Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
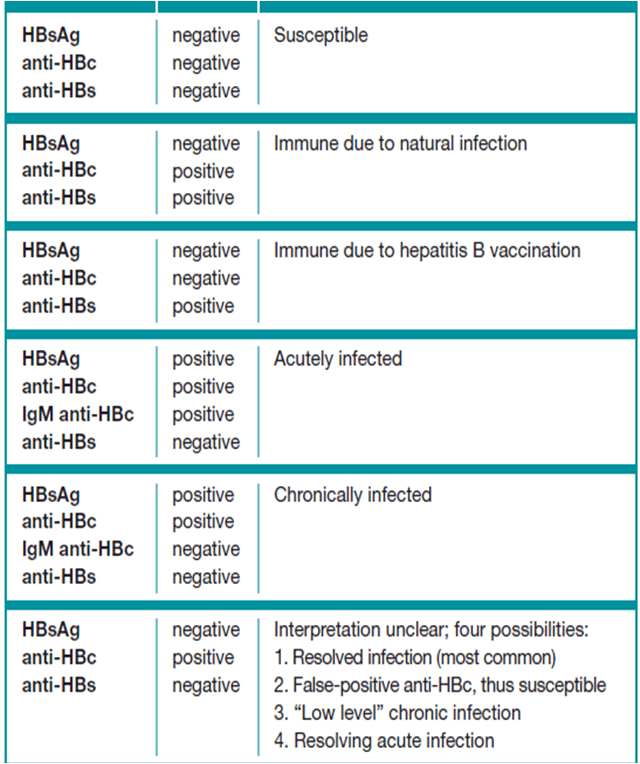
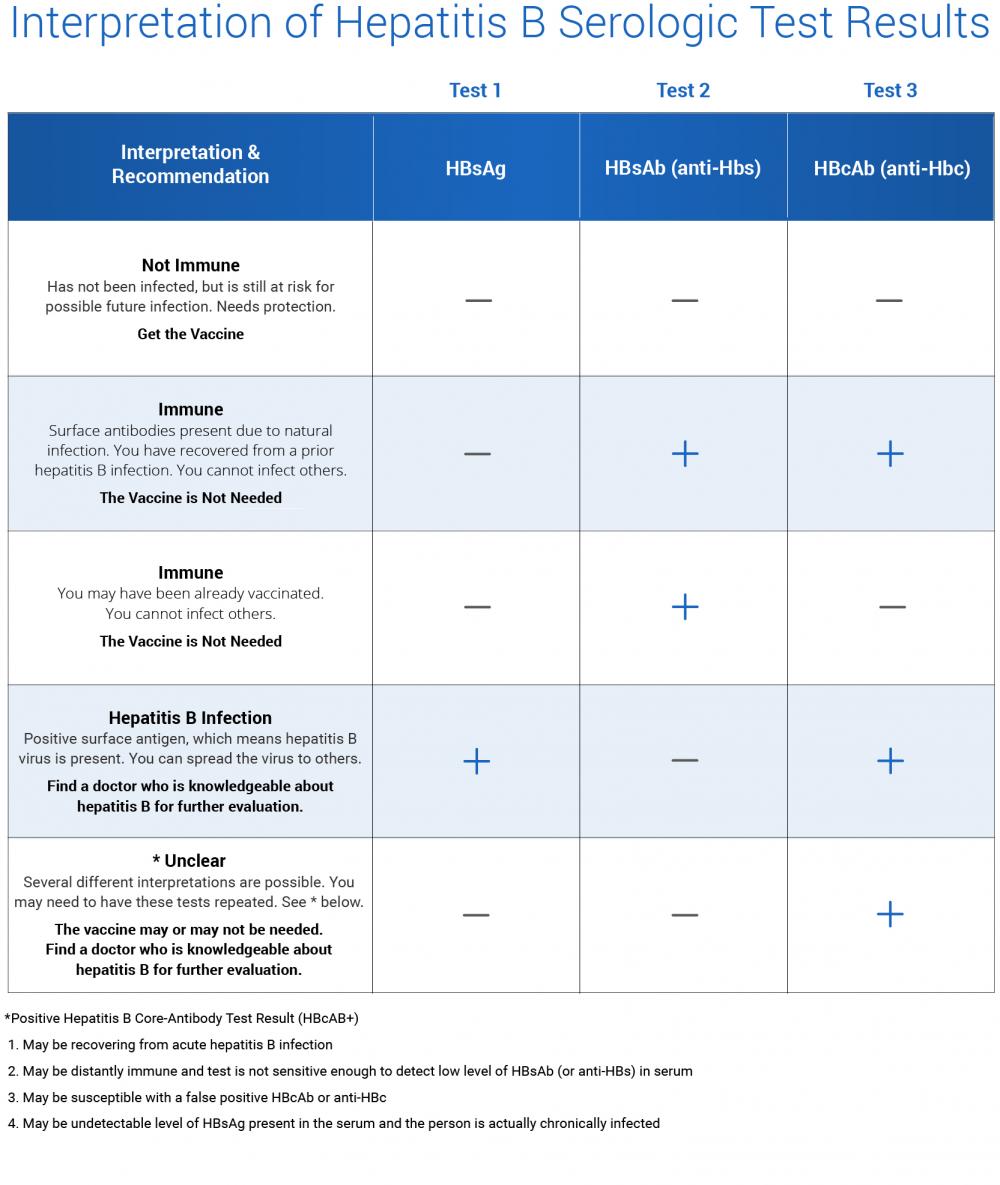
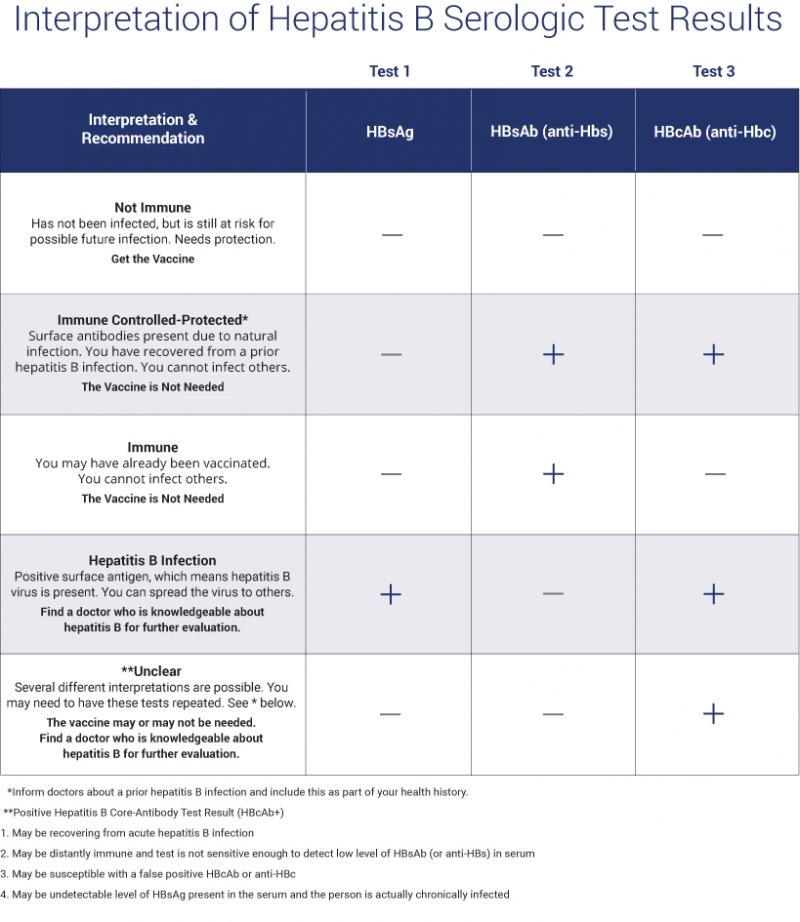
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturers instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Dont Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patientâs body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a personâs ability to spread HBV to others.
Also Check: What Is The Definition Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B E Antigen And Hepatitis B E Antibody
Hepatitis B e antigen is a secretory protein processed from the precore protein. It is a marker of HBV replication and infectivity. Its presence is usually associated with high levels of HBV DNA. During acute HBV infection, HBeAg appears shortly after the appearance of HBsAg. In persons who recover from HBV infection, HBeAg to hepatitis B e antibody seroconversion precedes that of HBsAg to anti-HBs seroconversion. Anti-HBe may persist for many years after the resolution of acute HBV infection. In persons with chronic infection, HBeAg may persist for years to decades. Seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe is usually associated with a marked decrease in serum HBV DNA levels and remission of liver disease, but some patients with anti-HBe continue to have high serum HBV DNA levels and associated active liver disease. The latter patients often have precore or core promoter HBV variants that prevent or decrease the production of HBeAg.37,38
Henry Lik-Yuen Chan, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, in, 2012
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
Two authors independently extracted data and reached agreement on the following variables: study author and year study location and design specimens tested eligibility criteria index test and reference standard, including manufacturer raw cell numbers HIV co-infection sources of funding and reported conflict of interest.
Study quality was evaluated using the QUADAS-2 tool , which evaluates risk of bias and applicability concerns .
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Be Spread Through Saliva
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Long Term Effects
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Recommended Reading: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Clinical Significance Of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Mutants
Correspondence to: Nicola Coppola, MD, PhD, Department of Mental Health and Public Medicine, Section of Infectious Diseases, Second University of Naples, Via: L. Armanni 5, 80131 Naples, Italy.
