But Even If You’ve Been Cured It Can Have Lifelong Health Implications
“Hepatitis C is a lot more than just a liver disease,” Reau says. “It has been associated with many medical conditions, such as an increased risk of developing diabetes, kidney disease and cancer.”
While curing hepatitis C significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, like liver failure, liver cancer and the need for transplantation, it doesn’t completely eliminate the health risks associated with the disease.
“Hep C is linked to scarring of the liver or cirrhosis and the more scar tissue that develops, the greater the likelihood of complications,” Reau says. “If there is a lot of scarring, you will need lifelong monitoring.”
Reau also recommends leading a healthy lifestyle to help prevent re-infection and further liver damage: Limit alcohol consumption, control your weight, avoid high-risk activities and manage diabetes if you have it.
The Evolution Of Hepatitis C Treatment
Hepatitis C has been around for a long time. Even before the development of these new treatments, between 15 to 25 percent of individuals infected with HCV did not become chronically infected. Their bodies were able to clear the virus on their own. However, until relatively recently there were few effective treatment options for hepatitis C.
Historically the major treatment regimen was a long course of pegylated interferon and ribavirin. However, these treatments have significant problems. They show an only moderate ability to get rid of the virus and they have significant side effects. For example, one study found that as many as a quarter of people taking interferon developed major depressive episodes due to the treatment regimen.
In addition, those drugs were contraindicated in individuals with advanced liver or kidney disease. That meant that many people with hepatitis C werent even eligible to take them.
Interferon and ribavirin were also least effective against the most common types of hepatitis C. Genotype 1 was historically difficult to treat with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. The treatment regimen worked slightly better with genotypes 2 and 3, but those types were also less common.
The combination of poor efficacy and high intolerance were driving forces for the development of interferon-free methods of hepatitis C treatment. These drugs are known as direct acting antivirals . Its DAAs that have led to hepatitis C being considered curable.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Read Also: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis B
Treating Hepatitis A B C: Id Care Infectious Disease Doctors
According to Dr. Aslam, ID Cares unique experience treating chronic illnesses like HIV is what sets us apart. We identify the risk factors, diagnose the strains, and do a lot of community teaching where our patients live. Some of the hepatitis patients were trying to help are IV drug users. Because of our experience treating people with HIV, we have a lot of community and healthcare connections, and we can help patients get into detox and recovery programs to break habits that raise the risk for hepatitis B and C.
Sometimes, the complex antiviral medicines used for hepatitis B and C can interact with other drugs, and some patients are resistant to their effects. Interestingly, some people who have hepatitis B or C along with HIV may be prescribed hepatitis medications that can affect their HIV as well. If you have both the diseases, a combination treatment is best, otherwise, patients can develop resistance, warned Dr. Aslam, adding that close monitoring is key in these cases.
Difficult, multi-disease scenarios do happen, and according to Dr. Aslam, ID Care is better trained, equipped, and experienced to detect and address the complications, drug interactions, and side issues like drug dependence, depression, and substance abuse that can interfere with successful treatment. We provide a uniquely high level of care to our patients with viral hepatitis and related problems.
Abcs Of Hepatitis: From Chronic To Curable What You Need To Know
This article was medically reviewed by Dr. Fazila Aslam.
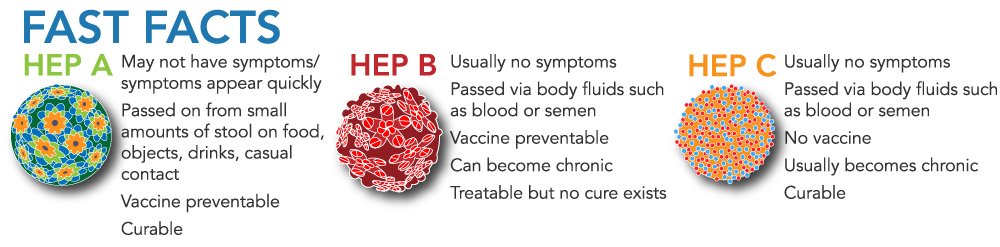
Though not uncommon, viral hepatitis is a serious illness that is often less understood than other infectious diseases. Hepatitis A, B, and C are types of viral hepatitis and share some common symptoms, but they infect different patient populations. The different strains are caused by different viruses and are transmitted and treated in different ways. Each hepatitis variant must be identified by a blood test so it can be properly treated, and viral hepatitis should never be ignored as it can cause serious health consequences. Learn more about the ABCs of Hepatitis in this article so this infectious disease is more easily understood and identified early.
Also Check: How Do You Contract Hepatitis A B& c
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Acute V Chronic Hepatitis C
Acute hepatitis C is used to describe a new infection it typically occurs within six months of exposure to the virus.
Chronic hepatitis C may last throughout a patients entire lifetime. This infection could result in scarring, cancer, or damage of the liver. In some cases, chronic hepatitis C may even result in death.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Curable Or Not
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B . Hepatitis B virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they 15):
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they:
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have diabetes
- have hepatitis C
- have lived in or travel often to parts of the world where hepatitis B is common External link
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact 16).
