Fatty Liver In Hepatitis B And Its Clinical Outcomes
Many cross-sectional studies have been conducted to examine the impact of the both hepatitis B and fatty liver on the liver and the clinical impact.
In his study from Taiwan, Lin et al. reported hepatitis B and fatty liver had a synergistic effect. Fatty liver was defined based on an ultrasound in a cohort of 5406 patients and liver disease was defined by an ALT more than 40 IU/mL. This was a cross-sectional, observational study . However, in a larger study of a general population of 33,439
Clinical Characteristics And Treatment Response In Different Degrees Of Hepatic Steatosis
The comparison of baseline clinical characteristics and treatment response among 102 steatotic patients with different degrees of histological steatosis is shown in Supplementary Table . As expected, patients with mild steatosis had significantly lower BMI than those with moderate steatosis and those with severe steatosis . The patients with severe steatosis had significantly lower mean HBV DNA level than those with mild steatosis , while the difference was not significant as compared to the mean HBV DNA level of those with moderate steatosis. The other clinical characteristics were comparable among these three groups. HBeAg seroclearance was achieved in 37 with mild steatosis, 14 with moderate steatosis and 5 with severe steatosis . The mean age at HBeAg seroclearance was 47.3, 42.6 and 40.8years and the median time to HBeAg seroclearance was 17.7, 15.2 and 16months , respectively in the corresponding subgroups. The VR rate was similar among three groups .
Diabetes Obesity And Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Several studies have shown a strong link between type II diabetes and liver cancer. Build-up of fat in the liver is common among persons with type II diabetes and may increase the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. This risk is higher in patients who also have other risk factors, such as heavy alcohol consumption or chronic viral hepatitis infections.
Obesity, which can contribute to fatty liver disease and cirrhosis, is a major risk factor for the development of type II diabetes, which, in turn, can increase the chance of developing liver cancer. It is unclear whether obesity directly causes liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis B and C infections are most strongly associated with liver cancer, but diabetes and obesity are major health problems that are becoming increasingly important risk factors for liver cancer.
In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, excess fat builds up in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol. The most severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis . People with NASH have fat in their liver, along with inflammation and liver damage. They usually have no symptoms and do not know that they have a liver problem. NASH can be severe and can lead to cirrhosis. NASH is estimated to be the third most common liver disorder in North America and the most common in Australia and New Zealand.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Get It
Laboratory Measurements And Definitions Of Treatment Response
The baseline clinical characteristics collected from the electronic medical records included aspartate aminotransferase , ALT, total bilirubin, platelet count, HBeAg, anti-HBe, anti-HCV, anti-HDV, HBV genotype, HBV DNA and quantitative HBsAg . Stored serums were retrieved for assays of HBV genotype, HBV DNA or qHBsAg for any incomplete data. HBV genotype was determined by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism of the surface gene of HBV. Serum HBV DNA was assayed by COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® HBV Test, version 2.0 . Serum HBsAg levels were quantified using the Roche Elecsys HBsAg II quant assay according to the manufacturers instructions. HBeAg, anti-HBe, anti-HCV and anti-HDV were tested with enzyme immunoassay kit .
What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis B
A majority of adults develop symptoms from acute hepatitis B virus infection however, young children often do not. Symptoms, when they occur, may include:
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Abdominal pain near the liver
On average, symptoms appear three months after exposure to the virus, but they can appear anywhere between six weeks and six months. Symptoms usually last for a few weeks, but can last up to six months. Most adults infected with hepatitis B virus recover fully even if their signs and symptoms are severe.
Some of the people who go on to develop chronic hepatitis B virus have ongoing symptoms similar to acute hepatitis B virus, but most people with chronic Hepatitis B remain symptom free for 20 or 30 years.
If you think you have signs of symptoms of Hepatitis B, contact your doctor.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Causes Symptoms And Treatment
What Is The Difference Between Hepatomegaly And Fatty Liver
September 30, 2022 Posted by Hasa
The key differencebetween hepatomegaly and fatty liver is that hepatomegaly is a medical condition due to enlargement of the liver, while fatty liver is a medical condition due to the storage of extra fat in the liver.
