Who Invented Hepatitis B Vaccine
Pablo DT Valenzuela /InventorPablo Valenzuela is a Chilean biochemist dedicated to biotechnology development. He is known for his genetic studies of hepatitis viruses participated as R& D Director in the discovery of hepatitis C virus and the invention of the worlds first recombinant vaccine.
Wikipedia
What Are Warnings And Precautions For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Warnings
This medication contains the hepatitis b vaccine. Do not take Engerix B or Recombivax HB if you are allergic to the hepatitis b vaccine or any ingredients contained in this drug.
Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center immediately.
Contraindications
- See “What Are Side Effects Associated with Using Hepatitis B Vaccine?”
Long-Term Effects
- See “What Are Side Effects Associated with Using Hepatitis B Vaccine?”
Cautions
- Not protective against hepatitis A, C, or E
- Gluteal muscle injection is not recommended
- Heptavax B is no longer used in the US
Pregnancy and Lactation
- Use the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy with caution if the benefits outweigh the risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies are not available, or neither animal nor human studies were done.
- It is not known if the hepatitis B vaccine is excreted in breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
Don’t Miss: How Do People Get Hepatitis B
Barriers To Increasing Hepb
Reaching babies within 24 hours of birth was a difficult problem in all five countries. Barriers to the timely administration of HepB-BD included weaknesses in national policies and lack of written guidelines to standardize HepB-BD implementation at health facilities. Evaluators did not find standard operating procedures at facilities to delineate when and where babies ought to be vaccinated, and which staff cadre was responsible for HepB-BD. As a result, many facilities were vaccinating babies at the point of hospital discharge instead of at birth. Vaccination services were often offered for half a day on weekdays and not on weekends or public holidays, and HepB-BD was not integrated into BEmONC packages in all countries.
Lack of training opportunities for HCWs was almost universally reported in all five countries. HepB-BD was often delayed or not given to infants because of inappropriate contraindication. Deficiency in knowledge about vaccine safety by HCWs has been linked to missed opportunities to vaccinate and low coverage rates27,28.
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is Caused By
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
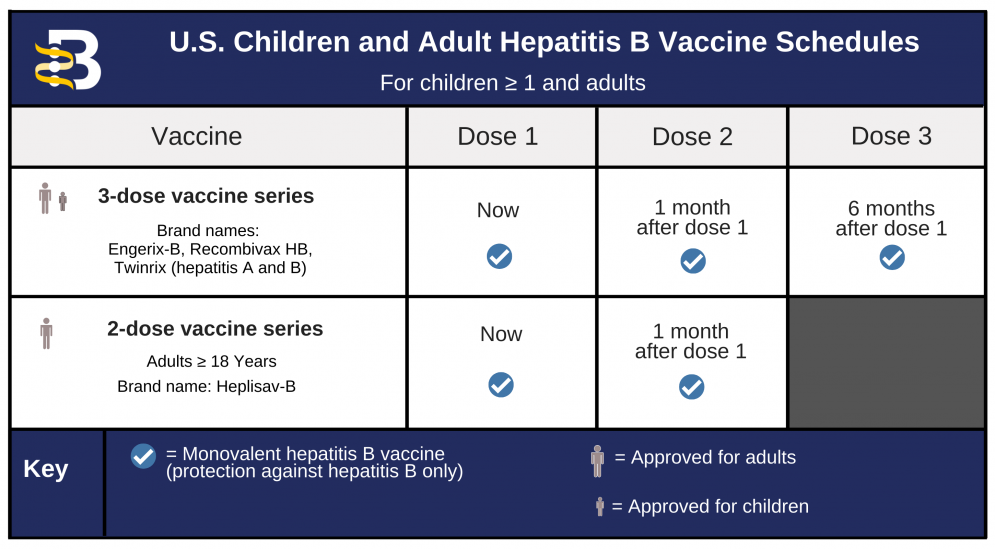
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
What Are The Side Effects
The most common of the hepatitis B vaccine are mild and include:
- Low fever or,
- Sore arm from the shot.
Prepare for your child’s vaccine visit and learn about how you can:
- Research vaccines and ready your child before the visit
- Comfort your child during the appointment
- Care for your child after the shot
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Dog Food
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
- hives
Before Taking This Medicine
Hepatitis B pediatric vaccine will not protect against infection with hepatitis A, C, and E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It may also not protect against hepatitis B if your child is already infected with the virus, even if he or she does not yet show symptoms.
Your child should not receive this vaccine if he or she ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis B. Hepatitis B pediatric vaccine should not be given to a child who is allergic to yeast.
If your child has any of these other conditions, this vaccine may need to be postponed or not given at all:
-
kidney disease
-
a bleeding or blood clotting disorder such as hemophilia or easy bruising
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a neurologic disorder or disease affecting the brain .
Your child can still receive a vaccine if he or she has a minor cold. If the child has a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, your child’s doctor may recommend waiting until the child gets better before receiving this vaccine.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity Qn
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
How Common Is Hepatitis B
One U.S. study following trends in hepatitis B infection over a three-year periodfound that 4.3% of the population had a past or present HBV infection.
