Blood Testing Odenton Maryland
A blood test performed in Odenton, MD is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse.
A basic metabolic panel measures sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate, blood urea nitrogen , magnesium, creatinine, glucose, and sometimes calcium. Tests that focus on cholesterol levels can determine LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, as well as triglyceride levels.
Some tests, such as those that measure glucose or a lipid profile, require fasting eight to twelve hours prior to the drawing of the blood sample.
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Donât Miss: What Is Hepatic Metastatic Disease
Std Testing Odenton Maryland
Our local Odenton, Maryland STD testing centers provide multiple STD tests for individuals who may have been exposed to or showing symptoms of an STD. Millions of Americans have some form of an STD and our testing is provided in a confidential manner. STD tests may be ordered for one specific type of test or you may order a multiple panel test which includes several STD tests. STD stands for Sexually Transmitted Disease, also known as STI or Sexually Transmitted Infection, meaning that these diseases are most often, but not exclusively, spread by sexual intercourse.
STDs do not always cause symptoms, or they may only cause mild symptoms. This makes it very possible to have an infection and not know it. Therefore, if you are sexually active it is important to get tested at least once a year.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Walmart
Is It Possible To Prevent Hepatitis
Hepatitis prevention is very much a possibility with the right strategies. A vaccine is available for hepatitis A. Healthcare providers recommend this vaccine for all people who are at high risk of exposure to the virus. Children- one year and above, should take this vaccine. Prevention of hepatitis A is possible with good hygiene and sanitation. Washing hands especially after using the toilet and before consumption of food can help with cutting hepatitis A transmission. Hepatitis B vaccine has become the norm in developed nations and most new-borns are given these shots. The hepatitis B shots are recommended for children and adolescents as well as adults in high-risk groups. Hepatitis C vaccine is not developed yet, and efforts are in the process to have a vaccine for this infection. Prevention of hepatitis C is possible by avoiding contact or exposure to blood and bodily fluids. Further, avoiding the sharing of needles or other instruments to inject drugs can cut the rate of transmission of this disease.
Hepatitis B Panel Blood Test
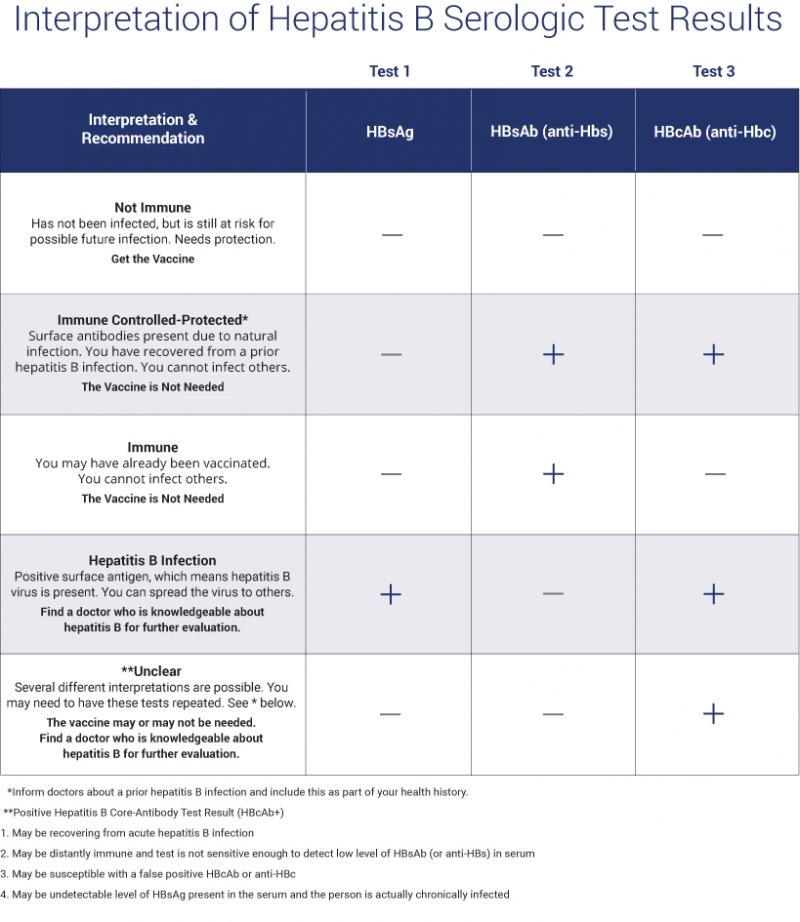
The Hepatitis B Panel is a series of blood tests used to detect current or past infections with the Hepatitis B virus. It can also be used to verify the status of immunity to Hepatitis B. The three tests included in this panel are the Surface Antibody, Surface Antigen, and Core Antibody.
