Can Hepatitis Be Treated
Today, hepatitis management is applicable through different medications and the blood product intravenous immunoglobulin for temporary immunity. However, specific antiviral effects like a nucleotide polymerase inhibitor work in slowing down the virus. Although there are famous names like Ledipasvir with sofosbuvir and Pegylated interferon and ribavirin, some of these medications arent prescribed anymore. However, modern medical technology is changing chronic liver diseases using oral tablets taken every day for at least two to six months.
Ask your pharmacist or your current liver doctor to know if certain drugs arent verified with FDA or harmful to your health status.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Females
How Is It Spread
The hepatitis C virus is spread by direct contact with blood of an infected person. This can happen through:
- Sharing equipment used to inject drugs
- Blood transfusions and organ transplants prior to 1992 when widespread screening of the blood supply began
- Pregnant women infected with the virus passing it to their babies at birth.
- Sharing personal items, such as a toothbrushes, nail clippers, or razors that have blood on it
- Getting tattoos or body piercings in informal settings or with non-sterile equipment
- Poor infection control in health care facilities and residential care facilities
- Sexual transmission is possible, although rare. Things that increase sexual transmission of hepatitis C include: having a sexually transmitted disease or HIV infection, sex with multiple partners, or rough sex
- The hepatitis C virus is NOT spread by casual contact, such as hugging, or through sneezing, coughing, or sharing food and drinks.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Kidney Problems
Recent Increases In Hepatitis C Infections
Between 2013 and 2020, the reported number of acute HCV infections more than doubled. High rates of new infections were predominantly among young adults aged 20-29 years and aged 30-39 years. The number of cases continues to increase, in 2020 an estimated 66,700 new HCV infections occurred in the United States. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
You May Like: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Symptoms Of An Acute Infection
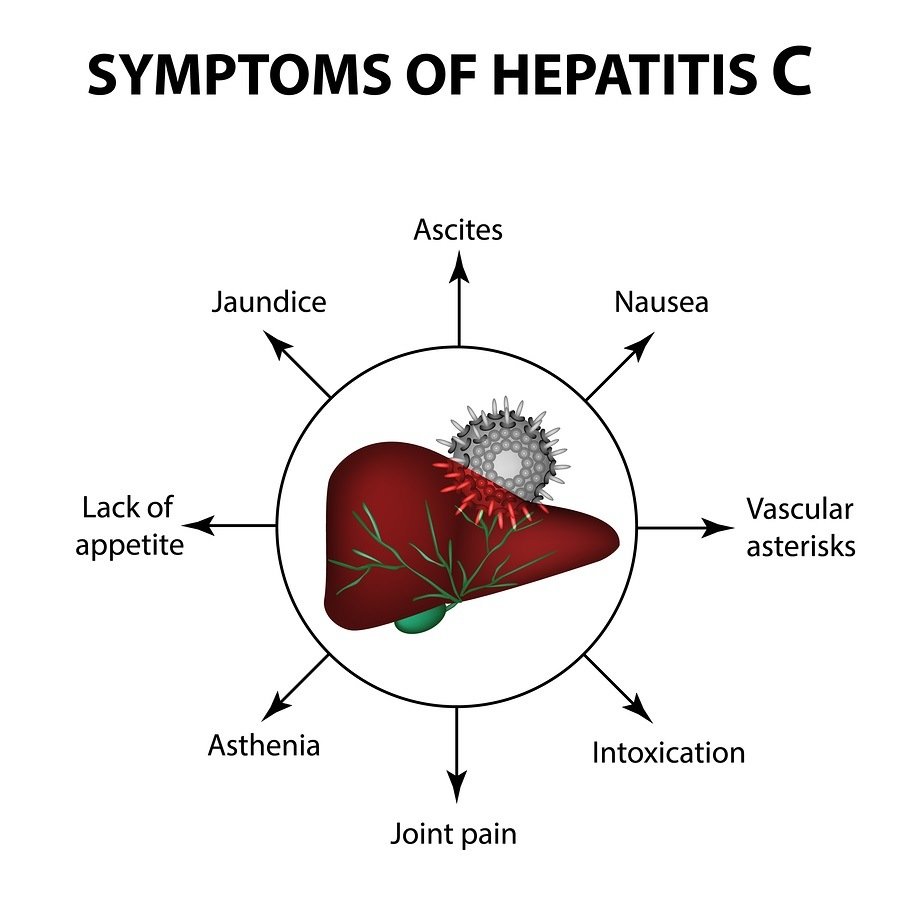
Few people show symptoms during acute infection . These symptoms can include: fatigue tenderness or an aching feeling on the right side of the abdomen decreased appetite perhaps with weight loss flu-like symptoms nausea tendency to bruise or bleed easily jaundice rash dark-coloured urine and light or clay-coloured stools. These symptoms often go away after a short time.