Estimates suggest that about 240 million people around the world have chronic hepatitis B. Up to 1.89 million people in the United States have a chronic HBV infection.
Also Check: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Read Also: Can I Get Disability For Hepatitis C
Overview Of The National Hepb
All five countries are highly endemic for HBV . However, none of the 5 countries had conducted nationally representative seroprevalence assessments. With the exception of STP, all are countries have policies for universal vaccination with monovalent HepB-BD given soon after birth, and 3 doses of pentavalent vaccine. STP introduced HepB-BD in 2002 and is using a selective screening and targeted vaccination approach. Women are routinely screened for HBsAg during antenatal care visits, and only babies of HBV-seropositive mothers receive HepB-BD. HBV+ mothers were counselled on importance of delivering in hospitals to ensure their newborns receive HepB-BD and other postnatal care services. In 2015, STP reported high national coverage for HepB3 but low HepB-BD 14. This low rate is thought to be due to denominator issues which did not allow for appropriate statistical analysis. However, coverage among infants born to HBV+ women is high . Nigeria introduced HepB-BD in 2004 but the 2015 coverage estimates for both HepB-BD and HepB3 are low. The Gambia introduced HepB-BD in the 1990s and has consistently maintained high coverage rates for HepB-BD and HepB3 . Botswana introduced HepB-BD in the 1990s and has maintained high national coverage rates. Namibia introduced HepB-BD in 2014 and in 2015 attained a high post-introduction coverage of 87%, and 92% coverage rate for HepB3.
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C And Herpes The Same Thing
What Happens If I Miss A Dose
Contact the doctor if your child misses a booster dose or if he or she gets behind schedule. The next dose should be given as soon as possible. There is no need to start over.
Be sure your child receives all recommended doses of this vaccine. Your child may not be fully protected if he or she does not receive the full series.
Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Read Also: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Infants Born To Mothers Who Have Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
Protecting Your Baby
Infants born to women with hepatitis B must receive accurate doses of hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin to ensure complete protection. In order to protect these infants, medications should be given immediately after birth in the delivery room or within the first 12-24 hours of life*.
* See Testing and Treatment During Pregnancy section for details. Please note that testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B is a global recommendation.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends that infants born to hepatitis B positive mothers receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth, and ideally a dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin . These shots must be followed by the additional vaccine doses given on the recommended schedule. In the U.S., infants should follow a 1 month and 6-month schedule for the additional two doses.
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
What Is Hepatitis B Pediatric Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a serious disease caused by a virus. Hepatitis B causes inflammation of the liver, vomiting, and jaundice . Hepatitis can lead to liver cancer, cirrhosis, or death.
The hepatitis B pediatric vaccine is used to help prevent this disease in children and teenagers.
The vaccine helps your child’s body develop immunity to hepatitis B, but will not treat an active infection the child already has.
