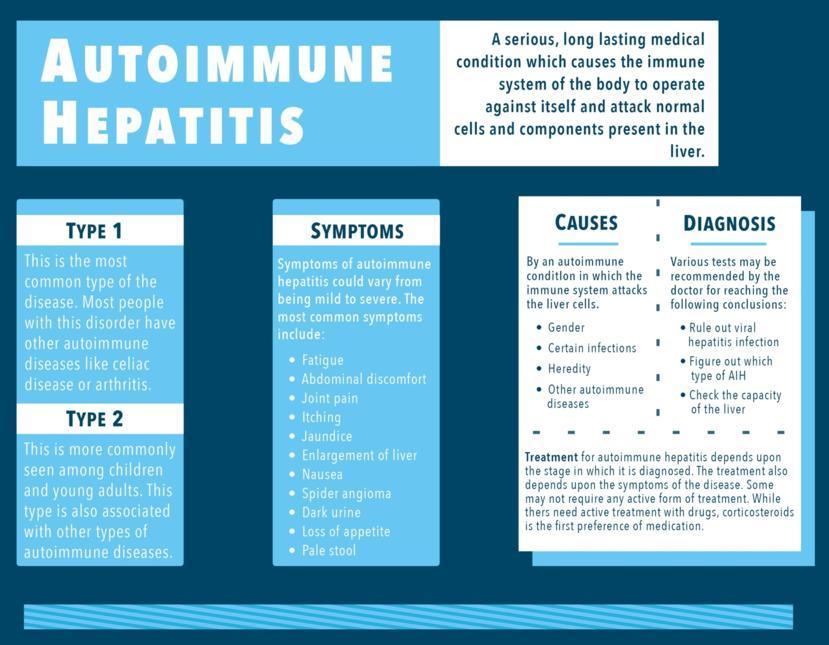
Causes And Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Mike, Facty Staff
Autoimmune hepatitis is a condition that affects the liver and is not contagious. It can cause inflammation and occurs when the body believes that the livers cells are harmful to the body, leading the immune system to attack them. When left untreated, autoimmune hepatitis can cause cirrhosis and lead to liver failure.
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated
Treatment works best when autoimmune hepatitis is found early. The goal of treatment is to control the disease and to reduce or get rid of any symptoms .
To do this, medicines are used to help slow down or suppress your overactive immune system. They also stop your body from attacking your liver.
Once you have started treatment, it can take 6 months to a few years for the disease to go into remission. Some people can stop taking medicine, but often the disease comes back. You may need treatment now and then for the rest of your life. Some people need to remain on treatment if they have relapsed many times or if their disease is severe.
In some cases autoimmune hepatitis may go away without taking any medicines. But for most people, autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease.
It can lead to scarring of the liver . The liver can become so badly damaged that it no longer works. This is called liver failure.
If you have liver failure, a liver transplant may be needed.
Be sure to ask your healthcare provider about recommended vaccines. These include vaccines for viruses that can cause liver disease.
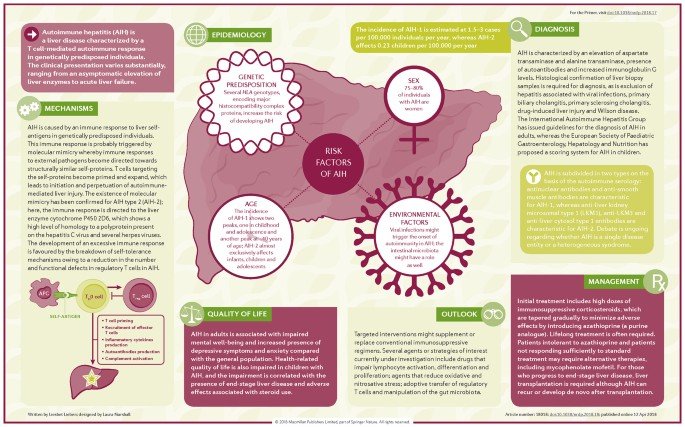
Clinical Presentation And Diagnosis
Most patients are currently diagnosed when asymptomatic, having been referred to the hepatologist for abnormal liver function tests performed for annual screening blood tests. Other frequent scenarios include screening of patients with nonliver autoimmune diseases, e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, or investigation of elevated cholesterol, evaluation of itch or unresolved cholestasis post partum. Diagnosing PBC is generally straightforward. The basis for a definite diagnosis are:
- Abnormalities in are usually present and elevated and are found in early disease. Elevations in occur in advanced disease.
- are the characteristic serological marker for PBC, being found in 90-95% of patients and only 1% of controls. PBC patients have AMA against , an enzyme complex that is found in the . Those people who are AMA negative but with disease similar to PBC have been found to have AMAs when more sensitive detection methods are employed.