You May Like: What Happens If You Have Hepatitis B
Who Should Have The Hepatitis A Vaccine
People usually advised to have the hepatitis A vaccine include:
- close contacts of someone with hepatitis A
- people planning to travel to or live in parts of the world where hepatitis A is widespread, particularly if levels of sanitation and food hygiene are expected to be poor
- people with any type of long-term liver disease
- men who have sex with other men
- people who inject illegal drugs
- people who may be exposed to hepatitis A through their job this includes sewage workers, staff of institutions where levels of personal hygiene may be poor and people working with monkeys, apes and gorillas
Contact your GP surgery if you think you should have the hepatitis A vaccine or youre not sure whether you need it.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
You May Like: I Think I Have Hepatitis
How Is The Virus Spread
Like hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus is spread when blood of an infected person enters the body of a person who is not infected, such as through sharing needles or “works” when shooting drugs or occupational needle stick injury. The risk of sexual transmission has not been thoroughly studied but appears to be low in long-term, monogamous relationships. There is no evidence that the hepatitis C virus can be transmitted by casual contact such as hugging or shaking hands, through foods, by sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, or by coughing or sneezing. Hepatitis C is not spread by breastmilk.
What Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Look Like
Hepatitis C infection can go through two stages: acute and chronic. In the early, or acute stage, most people dont have symptoms. If they do develop symptoms, these can include:
- flu-like symptoms, tiredness, high temperature and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- jaundice, meaning your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow
While for some people, the infection will clear without treatment, in most cases, acute infection will develop into long-term chronic infection. Chronic infection may not become apparent for a number of years until the liver displays signs of damage. These symptoms can include:
- mental confusion and depression these are specific to hepatitis C
- constantly feeling tired
- feeling bloated
- joint and muscle pain
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
You May Like: How To Get Tested For Hepatitis B
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a contagious disease caused by HCV, which is spread through contact with blood and bodily fluids that contain HCV. This disease damages your liver. There are two types of hepatitis C infection: acute and chronic.
Acute hepatitis C is a short-term viral infection. People with acute hepatitis C carry the infection for a small window of time, often just several months . Most people with the acute form of hepatitis C will experience illness and mild symptoms such as fatigue and vomiting within the first six months after exposure. In many cases, the disease causes no symptoms at all.
Acute hepatitis C may improve or resolve without treatment. It leads to chronic infection in 75 to 85 percent of cases. The chronic form may cause long-term problems in your liver, including liver damage and liver cancer.
HCV is spread through direct contact with blood or certain bodily fluids that contain HCV. Its safe to engage in the following activities without worry of transmission:
- light, clay-colored bowel movements
- jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
If your doctor suspects that you have hepatitis C, they will draw blood to check for HCV antibodies. Antibodies are substances your body produces when its fighting an infection. If you have them, your doctor may order a second test to confirm that the virus is still present.
You May Like: How Long Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
You Are Leaving Mavyretcom
You are leaving the AbbVie website and connecting to a site that is not under the control of AbbVie. AbbVie is not responsible for the contents of any such site or any further links from such site. AbbVie is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply the endorsement of the linked site by AbbVie. You should also be aware that the linked site may be governed by its own set of terms and conditions and privacy policy for which AbbVie has no responsibility.
Conversely, the presence of this link does not imply the linked site’s endorsement of MAVYRET.com or AbbVie.
Do you wish to leave this site?
US-MAVY-210359
MAVYRET is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 3 years of age and older with chronic hepatitis C virus :
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
What is the most important information I should know about MAVYRET?