Liver is the largest solid organ in the human body. It performs numerous vital functions, including the removal of toxins from the blood supply of the body, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and regulating blood clotting. Moreover, it also performs hundreds of other vital functions that are very important for the survival of humans. Hepatomegaly and fatty liver are two medical conditions that affect the structure and function of the liver.
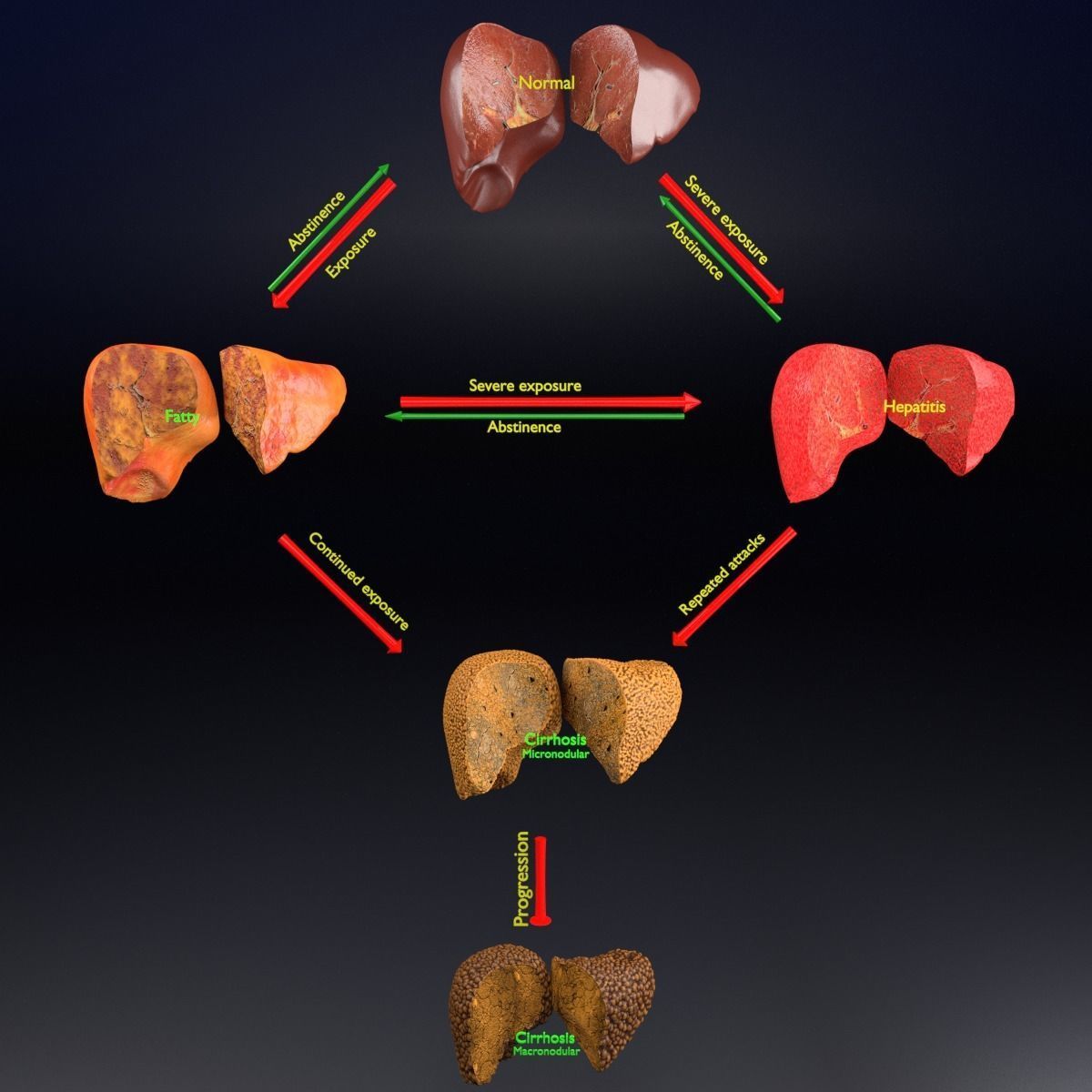
What Is Fatty Liver Disease
As the name implies, fatty liver disease occurs when fat deposits build up in your liver. The fat in the liver can damage it, causing inflammation and scarring, explains Rena Fox, M.D., a professor of general internal medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and a UCSF Health hepatitis specialist. Although doctors still arent sure exactly what causes it, NAFLD is linked to obesity, insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and high triglycerides levels.
