Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Lets look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
You May Like: The Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The best way to prevent hepatitis B is to get the hepatitis B vaccine.
You can also reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- Not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your health care provider right away. Your provider may give you a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, your provider may also give you a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin . You need to get the vaccine and the HBIG as soon as possible after coming into contact with the virus. It is best if you can get them within 24 hours.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
What If You Test Positive For Hepatitis
If testing discloses that you have viral hepatitis there are steps to prevent your passing the viruses to family and friends. Washing the hands helps prevent transmission of hepatitis A. Not sharing needles, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes also will reduce transmission of viral hepatitis. Everyone should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: How Does One Contact Hepatitis C
Questions For A Doctor Or Healthcare Professional
A doctor or healthcare professional can give you guidelines on how to best manage your chronic hep B. Together, you can develop a plan that minimizes your chances of complications.
Some questions you may want to ask a doctor include:
- Do I have acute or chronic hep B?
- What do the results of my blood test mean?
- Should I be taking medication?
- What should I do to monitor my disease?
- Are there any clinical trials that Im eligible for?
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Don’t Miss: What Should You Eat If You Have Hepatitis C
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
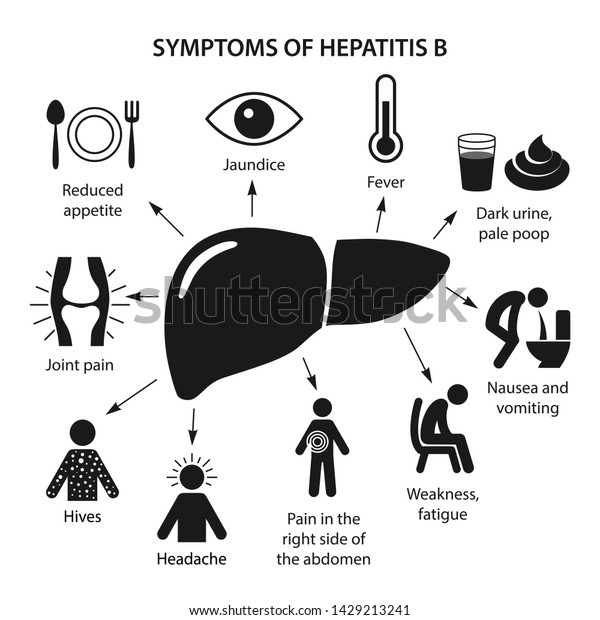
Acute Hepatitis B Symptoms
There are three phases of acute hepatitis B infection, and symptoms may differ depending on the stage. Early in the disease, called the prodromal phase, symptoms may include:
- Dark urine and light stool color
During the icteric phase:
- Jaundice develops
- Anorexia, nausea and vomiting may worsen
- Irritated skin lesions may develop
- Other symptoms may subside
Recommended Reading: Can You Give Plasma If You Have Hepatitis C
How Is Viral Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis is based on symptoms and physical findings as well as blood tests for liver enzymes, viral antibodies, and viral genetic materials.
Symptoms and physical findings
Diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis often is easy, but the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis can be difficult. When a patient reports symptoms of fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, darkening of urine, and then develops jaundice, the diagnosis of acute viral hepatitis is likely and can be confirmed by blood tests. On the other hand, patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV and HCV often have no symptoms or only mild nonspecific symptoms such as chronic fatigue. Typically, these patients do not have jaundice until the liver damage is far advanced. Therefore, these patients can remain undiagnosed for years to decades.
Blood tests
There are three types of blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis: liver enzymes, antibodies to the hepatitis viruses, and viral proteins or genetic material .
Liver enzymes: Among the most sensitive and widely used blood tests for evaluating patients with hepatitis are liver enzymes, called aminotransferases. They include aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase . These enzymes normally are contained within liver cells. If the liver is injured , the liver cells spill the enzymes into the blood, raising the enzyme levels in the blood and signaling that the liver is damaged.
Examples of tests for viral antibodies are:
Depression Can Play A Role In Fatigue
Anyone with a long-lasting illness can get depressed. Hepatitis C is no different. You may be angry, anxious, or sad about your health or the changes you’ve had to make in your life.
Your doctor can help. Tell them how you’re feeling. They may prescribe an antidepressant.
They can also help you find a therapist or support group, where you can talk to others who are facing the same problems as you.
Show Sources
You May Like: Current Treatment For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
Unadjusted And Adjusted Associations Between Fatigue And Demographic And Clinical Patient Characteristics
In unadjusted analyses, female sex, not being married, not being employed, higher BMI, lower income, higher APRI, being born in North or South America, currently taking medications, having co-morbid conditions , and lower mental health functioning were all significantly associated with higher fatigue scores . In particular, mean fatigue scores were 2.5 points higher in females than males, 1.9 points higher in those not employed compared to those who were employed, and 3.1 points higher in patients widowed, divorced, or separated compared to those who were married.