Telephone: +39-8-15666719 Fax: +39-8-15666013
You May Like: How Do People Contract Hepatitis C
Hbsag Mutants Associated With Immune Escape
The MHR region, which is exposed to the outer surface of the virion, is situated between aa 99-169 of HBsAg. The antibodies produced after HBV vaccination and those used in diagnostic assays to detect serum HBsAg are both directed against this region and, specifically, to a cluster of B-cell epitopes, common to all subtypes of the virus, called a determinant and showing a two-loop structure of aa . Mutations may occur on both loops of the a determinant and may be responsible for a lack of protection and the occurrence of HBV infection in immunized patients or for failure to protect by the HBIG administered as a prophylactic measure or failure to detect HBsAg in diagnostic assays. Table Table22 lists the studies suggesting the association of HBsAg mutants with vaccine escape or failed HBsAg detection.
Key Facts And Figures
- HBV is a vaccine-preventable disease that is highly infectious far more so than either HIV or HCV. It is transmitted through perinatal, percutaneous, or sexual exposure to an infected personâs blood / body fluids household contacts are also at risk of infection.
- Acute and chronic HBV infections are frequently asymptomatic or present with nonspecific symptoms about two-thirds of chronically infected people are unaware of their status, and most will only be detected through proactive screening.
- Of those infected as adults, 5% will become chronically infected in contrast, about 90% of infants infected at birth will develop chronic infection.Endnote 1
- Without intervention, 15%40% of chronically infected people will go on to develop cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and/or HCC.
HBV is a notifiable disease in all provinces and territories in Canada. As such, it must be reported to the regional/local Medical Officer of Health.
Don’t Miss: What Is Genotype 3 Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. There are several types of test, but the three generally included are the HBsAg, the antibody to HBsAg , and the antibody to hepatitis B core antigen .
These tests allow the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
Also Check: How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment Guidelines
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
The Treatment Programs Role In The Screening Process
Medical staff members at substance abuse treatment programs might assume the primary role for screening individuals for and explaining the screening process and test results. Opioid treatment programs with medical staff members should screen for and C at intake and periodically as indicated. In programs without onsite medical staff, clients may be referred elsewhere for screening with minimal involvement of the substance abuse treatment program.
Regardless of the type of program, counselors should have a basic understanding of the importance of screening, the screening process, and the meaning of the results. Counselors can encourage clients referred for screening to follow through and complete the screening and evaluation process . Clients might feel anxious about being diagnosed with hepatitis, and they might delay or avoid getting screened.
You May Like: Flu Like Symptoms Hepatitis C
Search Strategy And Identification Of Studies
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis on the diagnostic accuracy of HBsAg tests. The review was registered in PROSPERO and reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses check list. We utilised standardised methods for systematic reviews on diagnostics, including an a priori protocol .
Literature search strategies were developed by a medical librarian with expertise in systematic review searching, using a search algorithm consisting of terms for: hepatitis B, diagnostic tests, and diagnostic accuracy. We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Science Citation Index Expanded, SCOPUS, Literatura Latino-Americana e do Caribe em Ciências da Saúde , WHO Global Index Medicus, WHOs International Clinical Trials Registry and the Web of Science. We also contacted researchers, experts and authors of major trials, with no relevant manuscripts in preparation identified. Additional pertinent citations were identified through bibliographies of retrieved studies.
Abstracts were screened by reviewers AA and HK according to standard inclusion and exclusion criteria. All studies identified for full manuscript review were assessed independently by two reviewers against inclusion criteria. Papers were accepted or rejected, with reasons for exclusion specified. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion between review authors and, when required, a third independent reviewer .
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Also Check: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Chronic Hbv Infection Following Exposure In Neonatal Life
The majority of babies born to HBeAg-positive mothers become infected and over 90% of these develop a chronic carrier state. Although some cases have been documented of HBV infection during fetal life, it is thought that these infants probably receive a large inoculum of virus from maternal blood before or during birth, and by close contact with secretions soon after birth. HBeAg but not HBsAg has been detected in the cord blood of these neonates, suggesting that HBeAg crosses the placenta. The reason for the infants failing to clear the virus is unknown, but may relate to the induction of immune tolerance to HBeAg. Children born to HBeAg-negative/HBsAg-positive carrier mothers who are asymptomatic rarely become chronically infected.
Jia-Horng Kao, … Ding-Shinn Chen, in, 2010
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . For some people, hepatitis B infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer or cirrhosisa condition that causes permanent scarring of the liver.
Most people infected with hepatitis B as adults recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection.
Also Check: What Does Immunity To Hepatitis B Mean