Hep B is a viral liver infection which is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Hepatitis B infections often show no symptoms but when symptoms do occur they are often described as flu-like. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, joint pain, fatigue, jaundice, and dark colored urine. Chronic Hep B infections can cause serious health complications such as Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of Hepatitis B, this three part panel covers many aspects regarding the timeline of a possible infection.
- The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody looks for clinical recovery or subsequent natural or vaccinated immunity to Hepatitis B. The results are quantitative.
- The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is the earliest indicator of the presence of acute infection.
- The Hepatitis B Core Antibody is used in conjunction with the other Hepatitis B tests to assess the stage of Hepatitis B infection.
This panel is typically ordered by people who are experiencing symptoms, believe they may have been exposed to Hep B, or wish to determine their current state of immunity.
You May Like: How Do Doctors Test For Hepatitis C
How It Is Done
The health professional taking a sample of your blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Put pressure on the site and then put on a bandage.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
When Is It Ordered
The CDC, the Infectious Diseases Society of America , the American Association of the Study of Liver Diseases , and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend screening with an HCV antibody test at least once in your lifetime when you are 18 years old or older . The CDC also recommends HCV screening for women with each pregnancy or for anyone who requests it.
One-time screening is recommended regardless of age if you:
- Have ever injected illegal drugs
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992*
- Have received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- Were ever on long-term dialysis
- Are a child born to HCV-positive women
- Have been exposed to the blood of someone with hepatitis C
- Are a healthcare, emergency medicine, or public safety worker who had needlesticks, sharps, or mucosal exposure to HCV-positive blood
- Have evidence of chronic liver disease
- Have HIVabout 21% of those with HIV are also infected with HCV .
*The blood supply has been monitored in the U.S. since 1992, and any units of blood that test positive for HCV are rejected for use in another person. The current risk of HCV infection from transfused blood is about one case per two million transfused units.
Screening at regular intervals is recommended if you have ongoing risk of HCV infection, such as current injection drug use and sharing needles or syringes.
- Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting
- Yellowing of eyes and skin
An HCV RNA test is ordered when:
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contact Hepatitis B
Hep B Blood Test Results Explained
The Hep B blood test is used in several different ways. It may be used to detect antibodies that are produced when the hepatitis B virus is present within the body. It may also be used to detect the antigens that the virus can produce. It can also be used to detect the actual DNA of the virus. All of these tests are not generally needed for every patient, but can provide useful medical information to enhance the effectiveness of a treatment plan.
The primary use of the Hep B blood test is to determine if hepatitis-like symptoms are due to an HBV infection. It may be ordered with HAV and HCV blood tests to fully eliminate hepatitis as the health issue. It can also be used to diagnose a chronic HBV infection, monitor the implementation of a treatment plan, or detect exposure to the virus when it becomes reactivated.
The test results from the HBV blood test are conclusive. It can be used as a screening tool for those who are not infected or to determine if someone may be a carrier for the virus.
What Do The Results Mean
Labs report hepatitis panel results in different ways:
- A negative or normal result means you probably don’t have a hepatitis infection.
- A positive or abnormal result may mean you have a hepatitis infection now or had an infection in the past.
For hepatitis A and B, your test results will say whether you have a current or past infection, or if you have immunity because you had a vaccination.
If your test shows that you have signs of hepatitis C, you will need another test to find out if you are infected now, or if you had an infection in the past. There is no vaccination for hepatitis C.