- Other may be present:
- measurements are not diagnostic for PBC because they are not specific, but may have a role in prognosis.
- , and to a lesser degree , correlate with the disease’s progression toward end-stage liver failure. Anti-gp210 antibodies are found in 47% of PBC patients.
- often correlate with developing portal hypertension.
- Anti-np62 and anti-sp100 are also found in association with PBC.
Also Check: Hepatitis B How Do You Get It
Common Autoimmune Disease Symptoms
Despite the varying types of autoimmune disease, many of them share similar symptoms. Common symptoms of autoimmune disease include:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain or digestive issues
- Recurring fever
- Swollen glands
Many women say its hard to get diagnosed, something that Orbai agrees with. Its not black or white, she says. Theres usually no single test to diagnose autoimmune disease. You have to have certain symptoms combined with specific blood markers and in some cases, even a tissue biopsy. Its not just one factor.
Diagnosis can also be difficult because these symptoms can come from other common conditions. Orbai says women should seek treatment when they notice new symptoms.
If youve been healthy and suddenly you feel fatigue or joint stiffness, dont downplay that, she says. Telling your doctor helps him or her to look closer at your symptoms and run tests to either identify or rule out autoimmune disease.
Autoimmune Disease: Why Is My Immune System Attacking Itself?
Autoimmune disease affects 23.5 million Americans, and nearly 80 percent of those are women. If you’re one of the millions of women affected by this group of diseases, which includes lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and thyroid disease, you may be wondering why your immune system is attacking itself.
Would Imaging Studies Be Helpful If So Which Ones
Imaging studies are not necessary for the diagnosis of AIH however abdominal ultrasonography aids in detecting complications of AIH such as liver fibrosis/cirrhosis, evidence of portal hypertension, liver masses, and other conditions resulting in liver dysfunction, such as liver abscess, complicated choledochal cyst, or common bile duct obstruction.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Antibodies
Do Patients Recover From Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic condition, and while it can be managed, it usually cannot be cured. It is possible to achieve remission from autoimmune hepatitis with the use of steroids. However, most individuals will require treatment for the rest of their lives. The 10-year survival rate for people being treated for autoimmune hepatitis is between 83.8%94%. Without treatment, the survival rate falls to 50%60%.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Doctors aren’t sure exactly what causes your immune system to turn against your liver. Your genes may have something to do with it, since AIH can run in families.
But genes aren’t the whole story. Something you come into contact with may trigger your genes to set autoimmune hepatitis in motion. This could include:
- Medicines such as statins and hydralazine or antibiotics like nitrofurantoin and minocycline
- Infections such as viral hepatitis, herpes, Epstein-Barr, and measles
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Newborns
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis is a serious, long-lasting disease. Right now, there is no cure for autoimmune hepatitis. Fortunately, most children with autoimmune hepatitis respond well to treatment.
The goal of autoimmune hepatitis treatment is remission. This means symptoms become less severe and liver damage slows or stops. Some children are able to stop taking medicine after two or three years. These children will still need to be watched for a return of autoimmune hepatitis symptoms and other health issues.
Two main types of medicine are used to help control autoimmune hepatitis in children:
- Corticosteroids . Prednisone helps stop the immune system from attacking the liver. It also reduces liver inflammation. Budesonide is another corticosteroid that is sometimes used it has less side effects, but it is mostly given later on when the disease is under control already.
- Immunosuppressants. Azathioprine or mercaptopurine are often added to the treatment they work together with prednisone to get the immune system under control. There are other medications to suppress the immune system that can be used if the standard treatment is not working well.
Dos And Donts In Managing Autoimmune Hepatitis:
- DO remember that monitoring of your condition is important. Report any new symptoms to your health care provider promptly.
- DO call your health care provider if you notice skin color changes, side effects from medicines, joint pains, or abdominal swelling.
- DONT ignore drug side effects, such as weight gain, anxiety, confusion, thinning of bones , thinning of the hair and skin, diabetes, high blood pressure, and cataracts.
- DONT use alcohol. It may further damage your liver.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
What Is The Outlook
With treatment, most people with autoimmune hepatitis have a normal life expectancy and feel well most of the time. The treatment used for autoimmune hepatitis has improved the outlook tremendously. It is very important that you do not stop your treatment too early without your doctor’s knowledge, as your hepatitis may return. Although the condition usually returns at some point after stopping treatment, it can usually be treated again by quickly going back on medication.
There is a very small increased risk of developing liver cancer, especially if you also have ‘scarring’ of the liver due to your autoimmune hepatitis. Some doctors recommend a blood test and an ultrasound scan of your liver every so often to screen for this.
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
The liver is a large organ that sits up under your ribs on the right side of your belly . It helps filter waste from your body, makes bile to help digest food, and stores sugar that your body uses for energy. Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when your bodys infection-fighting system attacks your liver cells. This causes swelling, inflammation and liver damage.