There are different types of fatty liver disease, but NAFLD is the most common, affecting 30% to 40% of adults in the United States, according to the National Institutes of Health . While some types of fatty liver disease are linked to heavy alcohol use, people with NAFLD are not over-drinkers.
One of the challenging things about this disease is that it can be hard to detect, since it often has no obvious symptoms until the liver damage is already extensive. When someone is at a very advanced stage, they may have some pain in the upper-right part of the abdomen, and they may feel tired, says Dr. Fox. At a very late stage, they could have fluid in the abdomen, and they could develop yellowing of the eyes and skin. We want to help patients avoid getting to this point.
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis B
Evaluation Of Advanced Fibrosis Or Cirrhosis In Patients With Dual Pathology
In study by Fong et al., the FIB-4 was not statistically different in the groups with or without fibrosis.
Although liver biopsy is the gold standard for assessment of fibrosis and cirrhosis, it carries risk of complications due to its invasive nature. Scoring system such as Fibrosis-4 , NAFLD fibrosis score and AST to Platelet Ratio Index were developed and validated for detection of advanced fibrosis in patients with CHB, Chronic Hepatitis C and NAFLD. However, none of these scores were studied in patient with dual pathology. As ALT is frequency raised in these group of patients, the specificities of these scores may be affected.
Further studies are required for validation.
Subgroup And Sensitivity Analyses
The results of the subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses are shown in Table âTable2.2. When the analysis was stratified by study quality, study design and adjustment for cholesterol level or diabetes in the models, there was a significant difference between subgroups .2). For example, HBV infection was significantly associated with the risk of NAFLD in cohort and cross-sectional studies , but not in case-control studies .2). According to the sensitivity analyses, despite excluded the study using MRS, the results of the relationship between HBV infection and NAFLD remained stable . Additionally, the overall results remained consistent when the pooling model was changed .
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is when fat builds up in the liver of people who dont drink a lot of alcohol.
If you have excess fat in your liver and no history of heavy alcohol use, you may receive a diagnosis of NAFLD. If theres no inflammation or other complications, the condition is known as simple NAFLD.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is a type of NAFLD. Its when buildup of excess fat in the liver is accompanied by inflammation. Your doctor may diagnose NASH if:
- you have excess fat in your liver
- your liver is inflamed
- you have no history of heavy alcohol use
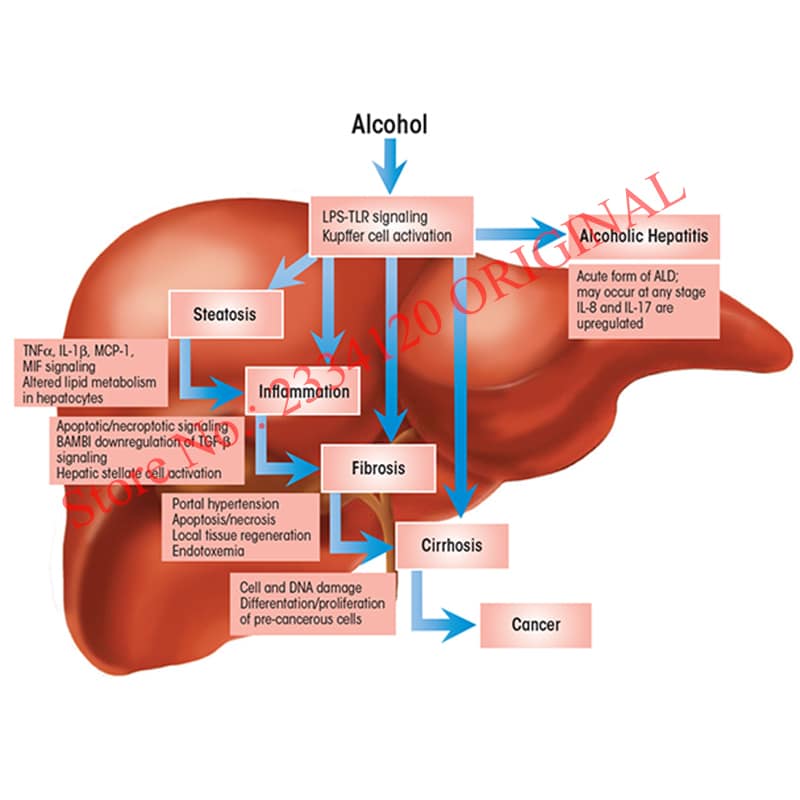
When left untreated, NASH can cause liver fibrosis. In severe cases, this can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Association Between Steatohepatitis And Severity Of Liver Fibrosis
The proportion of different fibrosis stages between NAFL and NASH subgroups was different . Percentage of patients with significant fibrosis or severe fibrosis was significantly higher in NASH subgroups than those in NAFL subgroups .
