Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Some people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Jaundice, yellowing of your skin and eyes
If you have an acute infection, your symptoms can start anywhere between 2 weeks to 6 months after you got infected. If you have a chronic infection, you may not have symptoms until many years later.
Acute Vs Chronic Infection
If you have been diagnosed with hepatitis B, it is important to understand if your infection is acute or chronic.
When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an “acute infection” . Many people are able to naturally get rid of an acute infection.
If the infection persists for more than 6 months, it is considered a chronic infection.
Acute infections have few, if any, lasting effects. People with chronic infections are at greater risk for developing serious liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, and should take precautions to keep their liver healthy.
Why do some people naturally get rid of the virus while others develop chronic infections? The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus. The younger a person is when they are first infected, the greater the risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection.
Read Also: Hepatitis C 0.1 Results
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment, says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Dont Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C Through Sex
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna
If I Have Hepatitis How Can I Avoid Giving It To Someone Else
For hepatitis A, one of the best things you can do is wash your hands a lot. That will keep the virus out of food and drinks.
If you have hepatitis B and C, you need to find ways to keep others from making contact with your blood. Follow these tips:
- Cover your cuts or blisters.
- Carefully throw away used bandages, tissues, tampons, and sanitary napkins.
- Dont share your razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush.
- If your blood gets on objects, clean them with household bleach and water.
- Dont breastfeed if your nipples are cracked or bleeding.
- Dont donate blood, organs, or sperm.
- If you inject drugs, dont share needles or other equipment.
Show Sources
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Also Check: What Is The Sign Of Hepatitis C
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called âfulminantâ hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
You May Like: Hepatic Artery Infusion Survival Rate
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
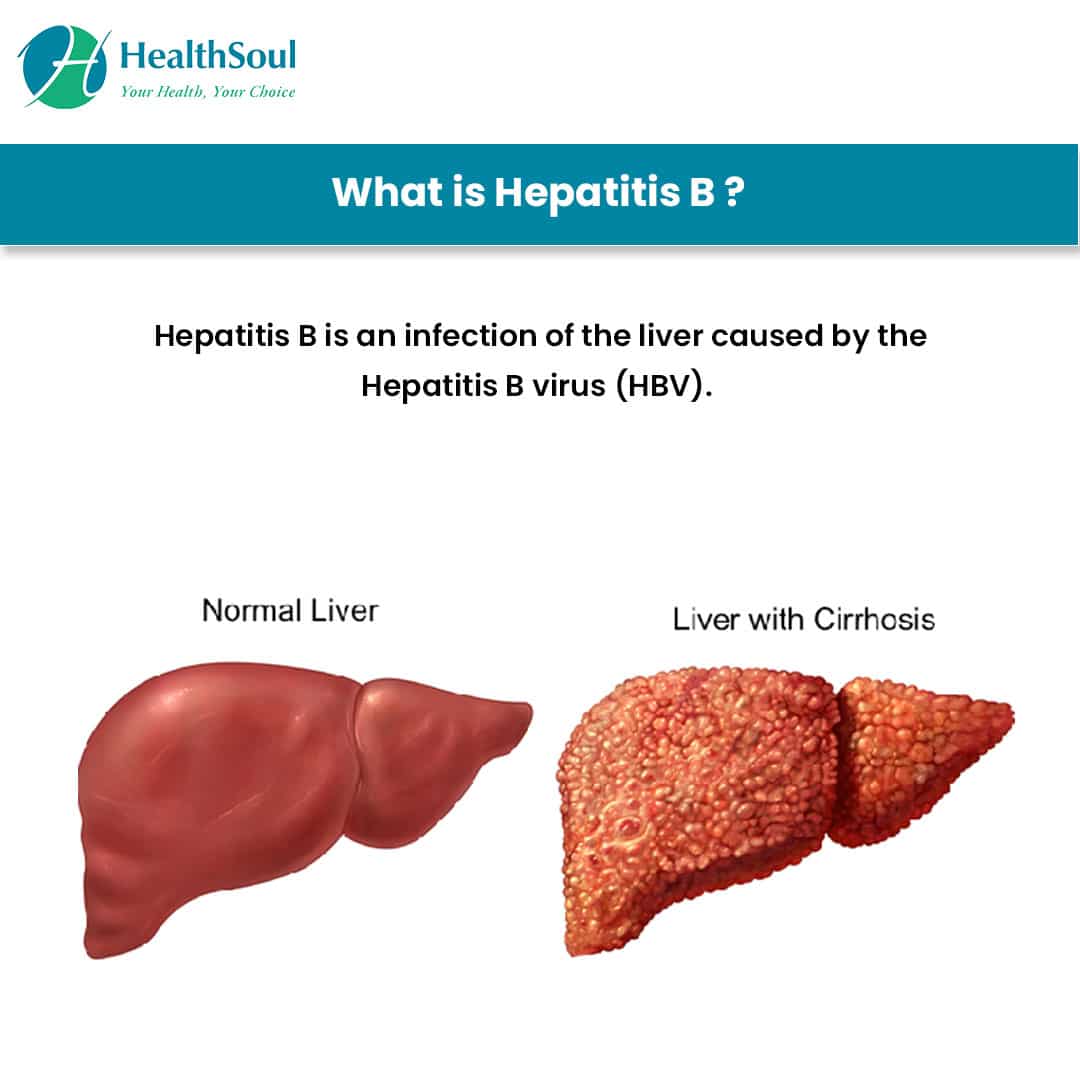
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . HBV infection causes inflammation of the liver. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected.
- The best way to prevent HBV infection is by getting vaccinated. Safe and effective vaccines are available and covered as a preventive service by most health plans.