It is a long-term or chronic inflammatory liver disease.
Autoimmune hepatitis:
- May occur at any age
- Affects women more than men
- Is often linked to other diseases where the body attacks itself
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Potential Outcomes Of Immunosuppressant Therapy
The goal of treatment is disease remission. In remission, patients experience the improvement of symptoms, the normalization of abnormal liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels, and the reduction or elimination of inflammatory activity on liver biopsy.
Most patients who embark on a course of immunosuppressant therapy respond well initially. More than 90% of adults started on corticosteroid treatment experience improvements in liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels within 2 weeks.
Remission, if it is to be achieved, typically requires 18-24 months of immunosuppressant therapy. Remission can be achieved in about 65% of patients within 18 months and 80% of patients within 3 years. Once a drug-induced remission is achieved, an attempt should be made to withdraw immunosuppression. However, a sustained remission after total drug withdrawal is seen in 13% of patients at 5 years. Patients who relapse need to restart long-term immunosuppressant therapy in an effort to normalize their biochemical abnormalities and to delay the progression of liver disease. Many such patients are maintained on chronic maintenance therapy with azathioprine.
About 13% of patients experience an incomplete response to treatment, without worsening of their condition. Most incomplete responders need long-term immunosuppression in an attempt to stabilize levels of aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase andby extensionprevent disease progression.
References
Symptoms Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Although autoimmune hepatitis is a serious condition, many patients often mistake the early symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis for flu symptoms. As the disease progresses, the severity and degree of symptoms also progress. Some common symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis include:
- Jaundice
- Fatigue
- Joint pain or joint swelling
- Cessation of menses
- Large abdomen due to large liver and spleen
- Spider-like blood vessels in the skin
- Abdominal pain or ascites
- Autoimmune hepatitis may resolve without treatment in some individuals. For the majority of individuals, it is chronic and can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure if left untreated.
Recommended Reading: Natural Cure For Hepatitis C
What Causes This Disease And How Frequent Is It
In general AIH-1 is the most common form. The prevalence is 1/200,000 in the US population however this could have been underreported, since AIH is an insidious disease and some cases could be asymptomatic. The prevalence of AIH-2 is unknown.
Previous hepatitis A virus infection has been proposed as a factor that results in molecular mimicry between the infectious particle and the liver parenchyma in AIH-1. Hepatitis C infection is frequently associated with AIH-2.
Individuals who are susceptible to AIH likely have allelic variants of DRB1 on their human leucocyte antigen region, suggesting a pathogenic role for HLA class II antigen presentation and T-cell activation. HLA DRB1*0301 and DRB1*0401 increase susceptibility for AIH-1 in North American and European populations, and DRB1*0405 and DRB1*0404 play that role in Japanese, Argentinean, and Mexican populations. In South America, individuals with DRB1*1301 likely have frequent exposure to HAV and are predisposed to AIH-1. Possession of HLA DRB1*701 and DRB1*0301 increases susceptibility to AIH-2, with the former carrying a more severe form of AIH.
About Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune liver diseases are typically long-lasting and recurring conditions. This means that you may experience persistent immune system attacks that destroy liver cells. As cells die, scar tissue known as fibrosis forms. Autoimmune diseases tend to progress slowly, and you may have long periods without symptoms. When scarring becomes extreme, liver function weakens and eventually may result in a condition known as cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is also known as liver failure or end-stage liver disease. The only cure for this condition is organ transplantation. While the only cure for severe cirrhosis is transplantation, we can help you manage the symptoms of the disease with medication before or instead of transplantation.
Our liver specialists work closely with other experts at Mount Sinai to provide a comprehensive approach to treating you if you have multiple autoimmune conditions. Our goal is to keep your immune system active and related symptoms under control.
Mount Sinai liver specialists work with colleagues in rheumatology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, radiology, and pathology to manage autoimmune liver disease. We use state-of-the-art methods of diagnosis and treatment.
If end-stage liver disease develops and you need liver transplantation, we have the expertise to help you. We have extensive experience treating patients with autoimmune liver disease. After living with chronic liver disease, through treatment, we can help restore your quality of life.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
What Is The Evidence
The evidence for treatment presented above is expert opinion only. There are no randomized controlled treatment trials in children with AIH.
McFarlane, IG. Definition and classification of autoimmune hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. vol. 22. 2002. pp. 317-24.
Krawitt, EL. Autoimmune hepatitis. N Engl J Med. vol. 354. 2006. pp. 54-66.
Mieli-Vergani, G, Vergani, D. Autoimmune hepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. vol. 8. 2011. pp. 320-9.
