections to others. The development of anti-HBe during acute Hepatitis B infection is a marker of resolution of illness.
- Synonyms
Also Check: How To Get Hepatitis B And C
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
Read Also: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
Clinical And Laboratory Assessments
Demographic data, medication history including antiviral agents and comorbidities such as malignancy were assessed based on electronic medical records.
Laboratory tests included assessments of serology associated with HBV infection, liver function, AFP levels, platelet counts, and antibodies against hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Serologic markers for HBV including HBsAg, anti-HBs, hepatitis B e antigen , and anti-HBe were assessed by chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassays . The concentration of HBsAg was determined using a previously generated Architect HBsAg calibration curve , and the samples with higher than 250 IU/ml HBsAg levels were diluted to 1:5001:1000. By June 2010, qHBsAg more than 250 were expressed as > 250 IU/ml without presenting an exact value. Thus, we divided subjects into 2 groups as those with qHBsAg> 250 IU/ml and those with qHBsAg250 IU/ml in this study.
Serum HBV DNA levels were measured with Roche COBAS TaqMan quantitative PCR assay, which has a low detection limit of 20 IU/mL. The threshold for anti-HBs positivity was an anti-HBs titer > 10 IU/mL. Blood samples were collected before 10:00 AM after the patients had completed a 12-h overnight fast. All laboratory tests were conducted using standard methods.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Also Check: How To Treat Alcoholic Hepatitis
We Implement Proven Measures To Keep Your Data Safe
At HealthMatters, were committed to maintaining the security and confidentiality of your personal information. Weve put industry-leading security standards in place to help protect against the loss, misuse, or alteration of the information under our control. We use procedural, physical, and electronic security methods designed to prevent unauthorized people from getting access to this information. Our internal code of conduct adds additional privacy protection. All data is backed up multiple times a day and encrypted using SSL certificates. See our Privacy Policy for more details.
Popular search
Read Also: How Do You Contact Hepatitis A
Case Reporting And National Notification
Cases of acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B, and hepatitis B during pregnancy should be reported to HDs as specified by state, territorial, or local regulations. Acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B are nationally notifiable conditions . Hepatitis B cases are identified using an event code corresponding to the hepatitis B condition . Data are sent weekly or more frequently, depending on the infrastructure of the jurisdiction sending the data. Cases might be re-classified or removed as needed after the initial transmission to CDC, as long as the changes occur before surveillance data are finalized each year.
You May Like: Xifaxan Dosage For Hepatic Encephalopathy
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Recommended Reading: Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 1a