- For some people, HBV infection is an acute, or short-term, illness for others, it can become a long-term, chronic infection. Risk for chronic infection is related to age at infection: approximately 90% of infected infants become chronically infected, compared with 2-6% of adults.
- Chronic hepatitis B can lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, and premature death.
- Hepatitis B is diagnosed with a simple blood test that can detect HBV infection years before symptoms develop and the virus has caused liver damage.
- There is no cure for hepatitis B, but there are several FDA-approved medications that treat HBV infection. People with chronic hepatitis B should be monitored regularly for signs of liver disease and evaluated for possible treatment.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Transferred Sexually
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious

Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Also Check: What Drug Is Used To Treat Chronic Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent And Without Coma
Chronic Hepatitis B Symptoms
Most patients with chronic hepatitis B are asymptomatic unless their disease progresses. Others might have nonspecific symptoms, such as fatigue.
Some patients experience worsening of the infection and develop signs and symptoms similar to acute hepatitis.
If patients with chronic hepatitis B progress to cirrhosis they will develop signs and symptoms of liver failure, including:
- Peripheral edema
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Also Check: How Can I Tell If I Have Hepatitis C
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Mental Health
Prevent Infection After Contact With The Virus
If you think you have been in contact with the hepatitis B virus, see your doctor right away. Doctors typically recommend a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent infection. In some cases, doctors may also recommend a medicine called hepatitis B immune globulin to help prevent infection. You must get the vaccine dose and, if needed, HBIG shortly after coming into contact with the virus, preferably within 24 hours.
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
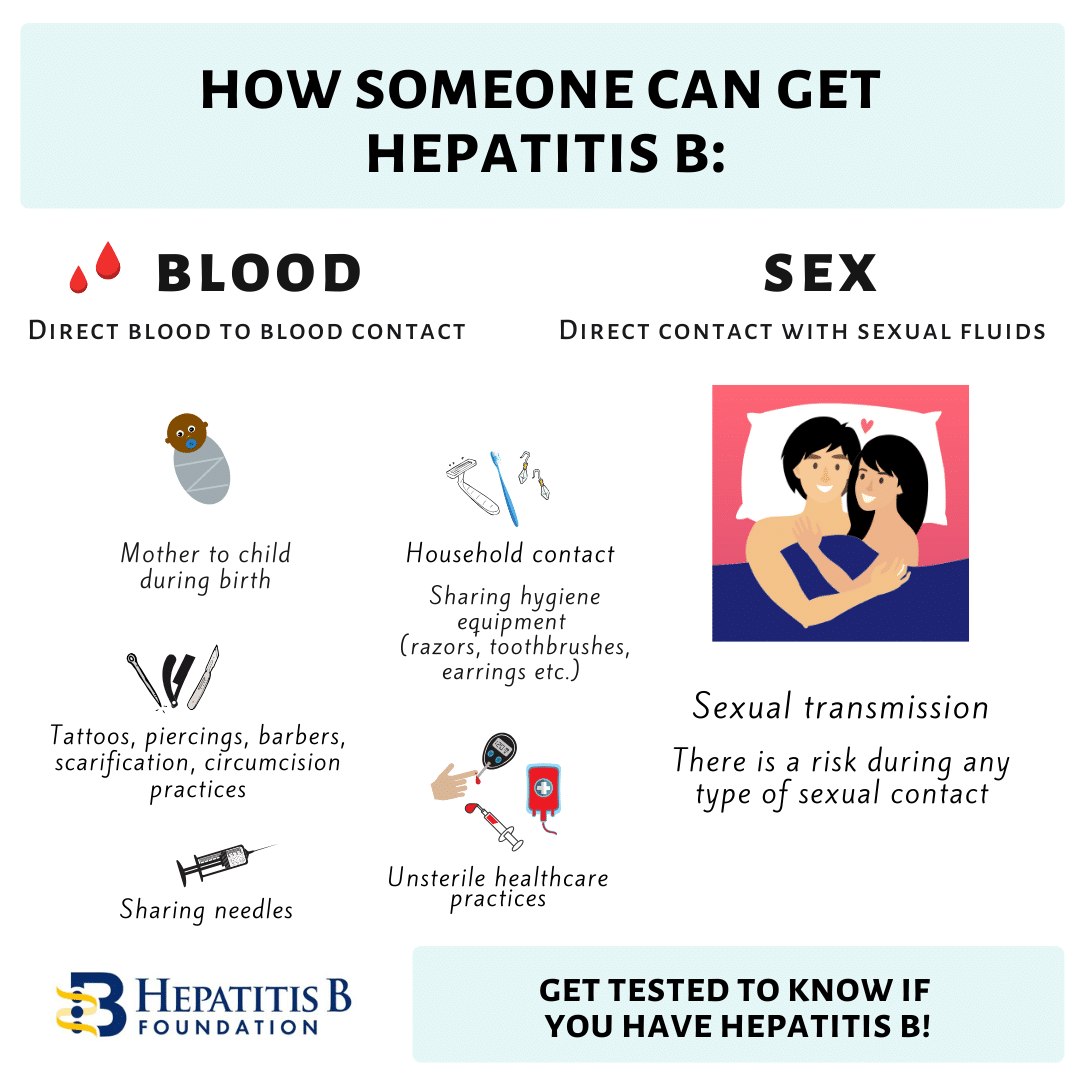
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
You May Like: How To Cure Alcoholic Hepatitis
Treatment To Prevent Hepatitis B Infection After Exposure
If you know you’ve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and aren’t sure if you’ve been vaccinated, call your doctor immediately. An injection of immunoglobulin given within 12 hours of exposure to the virus may help protect you from getting sick with hepatitis B. Because this treatment only provides short-term protection, you also should get the hepatitis B vaccine at the same time, if you never received it.
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Don’t Miss: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Read Also: Drug Treatment For Hepatitis C