Codified Diagnostic Criteria Of The Iaihg
The diagnostic criteria of the IAIHG require the presence of compatible laboratory , serological and histological findings .19 Diseases that can resemble autoimmune hepatitis must also be excluded by appropriate tests, and these include virus-related, drug-induced, alcoholic, hereditary , metabolic , and immune-mediated cholestatic diseases .19 The designation of definite or probable autoimmune hepatitis reflects the level of confidence in the diagnosis based on the compatibility of the clinical features with classical autoimmune hepatitis. Two scoring systems are available for challenging cases.19,20
Dos And Donts In Managing Autoimmune Hepatitis:
- DO remember that monitoring of your condition is important. Report any new symptoms to your health care provider promptly.
- DO call your health care provider if you notice skin color changes, side effects from medicines, joint pains, or abdominal swelling.
- DONT ignore drug side effects, such as weight gain, anxiety, confusion, thinning of bones , thinning of the hair and skin, diabetes, high blood pressure, and cataracts.
- DONT use alcohol. It may further damage your liver.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease
Managing The Suboptimal Response
Liver tests worsen during therapy in 7% of patients,252 and they improve but not to normal levels in 14%.242,253 Treatment-ending side effects associated with corticosteroid therapy occur in 12% to 29%, and they are mainly intolerable cosmetic changes, obesity, emotional instability, and vertebral compression.74,245,254 Treatment ending side effects associated with azathioprine therapy occur in 5% to 10% of patients, and they are mainly nausea, vomiting, rash, cytopenia , pancreatitis, and liver toxicity.223,254,255 Patients with cirrhosis develop corticosteroid-induced side effects more commonly than patients without cirrhosis presumably because of increased systemic levels of unbound prednisolone,48,223 and they develop cytopenia that can suggest azathioprine toxicity more often .239,240
1) Treatment failure
Patients who fail conventional treatment are treated with high doses of the original medication . The dose of prednisone or prednisolone is increased to 30 mg daily and the dose of azathioprine is increased to 150 mg daily.18,34,39,253,256 Patients receiving monotherapy are treated with prednisone or prednisolone, 60 mg daily. Treatment is continued at a fixed dose for one month. Thereafter, the doses of medication are reduced by 10 mg of prednisone or prednisolone and 50 mg of azathioprine after each month of laboratory and clinical improvement until conventional maintenance levels for that particular regimen are reached.
2) Incomplete response
3) Drug-intolerance
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Who Is At Risk For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis affects one in every 100,000 people. The disease is more common in women than in men, and women are typically diagnosed in their 40s or 50s. Girls between two and 14 years old may also get the disease.
Those who may suffer from other autoimmune conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease and celiac disease, are also at risk to develop autoimmune hepatitis .
A person who has a family history of autoimmune hepatitis also has a higher risk of developing the disease.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Are my symptoms that I am experiencing such as fatigue and lethargy due to AIH?
- Which type of Autoimmune Hepatitis do I have? Type 1 or Type 2?
- What is the status of my liver?
- Do I have liver damage?
- Will I need a liver transplant?
- Is it possible for me to have AIH along with other autoimmune diseases?
- Will blood tests be performed to check for autoantibodies?
- Will a liver biopsy be needed?
- What kind of medications might be possible to treat AIH?
- Will I be tapered off over time if I respond well to therapy?
- Will there be routine imaging/screening to check for other kinds of liver diseases such as liver cancer?
- Will I need a booster vaccine of for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B?
Also Check: Screening Test For Hepatitis B
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
What Are The Treatments Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
The treatment plan usually differs from patient to patient. Every patient reacts differently to the line of treatment. Doctors do not recommend any treatment until there are any visible symptoms. Treatment starts if symptoms can be seen or the blood test reports are bad.
1) Medication –
- In order to subside the inflammation of liver cells, the most common drug used is a corticosteroid named Prednisone. A higher dose of Prednisone is prescribed, and the dosage is lowered along the course of treatment. Another drug called Azathioprine or Purinethol, also a corticosteroid, would be added to the line of treatment after lowering the dose of Prednisone.