You may need more tests to confirm a diagnosis and to see how hepatitis has affected your liver. If you have questions about your results, talk with your provider.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Read Also: Natural Remedies For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
Some groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C, including:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991 or blood products before 1986 in the UK
- UK recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high-risk areas include Africa, the Middle East and central Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners, family members and close contacts of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturerâs instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis B And C Transmitted
Recommended Reading: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
Testing For Hepatitis C
Two tests need to be done to discover if you have hepatitis C:
- Antibody test: Which establishes whether you have ever been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
- PCR test: Which establishes whether the virus is still active and needs treating.
The two tests can often be done from one sample of blood which means you may only need to provide the sample once. Both tests can then be done on your sample at the laboratory. However, some services will perform one test and then call you back for a further blood sample to perform the second test.
Antibody test
A hepatitis C antibody test is the first test undertaken. This is to determine whether you have ever been exposed to the hepatitis C virus. It works by testing for the presence of antibodies to the virus generated by your immune system. If you receive a negative hepatitis C antibody test but have been experiencing symptoms or have been recently exposed to hepatitis C, then you are likely to be advised to have a second test.
It is important to remember that there is a ‘window period’. This is the short period of time when your immune system may not have had time to produce antibodies. It usually takes between six and twelve weeks for these antibodies to develop. However, in a few people it can take up to six months. So if you have the test within this window period and the result is negative, it does not necessarily mean that you don’t have the virus.
PCR test
Can Hepatitis Patients Spread The Infection To Others
Patients can spread hepatitis infection and the spread depends on the type and stage of the hepatitis infection. Those suffering from viral hepatitis can easily spread the infection even while being asymptomatic. Those with hepatitis A can spread the infection from the time they are infected. Those with hepatitis B are contagious as long as the virus is present in the blood. Those with hepatitis C infection are contagious and can transmit the infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Shot Side Effects
What Is Being Tested
Hepatitis C is a virus that causes an infection of the liver that is marked by liver inflammation and damage. Hepatitis C tests are a group of tests that are performed to diagnose hepatitis C infection and to guide and monitor treatment of the infection.
Hepatitis C tests include:
Hepatitis C is one of five viruses identified so far, including A, B, D, and E, that are known to cause hepatitis.
HCV is spread when contaminated blood enters the body, primarily though sharing needles and syringes during IV drug use. HCV is spread less commonly by sharing personal items contaminated with blood , through sex with an infected person, needlestick injuries to healthcare workers, unregulated tattooing, and from mother to baby during pregnancy and childbirth. Before tests for HCV became available in the 1990s, HCV was often transmitted by blood transfusions. Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C.
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis B From Saliva
Hepatitis C Virus Test Results
The Hepatitis C virus is considered cured if the virus is not detected in your blood when measured with a blood test 3 months after treatment is completed. This is called a sustained virologic response and data suggest that you will stay virus free indefinitely.
Hepatitis C tests are a group of tests that are performed to detect, diagnose, and monitor the treatment of a hepatitis C viral infection. The most common test for HCV looks for antibodies in the blood that are produced in response to an HCVinfection.
Hepatitis C is spread through contact with an infected persons blood which may be present because of genital sores or cuts or menstruation.HCV has been detected with greater-than-average frequency among people who have a history of sexual promiscuity which can be defined as a history of a sexually
Hepatitis A Test Results
A total antibody test detects both IgM and IgG antibodies but does not distinguish between them. If the total antibody test or hepatitis A IgG result is positive and someone has never been vaccinated against HAV, then the person has had past exposure to the virus.
Hepatitis A infection is typically diagnosed through blood tests. Fortunately, blood tests are widely available to accurately diagnose hepatitis A, including tests for antibodies, or the affected persons immune response to hepatitis A proteins. The IgG antibodies are present for life, indicating immunity.
Treatment generally involves supportive care, with specific complications treated as appropriate. Liver transplantation, in selected cases, is an option if the patient has fulminant hepatic failure . Patients at risk of developing acute hepatitis A virus infection should undergo immunization for the virus.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C Screening Test
Read Also: Fatty Liver And Hepatitis B