Ferrari, R, Pappas, G, Agostinelli, D. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis: patterns of clinical presentation and differential diagnosis of the ‘acute’ type. QJM. vol. 97. 2004. pp. 407-12.
Al-Chalabi, T, Underhill, JA, Portmann, BC. Impact of gender on the long-term outcome and survival of patietns with autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. vol. 48. 2008. pp. 140-7.
Czaja, AJ, Davis, GL, Ludwig, J. Autoimmune features as determinants of prognosis in steroid-treated chronic active hepatitis of uncertain etiology. Gastroenterology. vol. 85. 1983. pp. 713-7.
Gregorio, GV, Mieli-Vergani, G. Autoimmune liver disease in childhood. Indian J Gastroenterol. vol. 16. 1997. pp. 60-3.
Castiella, A, Lucena, MI, Zapata, EM. Drug-induced autoimmune-like hepatitis: a diagnostic challenge. Dig Dis Sci. vol. 56. 2011. pp. 2501-3.
Mieli-Vergani, G, Heller, S, Jara, P. Autoimmune hepatitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. vol. 49. 2009. pp. 158-64.
Donaldson, PT. Genetics in autoimmune hepatitis. Semin Liver Dis. vol. 22. 2002. pp. 353-64.
Autoimmune Disease Risk Factors
Researchers dont know what causes autoimmune disease, but several theories point to an overactive immune system attacking the body after an infection or injury. We do know that certain risk factors increase the chances of developing autoimmune disorders, including:
- Genetics: Certain disorders such as lupus and multiple sclerosis tend to run in families. Having a relative with autoimmune disease increases your risk, but it doesnt mean you will develop a disease for certain, says Orbai.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese raises your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis. This could be because more weight puts greater stress on the joints or because fat tissue makes substances that encourage inflammation.
- Smoking: Research has linked smoking to a number of autoimmune diseases, including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, hyperthyroidism and MS.
- Certain medications: Certain blood pressure medications or antibiotics can trigger drug-induced lupus, which is often a more benign form of lupus, Orbai says. Our myositis center also discovered that specific medications used to lower cholesterol, called statins, can trigger statin-induced myopathy. Myopathy is a rare autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness. Before starting or stopping any medications, however, make sure to talk to your doctor.
You May Like: Do You Ever Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis can cause scar tissue to start forming on the damaged liver . This makes it harder for the liver to work properly. Over time, lots of scar tissue can build up in the liver . This can block the blood flowing through the liver and may lead to problems such as bleeding in the esophagus or stomach, or water in the belly . Cirrhosis also can cause the liver to fail signs may be jaundice , bleeding/bruising, or confusion.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis In Children
The liver is a large organ in the abdomen that performs many important tasks: It removes toxins from the blood, makes substances that aid in digestion and blood clotting, and stores vitamins and minerals needed throughout the body.
Hepatitis refers to any inflammation of the liver. Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when the immune system, which normally protects the body from infection, attacks healthy cells in the liver, causing chronic inflammation. Without treatment, this inflammation can cause scarring in the liver, known as cirrhosis, and ultimately, liver failure.
Doctors at Hassenfeld Childrens Hospital at NYU Langone have extensive experience in diagnosing and treating autoimmune hepatitis in children.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Treatment
How Can Diet Improve The Condition
As the NIDDK note, there is no direct research to suggest diet or nutrition improve autoimmune hepatitis.
Doctors may, however, recommend changes in diet, as part of a general treatment plan. This may be especially important if damage to the liver leads to complications, such as cirrhosis.
Doctors will warn people to avoid alcohol in most cases, as autoimmune hepatitis can damage the liver.
Genetics And Predisposing Factors
Autoimmune hepatitis is thought to result from an environmental trigger in a genetically predisposed individual, leading to loss of tolerance of T lymphocytes with subsequent hepatocyte attack.
It is a polygenic disease and does not follow a Mendelian distribution. Therefore there is no need to screen family members of patients with AIH. There is a strong genetic association with the alleles of the major histocompatibility complex class II. The presence of human leukocyte antigen genes HLA DRB1*03 and HLA DRB1*04 predisposes to AIH type 1 and affect the disease course and response to treatment. Individuals who are positive for HLA DRB1*03 are younger, respond less favorably to corticosteroid therapy, and progress more often to liver failure. On the other hand, the presence of HLA DRB1*04 is associated with higher rates of concomitant autoimmune disorders.
Autoimmune hepatitis can also be associated with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy syndrome, an autosomal recessive disease characterized by hypoparathyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy is the only AIH-associated disease that follows a Mendelian pattern of inheritance and genetic counseling should be offered for patients and family members.
Table 1: Drugs Associated With Drug-Induced Autoimmune-Like Hepatitis
| Association |
|---|
Read Also: Is Hepatitis C Considered An Std