Certain Transfusion And Transplant Recipients
People with hemophilia dont have enough of a certain substance that allows their blood to clot normally, increasing their risk for major bleeding episodes. As a result, they need clotting factor replacement therapy to prevent them from bleeding or even treat bleeding after it starts. People who received therapy prior to 1987 are at increased risk for HCV infection because better, safer methods of developing clotting factor concentrates had not yet been developed.
Similarly, more advanced methods of testing of blood donors were implemented in 1992, and the blood supply was more carefully screened from that point onward. That means that people who received blood transfusions or solid organ transplants prior to 1992 are also at increased risk.
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is found in the blood of people with HCV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Until reliable blood tests for HCV were developed , people usually got hepatitis C from blood products and blood transfusions. Now that blood and blood products are tested for HCV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
Currently, people usually get hepatitis C by sharing needles for injection drug use. An HCV-infected woman can pass the infection to her baby during birth. It is also possible to get hepatitis C from an infected person through sexual contact, an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Read Also: Hepatitis C In Babies Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms Of Hcv
Many cases of HCV are not found because there are no symptoms, or the symptoms are vague and may seem like the flu. Symptoms may start from two weeks to six months after exposure, though the average is six to seven weeks.
Some people with HCV may have:
- Muscle and joint aches.
- Changes in the color of urine and stool.
- Jaundice . Jaundice may also cause itching.
- Take your medical history.
- Do a physical exam.
- Order blood tests.
- Many blood tests are used to look for HCV, so your doctor may choose to do one or many at once.
- In the past, this was the widely used treatment for HCV.
- Patients stay on these drugs for 2448 weeks.
- It only cures 2040% of patients and is associated with significant side effects.
- These are newer option to care for HCV. They are sometimes called direct-acting antivirals .
- These treatments do not use interferon.
- Patients stay on these for 1214 weeks.
- Most cases on these treatments have a greater than 90% chance of cure.
- Patients on these have fewer side effects, are better tolerated and have much better success rates than earlier treatments.
- These drugs are very high priced and not all health plans cover them.
A variety of drugs that work in different ways are used together to treat HCV so that the virus can be attacked in different ways to increase your chance of a cure. Your gastroenterologist or liver specialist, called ahepatologist, will help guide you through complex treatment options.
Blood Donations Before September 1991
Since September 1991, all blood donated in the UK is checked for the hepatitis C virus.
There’s a small chance you may have been infected with hepatitis C if:
- you received a blood transfusion or blood products before September 1991
- you received an organ transplant before 1992
Before 1992 donated organs were not routinely screened for hepatitis C and there is a very small risk a donated organ from someone with hepatitis C could spread the infection.
There are blood tests to check for hepatitis C infection
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Be Transmitted Through Saliva
Are You At Risk For Liver Cancer Without Knowing It
Whats the biggest threat to your liver? Its not alcohol, despite what you may have heard. It is hepatitis C, a viral infection thats transmitted through the blood.
Beforeyou assume hepatitis C doesnt affect you, know this: It’s the most common bloodborneinfection in the U.S., and approximately half of those who have it dont know becausethey have no symptoms.
Whilehepatitis C itself isnt particularly menacing, it can cause inflammation inthe liver. And this inflammation can progress to cirrhosis and ultimately livercancer, which can be deadly. Amit Singal, M.D., Medical Director of the LiverTumor Program at UT Southwestern Harold C.Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center, describes liver disease as a continuum:
Liverhealth is a spectrum, where on one end you have a normal liver, he says. Somepeople develop chronic liver disease and move along thespectrum. If this is not treated, they can develop cirrhosis over time. Andonce a patient has cirrhosis, he or she has a risk of developing liver cancerbetween 2% to 4% percent each year.
Livercancer is one of the few cancers increasing in prevalence, while the incidenceof most other types of cancer is decreasing.
Others At Increased Risk
Others at elevated risk for contracting hep C include:
- People receiving dialysis treatment for a long period of time. These people may have been exposed to infection in the healthcare setting when they were receiving dialysis.
- Children born to mothers with HCV. The CDC recommends that babies born to HCV-infected mothers be tested after 18 months of age so the test wont inadvertently pick up on any remaining maternal antibodies.
- Healthcare workers with known exposure to hep C. Needlestick injuries are a primary method of transmission of the virus in a healthcare setting.
- People who have had sex with someone whos infected with hep C. Hep C is usually transmitted through blood-to-blood contact, but sexual transmission is also a possibility.