Vaccination with hepatitis B pediatric vaccine is recommended for all children beginning at birth, especially children and adolescents who are at risk of getting hepatitis B. Risk factors include: living with someone infected with hepatitis B virus being born to a mother who is infected with hepatitis B being on dialysis living in a facility for developmentally disabled people traveling to areas where hepatitis B is common being an adolescent who has never received a hepatitis B pediatric vaccine during childhood.
Like any vaccine, the hepatitis B pediatric vaccine may not provide protection from disease in every person.
Don’t Miss: Royal Canin Hepatic Cat Food
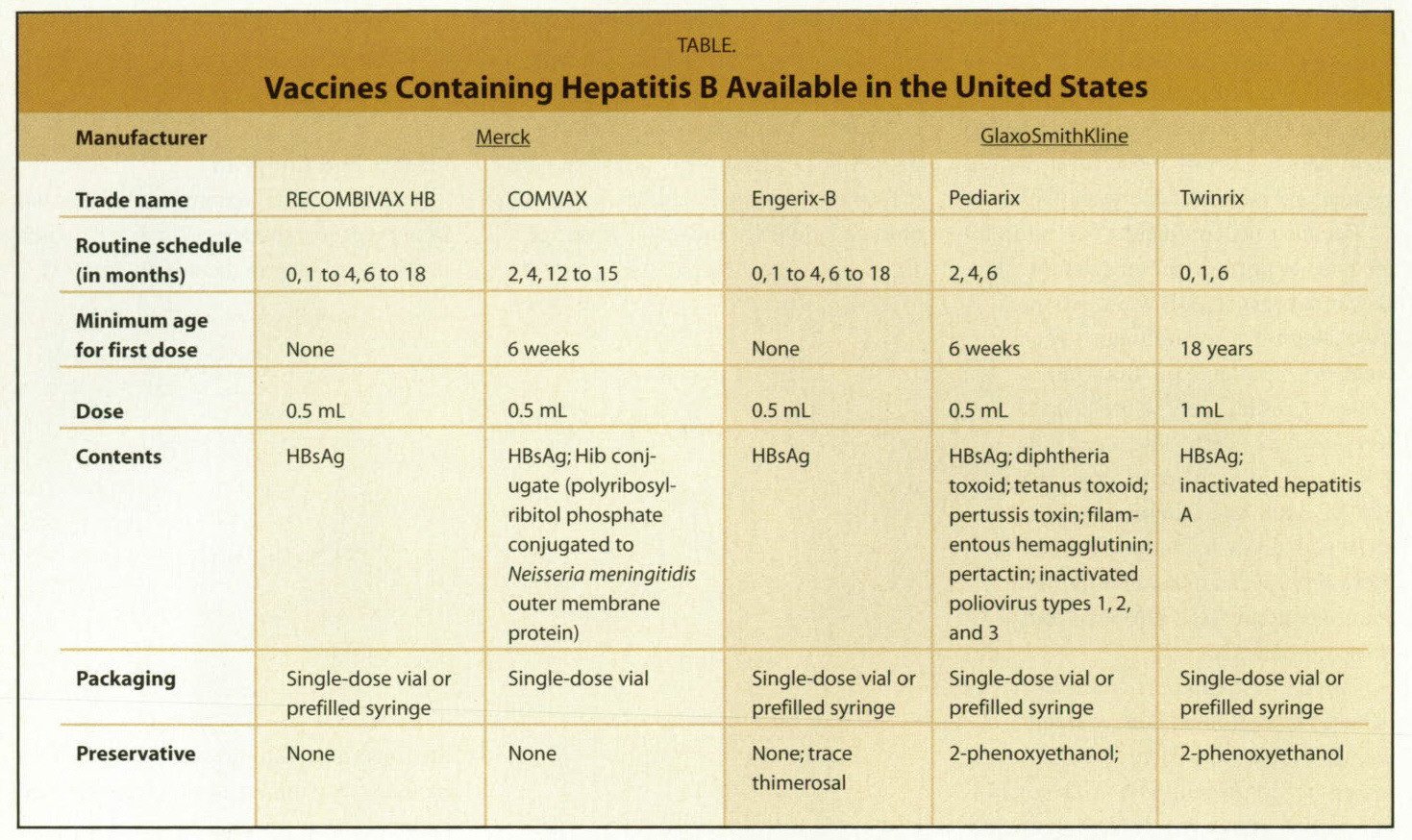
What Are Dosages Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Dosages of Hepatitis B Vaccine:
Intramuscular suspension
- 40 mcg/ml
Intramuscular suspension
- 5 mcg/0.5 ml
- 10 mcg/0.5 mg
Dosage Considerations Should be Given as Follows:
- Engerix B: 1 mL intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
- Recombivax HB: 1 mL intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
- Adults receiving dialysis or other immunocompromising conditions
- Recombivax HB : 40 mcg intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months, OR
- Engerix-B : 40 mcg intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
Routine vaccination
Catch-up vaccination
- Unvaccinated children should complete a 3-dose series
- Children aged 11-15 years: 2-dose series of adult formulation Recombivax HB is licensed for use in children aged 11 through 15 years
Dosing Considerations
Administration
- Administer intramuscularly in the deltoid muscle
- Do not give IV/intradermal
Pediatric:
- Administer in deltoid muscle for older children and adolescents anterolateral thigh preferred for neonates/infants/small children
- Do not give intravenously/intradermal
- low blood pressure
- pain when urinating
Suspected adverse events after administration of any vaccine may be reported to Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System , 1-800-822-7967
This document does not contain all possible side effects and others may occur. Check with your physician for additional information about side effects.
A Look At Each Vaccine: Hepatitis B Vaccine
View larger image The hepatitis B vaccine is given to prevent the severe liver disease that can develop when children or adults are infected with hepatitis B virus. The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age. The vaccine is also recommended for those up to 60 years of age who have not previously received it and those 60 years and older who are at increased risk or who simply want the protection afforded by vaccination.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis C Virus
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Other Reported Adverse Events And Conditions
While serious events and chronic illnesses such as chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and sudden infant death syndrome have been alleged or reported following HB vaccination, no evidence of a causal association has been demonstrated in a number of studies.
You May Like: How Does A Person Contract Hepatitis C
Do The Benefits Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine Outweigh Its Risks
Every year in the United States about 2,000 people die following an overwhelming hepatitis B virus infection. In addition, every year about 22,000 people are infected with hepatitis B. Some of them will remain chronically infected, putting them at high risk of the long-term consequences of hepatitis B virus infection: cirrhosis and liver cancer. In fact, with the exception of influenza and COVID-19 viruses, hepatitis B virus causes more severe disease and death in the United States than any other vaccine-preventable disease. On the other hand, the hepatitis B vaccine is an extremely rare cause of a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. To date, no one has died from this reaction, but it is theoretically possible that this could occur.
Because hepatitis B virus is a common cause of severe disease and death in the United States, and because the hepatitis B vaccine does not cause permanent damage or death, the benefits of the hepatitis B vaccine clearly outweigh its risks.