Liver Cancer Risk Factors
A risk factor is anything that increases your chance of getting a disease, such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like a person’s age or family history, can’t be changed.
But having a risk factor, or even several risk factors, does not mean that you will get the disease. And some people who get the disease may have few or no known risk factors.
What You Can Do To Help Manage The Symptoms Of Liver Cancer
Symptom management is an important aspect of coping with liver cancer. When symptoms are properly addressed and managed, it can significantly strengthen the capability of your loved one and their overall quality of life. Below are common symptoms experienced by those with liver cancer and suggestions that caregivers can use to help manage these symptoms. Always consult with your healthcare provider before trying any of the following suggestions:
Screening Patients With Chronic Hepatitis For Liver Cancer Improves Survival And Cure Rates
Researchers evaluated the impact of screening for liver cancer among 1,366 patients diagnosed with hepatitis B or C. These patients were divided into two groups based on how they were diagnosed with liver cancer: those diagnosed through screening and those diagnosed with they developed symptoms. Survival rates between the two groups were compared. Further comparison evaluated the management and survival of these patients during two seven-year periods: 19911997and 19982004).
- Long-term survival was significantly better among the patients who had been part of the screening group compared with those in the symptomatic group. Average survival times were 61.9 months for the screening group versus 11.5 months for the symptomatic group.
- The number of screened patients who received curative treatment for liver cancer increased from 50% during 19911997 to 67% during 19982004. There was no change in treatment strategies among the symptomatic patients during either time period.
- Long-term survival also improved among members of the screening group who were treated during the years of 19982004 compared with those treated from 19911997.
Also Check: Best Medication For Hepatitis C
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Can Hepatitis B Be Controlled By Eating Right And Exercising
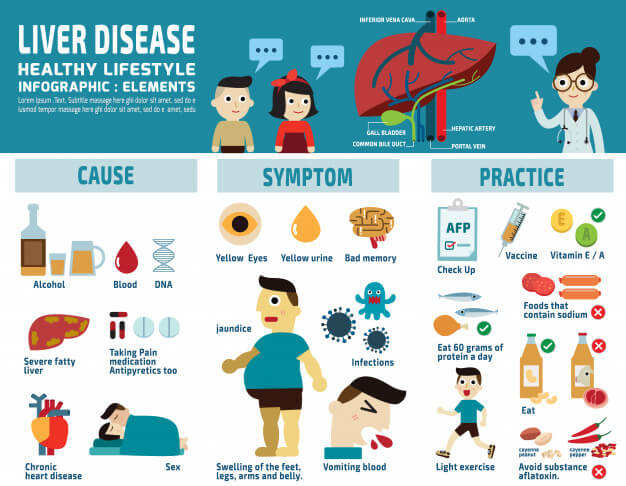
It is important that people with liver disease follow a healthy, nutritious diet as outlined by Health Canada in Eating Well with Canadas Food Guide.
Alcohol can also damage the liver so it is best that people with hepatitis B do not drink. Following a healthy lifestyle may also prevent fatty liver disease, another liver disease highly prevalent in Canada.
However, hepatitis B cannot be controlled by healthy eating and exercise alone. Hepatitis B can only be controlled by currently available treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will need to do regular blood tests to know how much of the active virus is in your blood . The viral load test is used to monitor and manage hepatitis B patients. Viral load can tell your doctor if you need treatment for hepatitis B and how well you are responding to treatment.
Also Check: Natural Remedy For Hepatitis B
What Are The Symptoms
What happens to you when you contract hepatitis B depends largely on the age at which you first become infected and how well your immune system copes with the virus. If you are infected as an adult, you may have a brief illness with mild or moderate symptoms such as jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and loss of appetite. As an adult, you have a 95% chance of clearing the infection completely and developing lifelong protection against this virus. The acute infection rarely leads to severe illness that requires a liver transplant.
Most babies and children exposed to this virus never have signs and symptoms. Unfortunately, they are more likely to become carriers of hepatitis B for life because their immune system is unable to fight and clear the virus from their body. In these cases, chronic infections are often not detected or picked up until much later in life when the person becomes seriously ill with liver disease.
Chronic hepatitis B infection goes through different phases that also show how well your body is coping with the virus. Although most people with chronic hepatitis B have an inactive disease and will remain healthy, about one in four will have active disease that may lead to cirrhosis , liver failure, and liver cancer.
People who are healthy with an inactive disease may still be at risk of virus reactivation, especially when their immune system is weakened by medicines such as chemotherapy or by other viral infections.
Testing Treating And Reducing Risk Of Hepatitis
If you think youre at risk for hepatitis infection, talk to your healthcare provider about getting tested. A blood test is usually done to see if you have been exposed to the virus. Women who are pregnant or trying to become pregnant should get tested for hepatitis.
Get treated for hepatitis infection
There are treatments for hepatitis. Treating long-lasting hepatitis B or C infection can reduce the amount of the virus in a person, which may lower the risk of liver cancer.
Read Also: Can You Drink Alcohol If You Have Hepatitis C
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
Blood tests are available to determine if you are or have been infected with hepatitis B. It may take 6 months from the time of infection before a blood test can detect antibodies to hepatitis B, so follow-up testing may be required. During this 6-month period, until you know whether you are infected or not, take action to prevent potential infection of other people.
There are also tests that can assess liver damage from hepatitis B. The interpretation of these tests can be complicated and specialist advice is needed, so talk to your doctor.
All pregnant women are tested for hepatitis B. If you are found to have chronic hepatitis B, your doctor can help reduce the risk of transferring the infection to your newborn child.