Table 2 shows results for adjusted regression models with race, age, APRI, and viral load forced into the model. Sex, mental health functioning, and having a history of diabetes remained significant independent predictors of fatigue. In the adjusted analysis, the estimated mean fatigue score for females was 2.18 units higher than for males . The estimated mean fatigue score for those with APRI > 1.50 was 4.41 units higher than for those with APRI ⤠0.50 . Those with a history of diabetes had a mean fatigue score that was 2.22 units higher than those without a history of diabetes . Finally, as mental health functioning deteriorated, mean fatigue scores increased . A 10 unit decrease in mental health functioning was associated with a 4.4 unit increase in mean fatigue score .
Association between Fatigue T-Score and Mental Health Functioning
Don’t Miss: What Is The Test For Hepatitis
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B, and most people recover within one to two months. Usually, you can manage symptoms at home with painkillers if necessary. Your healthcare professional should advise you to have regular blood tests and physical check-ups. Most people make a full recovery from acute hepatitis B.
Lifestyle And Medication Fixes May Improve Energy Levels

Fatigue is a common problem for people who have hepatitis. Whether it is brought on directly by liver disease or is the side effect of medication, sufferers may feel extremely tired even after a full night of sleep. According to a 2012 study in the Journal of Hepatology, 53% of people with hepatitis C experience some level of fatigue. Another study published in July 2019 showed that fatigue was a significant problem for people with chronic hepatitis B.
Fatigue can range from mild to severe and can affect every area of life. Some people experience constant fatigue while others experience cycles of fatigue.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Dosage For Adults
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Clinical Outcomes Of Dual Chronic Hepatitis C And B Are Usually Worse
Several hospital or community-based studies demonstrated that in patients co-infected with chronic hepatitis C and B, the disease outcomes are usually worse than those with either chronic HCV or HBV infection 1-7. Patients with HCV/HBV co-infection may exhibit various fluctuating virological profiles basically HCV and HBV can alternate their dominance during long-term follow-up. In Italy, a longitudinal follow-up study revealed the patterns and dynamics of virological dominance in these cases 11. Of 103 untreated HBV/HCV coinfected patients, active infection with HBV and HCV was revealed in 24 cases, inactive infection of both viruses was seen in 15 cases, active HBV and inactive HCV infection was seen in 15 cases, and active HCV and inactive HBV infection was found in 49 cases. During one year follow-up, fluctuation of HBV and/or HCV viremia levels was documented in 32 subjects . Based on these findings, careful evaluation of serum HBV DNA and HCV RNA levels is essential before the diagnosis of the viral dominance which will influence the therapeutic strategies in the co-infected patients.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Drug Information
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C In Babies Symptoms
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Once you are vaccinated, you will not have a chance of getting the hepatitis B virus. For others who have undergone the treatment options, you would not have the symptoms again, but still, the damage to your liver in some cases can be permanent. It depends on how far the virus has affected your liver and how your body has responded to the treatment.
Modifying Behavioural Components To Fatigue
Significant central fatigue warrants lifestyle changes, which may include rest periods and reduced workloads . However, the maintenance of physical activity is of paramount importance. The natural inclination of patients with central fatigue is to decrease physical activity. However, decreased physical activity over time will lead to cardiovascular and muscular deconditioning, which then makes physical activity even more difficult . Therefore, all patients need to be counselled with regard to maintaining an appropriate level of activity. In addition, an increase in activity should be attempted through the institution of a graded exercise program .
You May Like: Medicine To Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Read Also: How Can I Catch Hepatitis C
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Don’t Miss: Why Does Hepatitis Cause Joint Pain
What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis B
About 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments almost always work if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Read Also: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
What Are The Treatment Options For Chronic Hep B
For people with acute hep B infection experiencing mild symptoms, doctors often recommend rest, a healthy diet, and fluids to speed up recovery. Severe symptoms may need to be treated in a hospital.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, there are currently seven drugs approved by the FDA to treat chronic hep B in the United States. Not everybody needs to take medication, but some people will need to take medication for the rest of their lives.
These drugs fall into one of two categories:
- Antiviral drugs. These drugs help reduce inflammation and liver damage. Theyre usually taken daily in pill form for at least a year.
- Immune modulator drugs. These drugs boost your immune system to help your body fight off the virus. Theyre administered as an injection over 6 to 12 months.
Theres no cure for hep B, acute or chronic, at the moment. However, clinical trials continue to investigate new treatment options.