Factors associated with significant fibrosis or severe fibrosis are shown in Table 2. The presence of NASH, overweight, age, blood platelets count, ALT, hepatitis B surface antigen level, HBeAg status, and serum HBV DNA level were significantly associated with the presence of significant fibrosis . Among these factors, the presence of NASH, overweight, age, and blood platelets count were independent predictors for significant fibrosis under a multivariable analysis. Using the same analytic strategy, we identified the presence of NASH, diabetes, overweight, blood platelets count, albumin, and HBV DNA level as independent factors associated with severe fibrosis .
Table 2 Factors associated with significant fibrosis and severe fibrosis among patients with chronic HBV infection.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Saliva
What Are The Risk Factors For Liver Disease
The two most common forms of liver disease in the United States right now are both forms of fatty liver disease alcohol-related liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, according to Dr. Lindenmeyer. As its name suggests, alcohol-related liver disease is linked with heavy alcohol ingestion, she says, while nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is linked with metabolic syndrome.
Risk factors for liver disease include the following:
- Metabolic syndrome, which is a term for a group of risk factors including high triglycerides, high levels of blood sugar, low levels of HDL , high blood pressure, and carrying extra weight around your midsection
- Excessive alcohol use
- Chronic liver infections such chronic hepatitis B or C
- Genetic or acquired medical conditions that make liver disease more likely
- Autoimmune-associated disorders of the liver
Summary Hepatomegaly Vs Fatty Liver
The liver is the largest solid organ in the human body, doing various important functions. Hepatomegaly and fatty liver are two medical conditions that cause problems in the liver. Hepatomegaly refers to the enlargement of the liver, while fatty liver refers to the storage of extra fat in the liver. So, this summarizes the difference between hepatomegaly and fatty liver.
Reference:
You May Like: How To Catch Hepatitis B And C
How Is Liver Disease Diagnosed
Screening for liver disease typically starts with blood tests that check what is called liver biochemistries, or tests of the liver function, says Lindenmeyer.
If those are abnormal, then frequently we follow that up with an imaging study of the liver, whether it be an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI, she says. A specialized ultrasound device called FibroScan can give an estimate of the amount of scarring and fatty buildup in the liver.
Its important to note that sometimes people who have liver disease may have no evidence of abnormalities in their blood, says Lindenmeyer.
In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to see how much scarring is in the liver.
Given that hepatitis C is often asymptomatic, screening baby boomers is critical for early diagnosis, says Lindenmeyer. We have excellent medications for hepatitis C that have excellent cure rates. Its something that can halt the progression of liver disease and potentially even improve the liver once its been treated, she says.
People who have a history of alcohol abuse or are known to drink alcohol excessively should have their liver function tested, along with those with a history of liver disease, as well as people at risk for having a genetically inherited form of liver disease, says Lindenmeyer.
Who Is At Risk Of Having Hepatitis B
- Anyone who has come in direct contact with hepatitis B virus-infected bodily fluids is at risk.