Hepatitis B virus reactivation: Before starting treatment with MAVYRET, your doctor will do blood tests to check for hep B infection. If you have ever had hep B infection, hep B could become active again during or after treatment for hep C with MAVYRET. Hep B that becomes active again may cause serious liver
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Don’t Miss: How To Check If You Have Hepatitis
Testing Bilirubin Levels In Babies
While most newborns have higher levels of bilirubin that level out on their own, sometimes levels that stay too high for too long can cause a type of brain damage known as kernicterus. Kernicterus can lead to hearing loss, as well as problems with vision and teeth.
To prevent this, healthcare providers should check for jaundice every eight to 12 hours during the babys first two days. Then the baby should be checked again when they are between three and five days old since this is when a babys bilirubin level is typically highest.
To treat jaundice in babies, healthcare providers use light therapy or phototherapy. For this, the baby is placed under special lights to reduce high bilirubin.
Who Should Get Tested
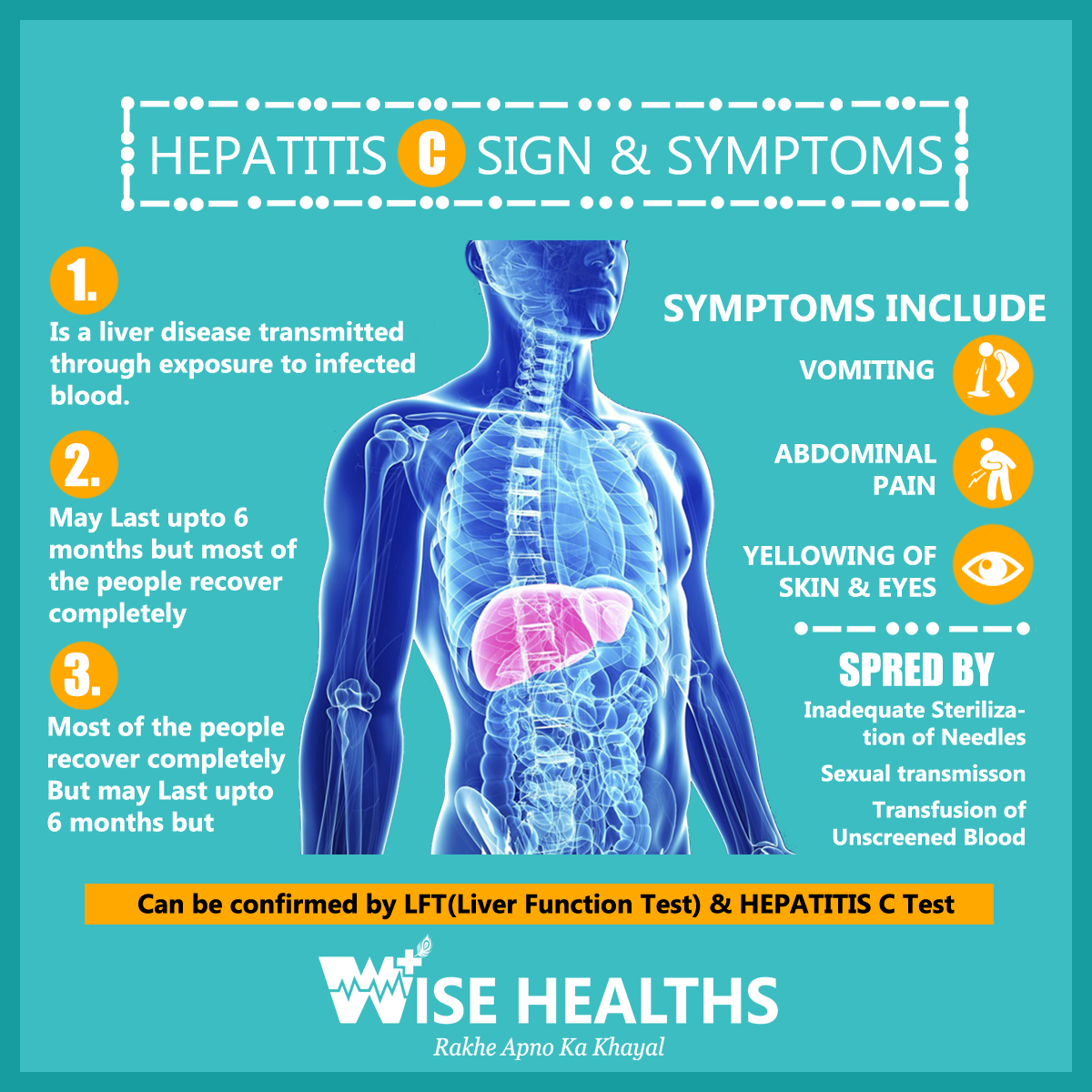
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if you’re worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
- Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
- The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high risk areas include North Africa, the Middle East and Central and East Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Don’t Miss: Confirmatory Test For Hepatitis C
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Treatment For Hepatitis C
The goal of treatment is to clear the virus from the body. If you have acute hepatitis C, you probably wont have symptoms, and the virus will clear on its own without treatment. In the case of chronic hepatitis, your doctor may treat the virus with antiviral medication for 12 to 24 weeks.