- The alternative treatment to Azathioprine is Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus. People may have side effects because they are under steroid medication, such as weak bones, high blood sugar levels, and increased urge to eat, leading to increased weight, eye problems, anxiety, and depression.
- After treatment of about three years, the majority of the patient’s symptoms and blood tests are under the normal range. Few doctors recommend immunosuppressants for life, or else recurrence rates are really high. Few others recommend that patients can stop medication after the symptoms have subsided and blood reports are normal, but the patient has been continuously being observed by their doctor, and their medication would start again once there is a relapse.
Recommended Reading: What If You Have Hepatitis B
How To Prepare For Your First Appointment With A Hepatologist
Think through the questions that the doctor may ask you. Schedule some time to sit down and take notes before the appointment. Write down each of your symptoms and how long they have been going on. Think about any family members who have a history of liver disease or autoimmune conditions, and write them down as well. Finally, create a list of all of the medications, vitamins, and supplements you are currently taking.
Combination Therapy With Prednisone Or Prednisolone And Azathioprine
The preferred treatment regimen combining corticosteroids and azathioprine consists of an induction phase and a maintenance phase .34 During the 4-week induction phase, prednisone or prednisolone, 30 mg daily, is administered for 1 week. The dose is then reduced to 20 mg daily for 1 week and 15 mg daily for 2 weeks. Azathioprine, 50 mg daily, is given as a fixed dose during the entire induction phase. After 4 weeks of induction, the dose of prednisone or prednisolone is adjusted to 10 mg daily. The dose of azathioprine is maintained at 50 mg daily. The maintenance phase is continued at fixed doses of prednisone or prednisolone, 10 mg daily, and azathioprine, 50 mg daily, until normalization of serum AST, ALT, bilirubin, and -globulin or IgG levels and resolution of the histological abnormalities.17 In Europe, prednisolone is preferred over prednisone, and it is commonly administered in a weight-based dose during the induction phase. Similarly, the dose of azathioprine is commonly weight-based .33,234,235
Also Check: Different Ways To Get Hepatitis C
Search For A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
Mycophenolate Mofetil As Frontline And Salvage Therapy
Mycophenolate mofetil, a next generation purine antagonist, has been used as a frontline and salvage therapy for autoimmune hepatitis.34 As a frontline treatment in 59 patients treated for 3 to 92 months , mycophenolate mofetil in combination with prednisolone normalized serum ALT and -globulin levels in 88%, induced a partial laboratory improvement in 12%, allowed the withdrawal of corticosteroids in 58%, and induced treatment-ending side effects in 3% .47 Therapy with mycophenolate mofetil and prednisolone can be effective and safe in treatment-naïve patients, but comparative clinical trials with standard therapy are necessary to establish its preference.
Mycophenolate mofetil has also been used as a salvage therapy for patients with corticosteroid-refractory liver disease or azathioprine intolerance.34 Composite analysis of the several, small, single center experiences indicates that mycophenolate mofetil can induce improvement of laboratory tests in 45%, facilitate the withdrawal of corticosteroids in 40%, and cause treatment-ending side effects in 15% .34,50 Outcomes can be improved by using the treatment in a selective fashion. Therapy with mycophenolate mofetil has rescued patients who are azathioprine intolerant more commonly than patients who are refractory to conventional corticosteroid treatment ,34,41,45,46,50 whereas children with autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis have not responded.