Hepatitis C: Common Deadly And Curable
18 September 2017 By Rich Hutchinson, Pedro Valencia, Shana Topp, and Thomas Eisenhart
Consider some sobering and little-known facts: Hepatitis C is the most common and deadly infectious disease in the United States, beating out HIV, tuberculosis, and 57 other illnesses tracked by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . More than 4 million Americans are infectedmost of them baby boomers but only 50% have been diagnosed. The remainder are unaware that they have contracted the virus, thus putting themselves and others at risk. And while mortality rates for most infectious diseases are decreasing, deaths from HCV are rising over time. According to the CDC, nearly 20,000 deaths were reported in 2014, up from just 11,000 in 2003.
Perhaps worst of all is that although HCV is common and deadly, about 95% of the time it can be cured with antiviral treatments. Media attention has focused on the high cost of these therapies, but other roadblocks are even more problematic. For instance, there is a lack of awareness about the disease, its risk factors, and available treatments not only among patients and members of the general populationbut also among nurses, physicians, and other health care providers.
You May Like: Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Go Away
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is spread through exposure to blood from an infected person. In any case, in which the blood of an infected person enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person, the previously uninfected person is likely to become infected.
There are a few common scenarios in which this may happen:
- Sharing Drug Paraphernalia. When a drug user inserts a needle into his or her arm for example, when taking heroin the needle becomes contaminated with the userâs blood. If another user inserts that same needle into their arm, any contaminants in the first userâs arm are transferred to the second user.
- Sharing Toiletries. Although transferring hepatitis C is less likely in these cases, sharing razor blades and toothbrushes can lead to infection for the same reason that sharing needles causes an infection traces of blood passing from one person to another.
- Unsafe Sex. Having sex without a condom, particularly in sexual scenarios where blood is more likely to be drawn like anal sex, is another potential transfer case for hepatitis C.
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
Don’t Miss: How You Get Hepatitis A
What Are The Common Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Although the most common types of viral hepatitis are HAV, HBV, and HCV, some clinicians had previously considered the acute and chronic phases of hepatic infections as types of viral hepatitis. HAV was considered to be acute viral hepatitis because the HAV infections seldom caused permanent liver damage that led to hepatic failure. HBV and HCV produced chronic viral hepatitis. However, these terms are outdated and not currently used as frequently because all of the viruses that cause hepatitis may have acute phase symptoms . Prevention techniques and vaccinations have markedly reduced the current incidence of common viral hepatitis infections however, there remains a population of about 1 to 2 million people in the U.S. with chronic HBV, and about 3.5 million with chronic HCV according to the CDC. Statistics are incomplete for determining how many new infections occur each year the CDC documented infections but then goes on to estimate the actual numbers by further estimating the number of unreported infections .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis C
Types D, E, and G Hepatitis
Individuals who already have chronic HBV infection can acquire HDV infection at the same time as they acquire the HBV infection, or at a later time. Those with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HDV develop cirrhosis rapidly. Moreover, the combination of HDV and HBV virus infection is very difficult to treat.
- People with hemophilia who receive blood clotting factors
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Recommended Reading: What’s Hepatitis B Vaccine
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Preventing The Spread Of Viral Hepatitis
Having good personal health habits is the key to preventing the spread of many diseases, including hepatitis. Other preventive measures include:
-
Getting vaccines. A hepatitis B vaccine is given to newborns, babies, and toddlers. It is as part of the routine vaccine schedule. A hepatitis A vaccine is available for people at risk for the disease while traveling. There are no vaccines for hepatitis C, D, or E at this time.
-
Blood transfusion screening. Blood for transfusions is routinely screened for hepatitis B and C to reduce the risk of infection.
-
Antibody treatment. If a person has been exposed to hepatitis, an antibody treatment can be given to help protect him or her from the disease.
-
Safe sex. Practice safe sex, including using condoms.
-
Safe needle use. Dont share or reuse needles, syringes, or other equipment.
-
Not sharing personal items. Dont use personal items that may have even a small amount of an infected persons blood. These include nail clippers, toothbrushes, glucose monitors, or razors.
-
Getting tattoos safely. If you plan on getting a tattoo, use a licensed facility only. Dont get tattoos in an unsafe setting.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B And C Symptoms
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis A Spread
How Do You Get Hepatitis A
The main way you get hepatitis A is when you eat or drink something that has the hep A virus in it. A lot of times this happens in a restaurant. If an infected worker there doesn’t wash their hands well after using the bathroom, and then touches food, they could pass the disease to you.
Food or drinks you buy at the supermarket can sometimes cause the disease, too. The ones most likely to get contaminated are:
- Shellfish
- Ice and water
You could catch or spread it if you’re taking care of a baby and you don’t wash your hands after changing their diaper. This can happen, for example, at a day care center.
Another way you can get hep A is when you have sex with someone who has it.
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Read Also: How Can You Get Hepatitis B