- Were born to an hepatitis B virus-infected mother
- Work or live in a place where you can be exposed to infected blood, such as a healthcare institution or correctional facility
- Have ever lived with a person infected with chronic hepatitis B virus
- Have ever had unprotected sex with an infected person
- Have ever had multiple sexual partners
- Have ever had a sexually transmitted disease
- Are a man who has sex with men
- Have your blood filtered by a machine because your kidneys arent working
- Have ever traveled to or are born in countries where hepatitis B virus is common, including places in Africa, Central and Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe
Also Check: Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Development Of Hcc In Patients With Fatty Liver And Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B infection can cause hepatocellular carcinoma, and this can develop in patients with hepatitis B without cirrhosis, thus emphasising the need of continuous surveillance in patients with hepatitis B after a certain age . One of the key questions that come to cliniciansâ minds is whether the risk of getting HCC increases if the two factors coexist.
Yu et al. found in a population-based study of 2903 patients over a follow-up period of 14.3 years, that a high body mass index
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Fatty Liver Disease
Many people have trouble understanding the relationship between chronic hepatitis B infection and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease . While research studies are ongoing and the association between hepatitis B and NAFLD is indeed complex, a chronic hepatitis B infection does not cause NAFLD. It is important to understand both diseases independently of one another before studying the correlation between the two.
Hepatitis B and fatty liver disease both can damage the liver. This is why it is important to understand the role of the liver in maintaining overall health and well-being. The liver is an essential organ in your body and is responsible for supporting digestion and regulating nutrients. It plays a crucial role in removing toxic substances from your body.
Worldwide, almost 300 million people are living with hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is transmitted through direct contact with infected blood, unprotected sex with an infected individual, use of contaminated medical or injection equipment, and most commonly, from an infected mother to her newborn during childbirth. A chronic hepatitis B infection can damage the liver and may progress to more serious conditions like cirrhosis, fibrosis, and even liver cancer. While hepatitis B is a major public health problem, it can be prevented through a safe and effective vaccine. And even though hepatitis B is a serious disease, most people live healthy and productive lives with effective management and treatment.
Read Also: What Type Of Pathogen Is Hepatitis B
Correlation Between Histological Changes And Severity Of Liver Fibrosis
Based on the significant association of significant/severe fibrosis with the presence of NASH, we further compared the distribution of fibrosis stages based on Scheuers scoring system between patients with and without steatosis, lobular inflammation, or cytological ballooning and found that the proportion of significant fibrosis was significantly different between patient with or without lobular inflammation and patients with or without cytological ballooning . The proportion of significant fibrosis showed no difference between patients with or without steatosis . According to spearman correlation analyses, both the degree of lobular inflammation and degree of cytological ballooning were significantly associated with fibrosis stage . The presence of steatosis, presence of moderate-to-severe steatosis, and degree of steatosis were not related to the fibrosis stage .
Table 3 Spearmans correlation analysis between three histological changes and severity of fibrosis.
Difference Analysis Of Serum Metabolic Profiles
The score plot of OPLS of serum was depicted in Figure 2 where it could be found that DHHB, NDHHB, DHFL, and NDHFL groups were clearly separated from the control group. Then the most meaningful characteristics of every group were screened out by OPLS loading analysis. The information of models was summarized in Table 7. The detailed information of serum differential metabolites was also summarized in SI, and the brief information was listed in Table 5. Furthermore, the corresponding pathways of each group were analyzed by KEGG and MBRole as follows, based on the selected differential metabolites .
OPLS score plot of four ZHENGs compared to healthy control group by serum metabolic profiles. OPLS score plot between control and DHHB. OPLS score plot between control and NDHHB. OPLS score plot between control and DHFL. OPLS score plot between control and NDHFL.
Read Also: What Are The Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
Eligibility Criteria For Study Selection
The eligibility criteria were as follows: a cross-sectional, case control or cohort study design HBV as the exposure factor and NAFLD as the outcome and odds ratio /risk ratio values and corresponding 95% confidence intervals in the HBV-positive and HBV-negative groups described or sufficient information to calculate them. If two studies reported the same data, we selected the study with the larger sample.
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Problems Faced By Antiviral Therapy

-
State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, Hepatology Unit, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
Research funding:
National Science and Technology Major Project of China 2017ZX10202202
National Natural Science Foundation of China 82070614
National Natural Science Foundation of China 81871668
Local Innovative and Research Teams Project of Guangdong Pearl River Talents Program 2017BT01S131
- Received Date: 2021-06-08
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Vaccine Side Effects