Recommended Reading: What Kills The Hepatitis C Virus
Graft Dysfunction After Liver Transplantation
Autoimmune hepatitis can recur or develop de novo after liver transplantation, and it should be considered in all transplanted patients with graft dysfunction .108113 The frequency of recurrence ranges from 8% to 68%, depending in part on the performance of liver tissue examinations by protocol or by clinical indication.113118 Autoimmune hepatitis recurs in 8% to 12% after 1 year and 36% to 68% after 5 years .113,119122De novo autoimmune hepatitis occurs in 1% to 7% of patients 1 month to 9 years after transplantation for nonautoimmune liver disease.108,120,123125
Diagnostic criteria for recurrent or de novo autoimmune hepatitis after liver transplantation have not been codified.113 Most patients have hypergammaglobulinemia, increased serum levels of IgG, conventional autoantibodies, and interface hepatitis with or without portal plasma cell infiltration.119,126,127 Adults with de novo autoimmune hepatitis may develop antibodies against glutathione-S-transferase T1 .128 Recurrent and de novo autoimmune hepatitis are variably responsive to conventional corticosteroid therapy cirrhosis develops in as many as 60% graft loss is possible and retransplantation is required in 8% to 50%.113
Calcineurin Inhibitors As Frontline And Salvage Therapies
Cyclosporine has been used successfully as a frontline agent in children and adults with autoimmune hepatitis,36,274,275 but the only randomized clinical trial involving 39 patients has indicated equivalency rather than superiority of cyclosporine therapy to standard combination therapy .51 In the absence of clear advantages that outweigh the risks of treatment and its expense, frontline therapy with cyclosporine cannot be justified.49 Similarly, tacrolimus has also had success as a frontline treatment in 21 patients who improved their serum ALT and AST levels after 3 months.35 The cytopenia and nephrotoxicity that developed in these patients were not treatment-ending, but validation of this regimen by randomized clinical trial has not emerged after 20 years.
Treatment with the calcineurin inhibitors is commonly indefinite, and it requires experience to ensure careful monitoring and appropriate dose adjustment. Cyclosporine has been administered in doses of 2 to 5 mg/kg body weight with dose adjustments to achieve trough levels of 100 to 300 ng/mL,34,36,49 and tacrolimus has been administered at a starting dose of 0.5 to 1 mg daily and increased to 1 to 3 mg twice daily as tolerated to achieve a serum level of 3 ng/mL .34,35,38,49,276,279
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Autoimmune Hepatitis
If autoimmune hepatitis is diagnosed early, and treated with the proper medication, the liver may begin to heal and will be able to make healthy cells again to replace the inflamed and scarred cells. The patients symptoms will ease and the liver may begin to work normally.
The patient will need to be monitored and managed for the rest of his or her life, even if he or she is feeling better and liver function has improved. In many cases, the patient will need to be on medication for the rest of his or her life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2018.
References
Is An Aih Diagnosis Fatal
If left untreated, autoimmune hepatitis could be fatal. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to achieving a good prognosis.
For individuals who respond positively to treatment, the 10-year survival rate is about 83.8% to 94%. Without any treatment, 40% to 50% of individuals with severe autoimmune hepatitis will die within six months to five years.
National Organization for Rare Disorders. Autoimmune hepatitis.
Read Also: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis B Antibodies
Autoimmune Hepatitis & How It Is Diagnosed
Falk: What on earth is autoimmune hepatitis? What do those words really mean?
Darling: Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease. It can affect any aged patient, any ethnicity, it can affect either sex, usually has a female-to-male predominance of about 3:1. Hepatitis just means inflammation of the liver.
Falk: Remind me again, what does the liver do?
Darling: The liver does a lot of important things. For one, it metabolizes nutrients from the gut, it makes bile which helps you digest fats, it makes a lot of important proteins, specificallyall of your clotting factors except for one, and proteins that help fluids stay in the right spaces. It also detoxifies certain drugs or medications.
Falk: When you inflame a liver, just like when you inflame any other organ, the suffix is -it is the liver is the hepatic system, so hepatitis which is inflammation of the liver from any number of causes.
Darling: Absolutely. The liver is made up of liver cells or hepatocytes, and its made up of small and large bile ducts, and for the most part it implies that this is inflammation of the liver cells themselves, the hepatocytes. It is usually manifested as elevated liver enzymes, so AST, ALTthese are blood tests and it is reflective of turnover of liver cells.
Falk: The liver can be affected by a number of factors. One can get hepatitis from alcohol, one can get hepatitis from a number of drugs, one can get hepatitis from certain viruses. Whats the most common of those entities?
