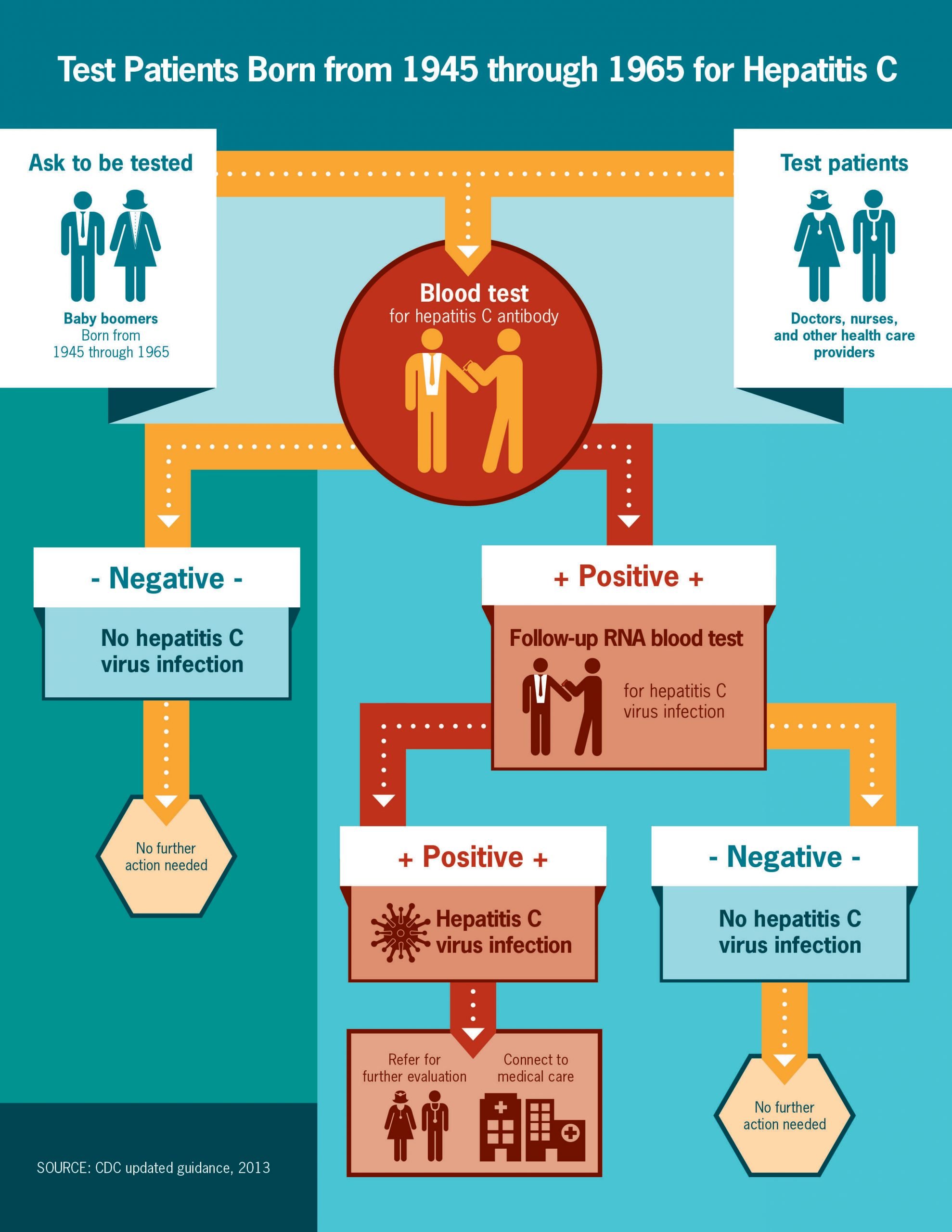
How Is A Person Tested For Hepatitis C
A viral-load test is used to check for hepatitis C in the bloodstream. Usually, hepatitis C virus can be found in a persons bloodstream two weeks after he or she becomes infected.
*Except in case of recent risk or in people with a weakened immune system**During the first six months after HCV infection, a person may spontaneously clear the virus if there was a recent risk, repeat viral-load testing to confirm chronic hepatitis C infection
When Should I Get Hepatitis C Testing
When used for early detection in patients without symptoms of hepatitis C, screening is recommended at least once for all adults aged 18 years or older, except in locations with very low prevalence of HCV. Screening is also recommended during pregnancy and for patients of any age with risk factors for HCV infection. In patients with risk factors, periodic screening is recommended for as long as risk factors persist.
Risk factors for HCV include:
- Current or past injectable drug use
- Having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Receiving kidney dialysis
- Pain in the abdomen or joints
- Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowish skin and eyes
Hepatitis C testing may also be performed when liver tests are abnormal or when diagnosing the cause of existing liver damage.
Should Every Patient Of Hepatitis Be Screened For All Types Of Hepatitis As Included In The Panel Tests
It is not necessary to conduct a hepatitis panel test on all patients. If the specific hepatitis virus that has caused the infection is known, then the specific hepatitis test may only be conducted. In some cases, doctors may want to know how the treatment is going on or to evaluate the progression of a disease. In such cases, only specific hepatitis tests are conducted.