All About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus causes hepatitis B disease. I know that is an unusual way to describe it, but one needs to contract the virus to get the disease. Its similar to AIDS which is caused by HIV of course, there are AIDS deniers who claim that it is not caused by the virus despite the settled science regarding the link between HIV and AIDS.
HBV is generally transmitted through blood and bodily fluids from an infected person. The signs and symptoms of an acute infection with HBV is associated with general ill-health, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, body aches, mild fever it can resemble a flu infection. However, the infection then progresses to developing jaundice, The illness lasts for a few weeks then, most individuals gradually improve. In some individuals, the infection may be asymptomatic however, they can still pass the HBV to other people.
A few individuals may contract a more severe form of hepatitis B which causes a form of liver disease, called fulminant hepatic failure these people may die as a result.
The most important issue is that a chronic hepatitis B virus infection, whether it is asymptomatic or not, leads to chronic inflammation of the liver. This leads to cirrhosis over a period of several years.
This type of infection increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. However, just to be absolutely clear, even in the absence of cirrhosis, the individual is still at risk from liver cancer.
Of course, this all makes sense to me.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Find Out If You Have Hepatitis C
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Don’t Miss: Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Worldwide, 140 million infections with hepatitis C virus are estimated . The lack of proof-reading capacity of the HCV-encoded polymerase along with high replication rates results in a high mutation rate and genesis of a heterogeneous but closely related quasi-species . HCV is transmitted via parenteral routes, occurs in industrialized countries via intravenous drug abuse or by invasive sexual practices and is rarely transmitted from mother to child. Transmission has been limited by improving hygienic standards. In contrast with HBV, the risk of viral persistence and the development of chronic HCV infection in children are lower than those in adults. HCV has a very different prevalence depending on demographic factors: approximately 1.6% in the USA, less than 0.5% in Northern Europe and up to 3% in rural regions of Romania the most-affected regions are Central and East Asia and North Africa.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant 3.1 Low
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Hbv And Immune Tolerance
With the development of research, an increasing number of researchers have realized that the occurrence and development of tumors is not only due to the proliferation and malignant transformation of the cells themselves, but that the immunosuppressive microenvironment also plays a decisive role. A variety of stromal cells, including immune cells, form a complex regulatory network with tumor cells, which jointly promote the occurrence and development of malignant tumors.
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Spit
New Hepatitis B Virus Paper
As I wrote above, the role of hepatitis B virus in certain forms of liver cancer is clear. But a new paper, published in the peer-reviewed, high impact factor journal, JAMA Network Open, determined that HBV may be linked to several other non-hepatic malignancies such as oropharyngeal, pancreatic, stomach, lymphatic, and colorectal cancers.
The researchers analyzed data in a cohort study, an epidemiological study that ranks near the top of the hierarchy of biomedical research, of nearly 500,000 individuals in China. The researchers identified 15,355 HBV-seropositive individuals in the group. After 4.4 million person-years of follow up, the researchers found the following hazard ratios for cancers in seropositive versus seronegative individuals:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma HR = 15.77, or a 1577% higher risk for this type of cancer in HBV positive individuals.
- Lymphoma HR = 2.10
How To Reduce Your Risk
Dont share needles or other drug-use equipment. If you use intravenous drugs, take part in a needle exchange program.
Dont share personal care articles, such as razors, scissors, nail clippers or toothbrushes, with an infected person.
If you get a tattoo, body piercing or acupuncture, make sure all equipment is clean and sterile. Needles should always be new, not used, and never homemade.
Wear latex gloves whenever you might come into contact with someone elses blood or body fluids.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Reactive
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
- Jaundice .
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
Can Infections Like Ebv & Hiv Cause Cancer
- Some infections increase the risk of cancer, including EBV, HIV, hepatitis, and certain parasites
- In the UK, these infections are rare and cause very few cancer cases
- There are lots of other things you can do to reduce your cancer risk, including stopping smoking
On this page we cover some of the key infections linked to cancer: EBV, HIV, hepatitis, and certain parasites. We have separate pages with information on HPV and H. pylori infections.
There are other infections that can cause cancer, but these dont have a large impact in the UK.
Also Check: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food
Hbv And Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular vesicles , as carriers and transporters, can directly transfer proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids between various cells in the microenvironment and play an important role in regulating the progression of malignant tumors. The level of miRNAs with negative immunologic modulation roles in EVs secreted by HBV-infected liver cells was increased. These EVs can be taken up by innate immune cells, inhibiting cellular function, and helping the virus resist the host immune response.138,139
Overview Of Hepatitis And Liver Cancer
The impact of hepatitis in the United States and abroad is undeniably significant. The virus, which causes illness and even death, can lead to scarring of the liver and liver cancer and affects 400 million people globally. Of those affected around the world, 1.45 million die every year. In fact, hepatitis is the seventh-leading cause of death worldwide, placing it ahead of HIV/AIDS.1
The United States is not immune to the burden of hepatitis. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , recent estimated numbers of new US infections for the three most common types of hepatitis were as follows: 3,000 for hepatitis A, 19,000 for hepatitis B, and 22,000 for hepatitis C.2
A hepatitis virus on its own causes enough undesirable complications to warrant awareness, prevention, and the development of effective treatment. But these measures become all the more pressing in light of the link between hepatitis and liver cancer. In fact, according to the CDC, hepatitis is the leading cause of liver cancer and the most common reason for liver transplantation. Hepatitis B can cause liver cancer even in the absence of cirrhosis whereas hepatitis C usually requires advanced liver disease in order for cancer to develop. In the case of hepatitis C, new treatments that get rid of the virus help lower the risk of cancer.2
Don’t Miss: How Can One Get Hepatitis C