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis
Experts dont know what causes autoimmune hepatitis, but it is more likely to show up in people with other autoimmune conditions, including:
- Fluid buildup in the belly
- Rectal bleeding or vomiting blood
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis may look like other health problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Borderline
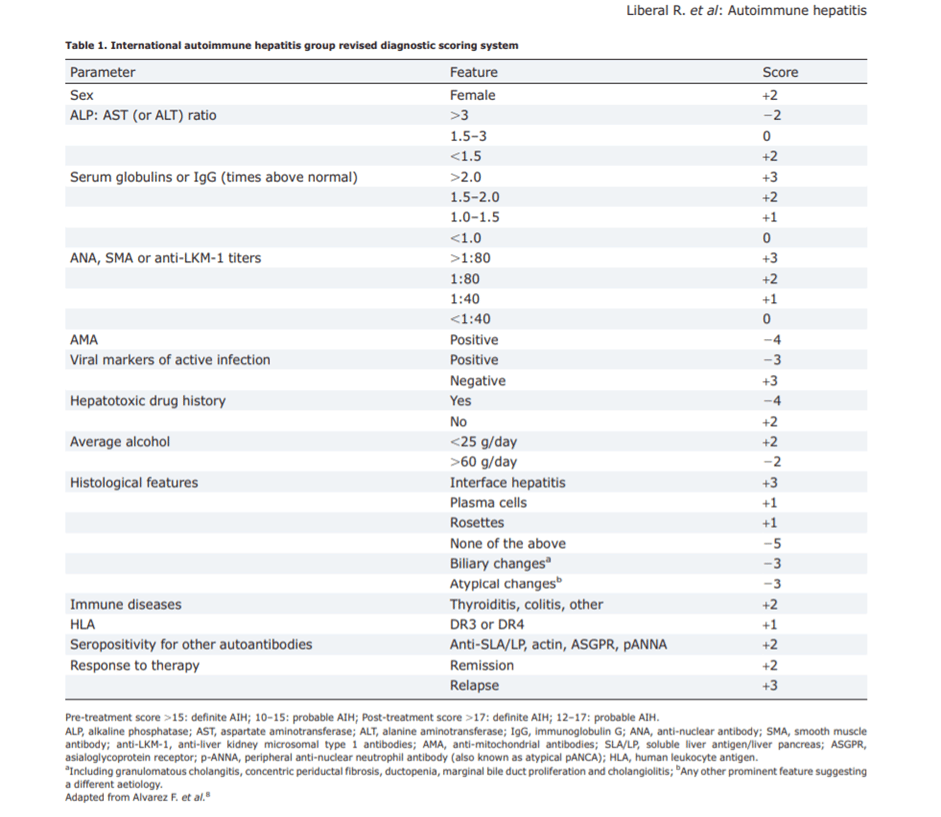
Revised Original Diagnostic Scoring System Of The Iaihg
The revised original scoring system is a comprehensive template that evaluates 13 clinical categories and renders 27 possible grades .19 This comprehensive scoring system was originally developed as a research tool by which to ensure the homogeneity of patient populations in clinical studies.139 It has emerged subsequently as a template by which to ensure the systematic evaluation of patients, and it can serve as a mechanism by which to bolster clinical judgment.21,140 The scoring system can accommodate deficiencies or inconsistencies in the clinical presentation and support the diagnosis in difficult cases by rendering a composite score before and after corticosteroid treatment.
Can An Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosis Be Something Else
Some symptoms and lab findings found in autoimmune hepatitis are also common in other chronic conditions. Your medical team will work to rule out any other possible causes for your symptoms. Some diseases to rule out include other types of hepatitis, certain viral infections, and other liver conditions such as cirrhosis and fatty liver disease.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Antibody
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
If autoimmune hepatitis leads to cirrhosis, doctors can treat health problems and complications related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have a greater chance of developing liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound or other types of imaging tests to check for liver cancer.
If autoimmune hepatitis causes acute liver failure or cirrhosis with liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant.