Until 2011, there were only two drugs available to treat hepatitis C: pegylated interferon and ribavirin . These drugs were often used in combination with each other.
The drugs currently used to treat hepatitis C include:
Read Also: What Age Do You Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis C Symptoms: What They Are And How They Differ From Hepatitis A And B
Posted on
Hepatitis C virus. | Source: BSIP / Getty
Originally on NewsOne
When it comes to hepatitis, the liver disease that disproportionately affects Black people can exhibit similar symptoms regardless of which of its variations one is inflicted with.
There are 11 main symptoms typically experienced by people who have hepatitis A , B or C , according to statistics provided by the Centers for Disease Control, which cautions that nu ber could rise or fall depending on the individual.
They include but are not limited to jaundice, fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint pain, dark urine and clay-colored stool. Diarrhea is typically a symptom only for HAV.
But when you get a little more granular, data shows that the likelihood of developing symptoms for HAV, HBV or HCV depends according to age as well as a couple of other demographics.
Three out of 10 children who are ages 6 and older can have symptoms of HAV, data shows. With HBV, up to 50% of children 5 and younger can develop symptoms while most children older than 5 are asymptomatic.
With HCV, theres up to a 30% chance of experiencing jaundice, a condition in which the skin and the whites of the eyes become yellow, urine darkens, and the color of stool becomes lighter than normal, as defined by the National Cancer Institute. However, there is no certain symptom assigned to up to 20% of the people with HCV.
SEE ALSO:
Are Some At Higher Risk Of Contracting It
People can be at a higher risk of contracting an illness or virus based on various factors, including age and underlying health conditions. It is important to understand if you are at a higher risk to take the necessary precautions and protect yourself. Elderly adults and those with underlying medical problems may be more susceptible to the dangerous effects of an illness, particularly one highly contagious such as a virus. While assessing your level of risk and taking certain measures may reduce your chances of contracting it, its important to practice preventive measures like hand washing and avoid contact with people who are ill regardless. Being informed and proactive can help reduce your risk of becoming ill from any disease.
Recommended Reading: Autoimmune Hepatitis Flare Up Symptoms
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C Infection
There are two types of hepatitis C infection:
- Acute: a short-term infection that occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to the virus. However, about 75 to 85 percent of people with the acute form go on to develop the chronic form.
- Chronic: a long-term illness that can continue throughout a persons life. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and other serious problems, such as liver failure or cancer. About 15,000 people a year die from liver disease associated with hepatitis C.
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic. How long you experience symptoms will depend on the type you have.
Acute hepatitis C involves more short-term symptoms that typically last 6 months or less but acute hepatitis often leads to chronic hepatitis. When hepatitis C lasts longer than 6 months, its considered chronic.
Without treatment, you may have chronic hepatitis your whole life, since your body often cant get rid of the virus easily. Some people do get better without treatment, although treatment can go a long way toward improving the outlook.
Hepatitis C wont necessarily become chronic.
As a matter of fact, for anywhere from 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C, the virus will clear up without treatment. In other words, if you dont have any symptoms, hepatitis C could improve on its own before you ever know you have it.
However, if your body cant get rid of the hepatitis C virus, the infection wont go away. Instead, it will become chronic, or long-term.
Experts arent sure why some people develop the chronic form of the disease and others dont. But more than half of all people with the hepatitis C virus will eventually develop the chronic form, according to the
Since hepatitis C symptoms can resemble those of other health conditions, your symptoms alone if you have any may not make it clear that you have hepatitis C.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may recommend getting tested if you:
Read Also: Can Hepatitis Cause Itchy Skin
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.