Also Check: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Iatrogenic Exposure And Postexposure Prophylaxis
The potential of health care delivery to transmit HCV to healthcare worker is increasingly being recognized especially if infection control or disinfection practices are inadequate and contaminated equipment is shared among patients. The mechanisms of transmission in the healthcare setting are related to:
-
Improperly cleaned, disinfected, or sterilized equipment
-
Medication administration
-
Blood sampling
The CDC in collaboration with healthcare infection control practices advisory committee has issued recommendations following occupational exposure to HCV. These recommendations emphasize that each institution should have its own policy regarding follow-up of personnel who sustain percutaneous or permucosal exposure to suspected HCV infected blood. They minimally recommend:
Baseline testing for anti-HCV in source.
Baseline and follow-up testing for anti-HCV and alanine aminotransferase levels in exposed at 6 months and 1 year postexposure.
Confirmation by NAT of all anti-HCV reactive results.
Education of workers about the risk for and prevention of blood-borne infections.
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Testing Types
Testing for hep C starts off with a hep C antibody test. This test looks for human antibodies something that your body produces to fight the virus. If your hep C antibody test result is positive, then it means you have been exposed to the hep C virus at some point.
If you get a positive antibody result, then your sample of blood is tested again using a PCR test. This test looks for parts of the actual hep C virus. If the PCR test result is positive it means that you have hep C. Have a look at our Hep C Testing chart for more info on hep C tests.
What Does Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Mean
Hepatitis B surface antigen : A protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus it can be detected in high levels in serum during acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection. The presence of HBsAg indicates that the person is infectious. The body normally produces antibodies to HBsAg as part of the normal immune response to infection.
Read Also: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Test Frequency And Turnaround Time
Hepatitis C Serology testing is performed daily Monday to Friday.
Turnaround time is up to 3 days from receipt by PHO laboratory for Non-reactive antibody results. Reactive and Indeterminate HCV antibody results are available and reported within 6 days.
Repeat testing may be indicated in those with ongoing risk factors for the acquisition of HCV.
Once a patient tests positive for HCV antibodies, other than in cases of maternal antibody transfer, there is no value in repeating the test as they will remain antibody positive for life regardless of whether they have cleared the virus or are chronic carriers.
Early Treatment Can Help You Prevent Liver Cancer Or Liver Failure
According to the CDC, out of every 100 people with hepatitis C:
- 75-85 will develop chronic liver disease.
- Up to 20 will get cirrhosis, a dangerous scarring of the liver.
- 1-5 will die from liver cancer or liver failure.
Getting tested and treated early can stop the hepatitis C virus from triggering cirrhosis or cancer. Your doctor will be able to keep an eye out for signs of liver trouble. They can start treatment before you serious damage starts.
Show Sources
CDC: “Hepatitis C FAQs for Health Professionals,” “Hepatitis C Fact Sheet,” “Hepatitis C: What to Expect When Getting Tested,” “Living with Chronic Hepatitis C.”
Don’t Miss: Medicine That Cures Hepatitis C
How Are The Tests Administered
Both the HCV antibody test and HCV RNA test are evaluated through a blood draw.
Newborn and very young infant blood draws are often done by a quick heel or finger prick, depending on the size and weight of the child. Heel or finger pricks are typically easier to perform on infants. These sticks can be painful, though, so a less painful vein puncture is sometimes preferred. Vein puncture can be done at any age, however this may require multiple attempts and cause discomfort.
Whenever possible, vein puncture on infants should be performed by a pediatric-trained phlebotomist using a butterfly needle. Phlebotomists are trained to draw blood. You may be asked to help immobilize your child during the process. If youd prefer not to participate, a second phlebotomist may assist.
After blood is drawn, pressure is applied to the needle entry point to ensure proper blood clotting and a bandage is applied. The area may be sore or bruise slightly. The drawn blood is labeled and sent to a lab for examination.
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.
Also Check: The Signs Of Hepatitis C
Risk Of Hcv Infection In Recipients Of Blood Transfusion
Prior to 1992, blood transfusions carried a high risk of HCV infection, approximately 15-20% with each unit transfused. In 1988, 90% of cases of posttransfusion hepatitis were due to NANBH viruses which was later found out to be due to HCV. The move to all-volunteer blood donors instead of paid donors had significantly reduced the risk of posttransfusion hepatitis to 10%. Screening of blood further reduced the rate of posttransfusion hepatitis C by a factor of about 10,000 to a current rate of 1 per million transfusions. The few cases that still occur are due to newly infected people donating blood before they have developed antibodies to the virus, which can take up to 6-8 weeks.