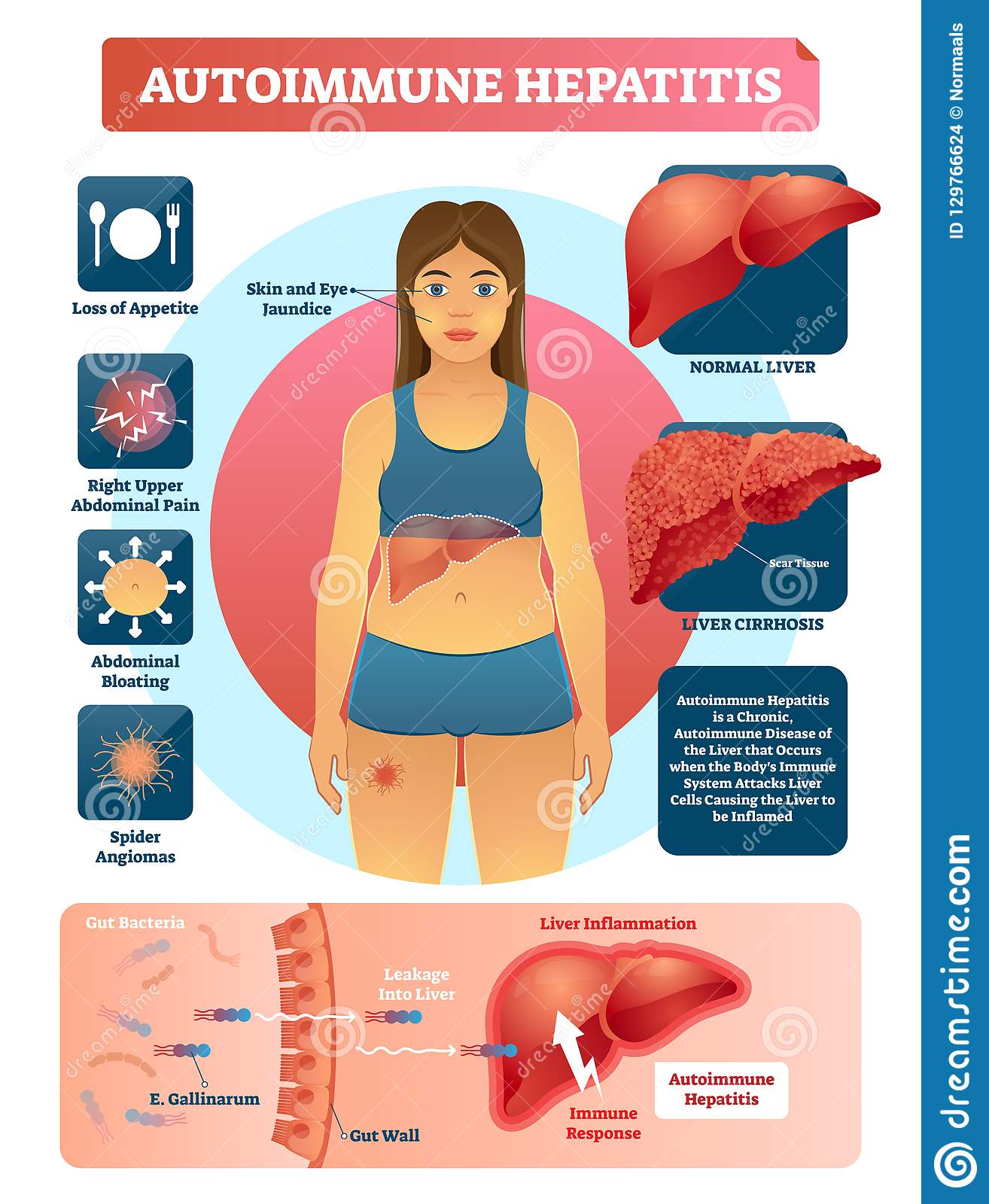
What Are The Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
People with autoimmune hepatitis may have some of the following symptoms
- pain over the liver, in the upper part of the abdomen
- yellowish color of the whites of the eyes and skin, called jaundice
- darkening of the color of urine
- lightening of the color of stools
- skin conditions, such as rash, psoriasis, vitiligo, or acne
When symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are present, they can range from mild to severe.
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have no symptoms. In such cases, doctors may find evidence of liver problems during routine blood tests that leads to a diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. People without symptoms at diagnosis may develop symptoms later.
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis dont have symptoms until they develop complications due to cirrhosis. These symptoms include
- feeling tired or weak
- bloating from a buildup of fluid in the abdomen, called ascites
- swelling of the lower legs, ankles, or feet, called edema
Read Also: Dna Test For Hepatitis B