How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
How Is Hepatitis Diagnosed
The first step in diagnosing a hepatitis infection is to receive a medical exam from your doctor. The doctor will perform a physical to look for signs of the illness. All the varieties of hepatitis present with a very similar set of symptoms, which includes:
You may also experience jaundice or a yellowing of the skin and eyes and bowel movements that appear gray. Michael says, Fortunately, most patients are asymptomatic. If you have hepatitis B and its an active condition, meaning youre sick from it, your skin and eyes are going to have a yellow tint.
The doctor will look for these telltale signs and then order blood work to spot the viral load for the type of hepatitis and whether the infection is dormant or active. If the virus is active, you are contagious. The blood test can also determine if the infection is acute or chronic .
If the blood test confirms hepatitis, the doctor may also order an ultrasound of the liver to see if it is inflamed. The ultrasound should also show if the liver is scarred with cirrhosis. You may also have a CT or MRI to look more closely at the liver or signs of liver cancer. This is especially important if you have a family history of the disease.
Finally, in the unusual event that the imaging tests arent shedding light on the situation, the clinician may order a liver biopsy.
What Is Hepatitis C
Caused by the hepatitis C virus , hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus that attacks the liver. There is currently no vaccine available for hepatitis C, but there are tablets that can be prescribed to help treat it. These are called direct-acting antiviral tablets and they are the safest and most effective medication for hepatitis C treatment. They have been found to clear the infection in 90% of people2 .
Unlike hepatitis A and B, it can take years before a person starts to feel unwell with hepatitis C and most people have no symptoms at all. But, as the liver becomes more damaged with time, an individual can feel increasingly sick. Only 1 in every 3 or 4 people will have any symptoms during the first six months of a hepatitis C infection .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Infants Schedule
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B & C
Hepatitis B is caused by coming into contact with bodily fluids of an infected person, where Hepatitis C is transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. Both are viral infections that affect the liver, and it is possible to have both Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C at the same time. Many people with Hepatitis C were born with the condition between 1945 and 1965.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
Don’t Miss: Anti Hepatitis B Virus Drugs
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Children
- All children aged 1223 months
- All children and adolescents 218 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine
People at increased risk for hepatitis A
- International travelers
- Men who have sex with men
- People who use or inject drugs
- People with occupational risk for exposure
- People who anticipate close personal contact with an international adoptee
- People experiencing homelessness
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Anti Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
How Do You Get It
HAV can be present in the stool and blood of someone with the virus. Its mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route, which involves ingesting virus thats present in the stool of someone with hepatitis A.
There are several ways you can get hepatitis A:
- having close person-to-person contact with someone who has hepatitis A, such as:
- taking care of someone whos currently sick
- having sex with someone who has the virus
How To Protect Yourself Against Hepatitis C
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine available for hepatitis C, but you can protect yourself by avoiding behaviors such as sharing needles and syringes. In addition, the CDC recommends people born between 1945 and 1965 get tested for hepatitis C. Testing is also recommended for people who were treated for blood-clotting problems before 1987 and recipients of blood transfusions or donated organs before 1992.
The UNC Liver Center has a clinic in Chapel Hill that specializes in hepatitis B and C, incorporating the latest clinical trials and most up-to-date therapies. Treatment for hepatitis is also available at our locations in Asheville, High Point, Raleigh and Wilmington. To learn more, call 966-2516.
Michael Fried, MD, is the director of the UNC Liver Center and a professor of medicine at the UNC School of Medicine.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Go Away
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
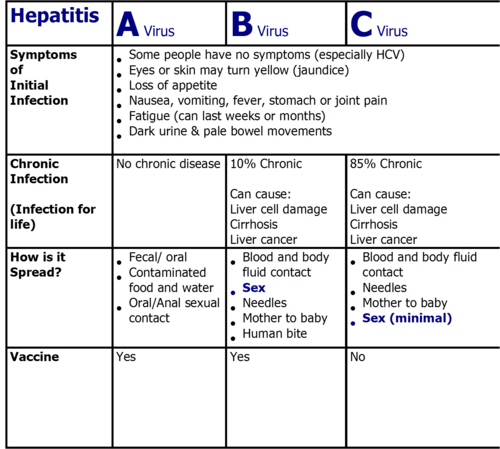
The A B Cs Of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus causes acute inflammation of the liver that almost always gets better on its own, although it can be more serious if you get it when you are older or if you already have liver disease. It is easily spread from person to person, in food and water, and can infect many people at once. For example, if a food handler at a restaurant is infected with hepatitis A, those who eat food prepared by that handler may be infected. Hepatitis A can be prevented by getting vaccinated.
Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus can be both acute and chronic and is spread through blood or other body fluids in various ways. Hepatitis B is very common in Asia and Africa and those who were born or lived in these areas should be checked for hepatitis B. Like hepatitis A, a vaccine is available to prevent HBV infection as long as you have not been previously exposed. Although chronic HBV cannot be cured, there are oral medications available to treat and control the virus.
Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is almost always chronic and spreads mostly by direct blood to blood contact. Although hepatitis A and B can be prevented by vaccination, hepatitis C cannot. However, there are currently oral medications available that are able to cure Hepatitis C in 95% of all cases regardless of prior treatment history.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Is There A Cure For Hepatitis
According to Zappas, there is no technical cure for viral hepatitis, and antibodies will always test positive in a patient who has experienced hepatitis A, B or C. The management of chronic hepatitis B is complex and based on a myriad of factors. Some patients manage their condition with long-term antiviral medications.
However, vaccinations for hepatitis A and B have proven highly effective. Hepatitis A and B vaccinations are recommended and routinely done in infancy, Zappas affirmed. Most people respond to these vaccinations, but post-vaccination testing may be indicated in high-risk patients.
The outlook is even brighter when it comes to hepatitis C: Over the last 10 years, the hepatitis C treatment regimens have evolved, Zappas said. Now, theres nearly a 90% cure rate with certain antiviral medications, which can eradicate the replication of the hepatitis C RNA and therefore abate the damage of the virus on the liver. It is important to note that patients are not immune to hepatitis C after treatment, and can be reinfected and/or contract another strain.
To measure the effects, providers look for a sustained virologic response indicating that the virus remains inactive, which is evaluated between 12 and 24 weeks after beginning the medication.
To reference the work of our faculty online, we ask that you directly quote their work where possible and attribute it to “FACULTY NAME, a professor in the USC Suzanne Dworak-Peck School of Social Work
How Long Before I Have Symptoms

Many people have mild symptoms or no symptoms, which is why hepatitis is sometimes called a âsilentâ disease.
Hepatitis A. The symptoms usually show up 2 to 6 weeks after the virus enters your body. They usually last for less than 2 months, though sometimes you can be sick for as long as 6 months.
Some warning signs that you may have hepatitis A are:
Hepatitis B. The symptoms are the same as hepatitis A, and you usually get them 3 months after you’re infected. They could show up, though, anywhere from 6 weeks to 6 months later.
Sometimes the symptoms are mild and last just a few weeks. For some people, the hep B virus stays in the body and leads to long-term liver problems.
Hepatitis C. The early symptoms are the same as hepatitis A and B, and they usually happen 6 to 7 weeks after the virus gets in your body. But you could notice them anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months later.
For about 25% of people who get hep C, the virus goes away on its own without treatment. In other cases, it sticks around for years. When that happens, your liver might get damaged.
Remember, it’s possible to spread all the types of hepatitis even if you don’t show any signs of being sick.
Also Check: If My Husband Has Hepatitis C Will I Get It
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis
The three most common types of hepatitis in the United States are A, B, and C, but there are five types in total. All of these forms of hepatitis target the livers ability to function. Here are the differences between them:
- Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus, which spreads through the blood and stool of people infected by the virus.
- Hepatitis B is also caused by a virus spread through bodily fluids from an infected person however, it can be prevented through the use of vaccines.
- Hepatitis C is also a viral form of hepatitis. It can be short-term or long-term. As a chronic infection, it can cause life-threatening health issues like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Hepatitis D, also known as delta hepatitis, only occurs concurrently within people who also have the hepatitis B virus.
- Hepatitis E,though not particularly common in the United States, can spread from eating raw or undercooked pork, shellfish, or wild game.
Read Also: Lactulose Dosage For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute infection with hepatitis viruses. Acute infection is a short-term condition, lasting under six months. Chronic infection is a long-term condition, lasting more than six months.
Hepatitis B infection can be either acute or chronic. Most people who get acute hepatitis B dont end up progressing to chronic hepatitis B. By contrast, acute hepatitis C tends to develop into chronic hepatitis C. Approximately 7585 percent of adults newly infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection, according to the CDC . Others clear the infection.
When you get acute hepatitis C you may or may not have symptoms. Most cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic, meaning people dont notice the symptoms. Symptoms are only noticeable in 15 percent of cases of acute hepatitis C.
What Are Some Of The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
It depends on the type of hepatitis, but symptoms common to all viral strains include nausea and vomiting, Zappas said. For hepatitis A, fever, jaundice, malaise, abdominal pain and discolored waste may also present as symptoms.
Arthralgia and joint aches may occur in hepatitis B patients, Zappas said, but unfortunately, many hepatitis B and C patients are asymptomatic, meaning they dont exhibit any symptoms. Due to a high volume of hepatitis cases, the Center for Disease Control recommends screening all baby boomers for hepatitis C.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis The Same As Hiv
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Which Is Worse Hepatitis B Or C
The scary thing about liver conditions like hepatitis is that you may be living with it and not even be aware.
Less than half of the people living with hepatitis B or hepatitis C are diagnosed. If you are one of these people living with an undetected case of hepatitis, you may be at risk for developing liver failure or liver cancer and transmitting the illness to other people.
What are the most common hepatitis infections? Is hepatitis B worse than hepatitis C? How is hepatitis detected and treated? Michael D. Cook, certified physician assistant at Gastroenterology Associates of Southwest Florida answers these questions and can help you understand the risks of hepatitis.
You May Like: How Long Can You Have Hepatitis C Without Knowing
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.