Hcv Core Antigen Detection
During the past decade, several assays for the detection of the core antigen of HCV by ELISA or CLIA have been developed. These assays were envisioned as alternatives to NAT to be used in resource-limited settings, where molecular laboratory services are either not available or not widely utilized owing to cost issues. Since these assays are either ELISA or CLIA based, they are user friendly, require less technical expertise and are less expensive compared to molecular techniques. Evaluations in transfusion settings have shown that the HCVcore Ag assay detects HCV infection as effective as NAT, about 40-50 days earlier than the current third generation anti-HCV screening assays. HCV core antigen levels closely follow HCV RNA dynamics, and allow clinical monitoring of a patient’s therapy, independently of HCV genotype. The major limitation of the HCV core Ag assay is its lower sensitivity limiting its utility. A new generation CLIA based quantitative test with sensitivity comparable to that of end point PCR but less than that of real time RT-PCR has been reported.
Also Check: Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Symptoms alone generally dont offer enough information for a doctor to diagnose hepatitis C. Whats more, you might not have symptoms or notice any signs of the condition.
Thats why its so important to connect with a doctor or other healthcare professional and ask about getting tested if youve been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
The also recommend hepatitis C testing for people who have abnormal liver tests, along with those who are:
- pregnant
- on hemodialysis
A healthcare professional can order a few different tests to help diagnose hepatitis C. These include:
- Blood tests. They may order a series of blood tests to check for the virus, starting with a hepatitis C antibody test. A PCR test can tell your healthcare professional whether the virus is currently active, and viral load testing can measure the amount of virus in your blood.
- Genotype test. This test can reveal which hepatitis C genotype you have. This information will help your healthcare professional find an effective treatment approach.
- Liver function test. If blood test results suggest chronic hepatitis C or your healthcare professional believes you could have liver damage, theyll order a liver function test. This test checks your blood for signs of heightened enzymes from your liver.
- Liver biopsy.This procedure can also help check for liver damage. A biopsy involves taking a small piece of tissue from your liver and testing it for cell abnormalities.
Articles On Reasons For Hep C Tests
As far as viruses go, hepatitis C is among the sneakiest. Once it’s in your blood, it travels to your liver, where it may settle in for a silent, long-term stay. This can lead to cancer or cause the organ to fail if you don’t treat it. In fact, hepatitis C is the top reason for liver transplants in the U.S.
If you think youâve been exposed, here are five reasons to get tested right away:
Don’t Miss: Hepatic Diet For Dogs Recipes
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Can Hepatitis Patients Spread The Infection To Others
Patients can spread hepatitis infection and the spread depends on the type and stage of the hepatitis infection. Those suffering from viral hepatitis can easily spread the infection even while being asymptomatic. Those with hepatitis A can spread the infection from the time they are infected. Those with hepatitis B are contagious as long as the virus is present in the blood. Those with hepatitis C infection are contagious and can transmit the infection.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Someone Live With Hepatitis B
What Does A Negative Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A negative antibody test result usually means that the person has not been infected with hepatitis C .
The body needs at least two months to make antibodies. People with weakened immune systems are not always able to produce antibodies. This might happen in people with autoimmune disorders , HIV-positive people with a CD4 cell count below < 200 cells/mm3, and people taking immunosuppressants.
Dried Blood Spot Testing
Dried Blood Spot testing uses drops of blood from the end of your finger. It doesnt use a needle and syringe and you can do it free of charge in the privacy of your home. Your details and the results are kept private. If your test result shows you have hep C, the people who give your results can help you access hep C treatment and cure.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Hepatitis C Medicine Cost
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than 7 days post collection will not be tested.
You May Like: How Can Someone Contract Hepatitis C
Testing Procedures And Costs
The test for HCV antibodies, as well as follow-up blood tests, can be done in most labs that perform routine blood work.
A regular blood sample will be taken and analyzed. No special steps, such as fasting, are needed on your part.
Many insurance companies cover hepatitis C testing, but check with your insurer first to be sure.
Many communities offer free or low-cost testing, too. Check with your doctors office or local hospital to find out whats available near you.
Testing for hepatitis C is simple and no more painful than any other blood test.
But if youre at risk for the disease or think you may have been exposed to the virus, getting tested and starting treatment if necessary can help prevent serious health problems for years to come.
CDC recommends that all adults ages 18 years and older should be screened for hepatitis C except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%.
Also, all pregnant women should be screened during each pregnancy, except in setting where the prevalence of HCV infection is less than 0.1%.
Hepatitis C is often associated with sharing needles . But there are other methods of transmission.
For example, healthcare workers who are regularly exposed to other peoples blood are at higher risk for contracting the virus.
Getting a tattoo from an unlicensed tattoo artist or facility where needles may not be properly sterilized also increases the risk of transmission.
Treatment For Hcv Infection
Treatment for HCV infection is available. The role of treatment in acute infection is being evaluated and currently the existing data shows that response to 6 months of standard therapy with interferon in terms of absence of HCV RNA from serum is excellent and progression to chronicity is reduced. The recommended treatment for chronic HCV infection is a combination of a pegylated IFN alpha and ribavirin. The treatment duration depends on the genotype of the virus and it has two goals. The first is to achieve sustained eradication of HCV, that is, sustained virologic response , which is defined as the persistent absence of HCV RNA in serum for 6 months or more after completing antiviral treatment. The second goal is to prevent progression to cirrhosis, HCC, and decompensated liver disease requiring liver transplantation.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Get It