Its a good idea to know if youre at increased risk for hep C because it might impact your overall liver function, future treatment options and your overall health. Long-term hep C can cause cirrhosis, which is scarring of the liver. It can even cause damage serious enough to possibly warrant a liver transplant. So when in doubt, err on the side of getting tested.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis C Do To The Body
Hepatitis C And Baby Boomers
According to the CDC, people born from 1945-1965, also referred to as baby boomers, are five times more likely than other adults to have hepatitis C. As a result, the CDC recommends that everyone born between these years be tested once for hepatitis C. Testing can help baby boomers that may have been living with the disease for decades to verify their health status and to determine the best course of action for treatment.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is transmitted when the blood of an infected person passes into the blood of an uninfected person. You may be at risk for hep C and should contact your health care provider for a blood test if you:
- Were born between 1945 and 1965, regardless of any other HCV-related risk factors
- Were notified that you received blood or an organ from a donor who later tested positive for HCV
- Have ever injected illegal drugs, even if you experimented only a few times many years ago
- Received a blood transfusion or solid- organ transplant before 1992
- Received a blood product for clotting problems before 1987
- Have ever been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have evidence of liver disease
- Have an HCV-positive mother
- Have been exposed to HCV through your occupation.
You may also be at risk for HCV if you:
- Have ever gotten a tattoo or piercing in a nonprofessional setting where equipment such as ink, inkwells or needles were used and potentially unsterilized
- Have had multiple sexual partners or sexually transmitted diseases
- Have ever inhaled cocaine or shared other non-injecting drugs.
Read More About:
You May Like: Hepatitis Panel Acute With Reflex To Confirmation
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Females
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
What Causes Hepatitis C
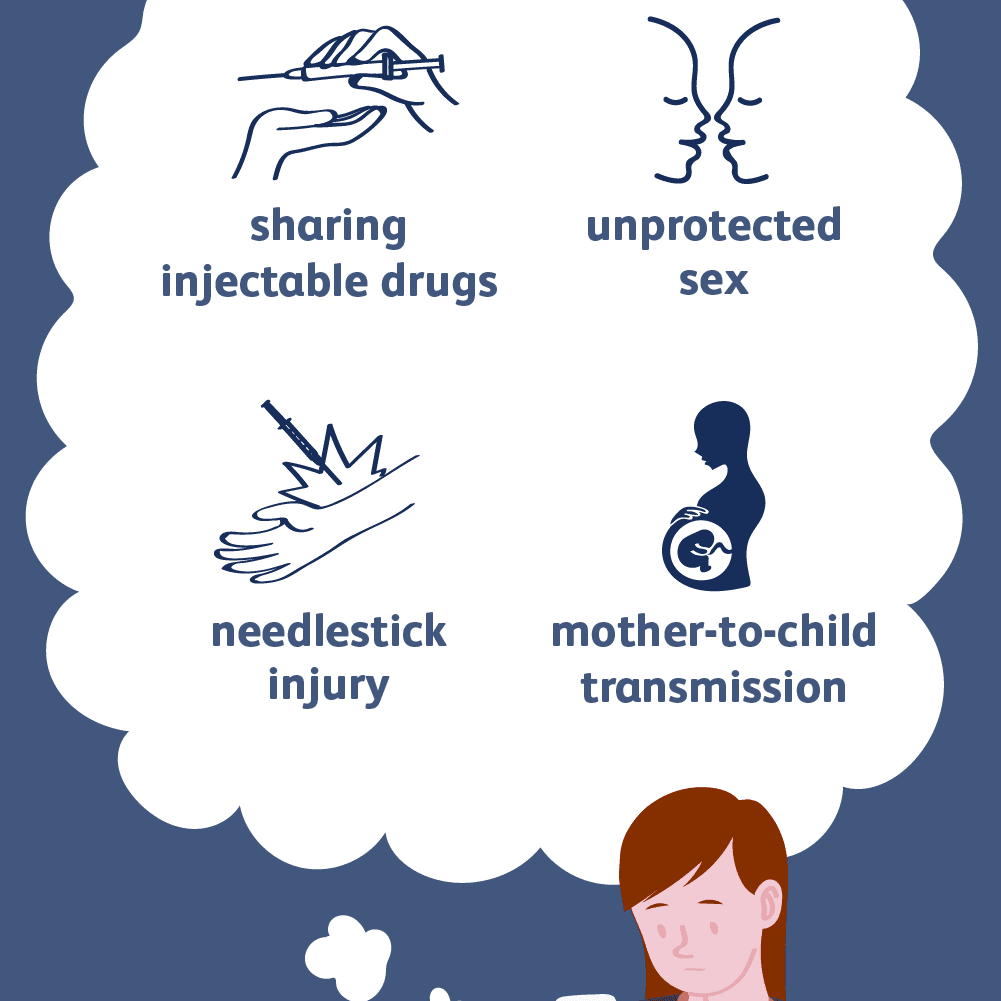
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Don’t Miss: What Drug Is Used To Treat Chronic Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Adults
How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Depending on the drug combination, the specific genotype of hepatitis C that is to be treated, any prior treatment, and whether the person has cirrhosis, the duration of medical therapy may be as few as 8 weeks, or up to 24 weeks. Most regimens are for 12 consecutive weeks. This is much shorter than the interferon-based treatments years ago that lasted up to 48 weeks. Generally, a person is not considered cured until the RNA viral load is undetectable for 24 weeks after therapy is stopped. This is called sustained virologic response or SVR.
The presence of cirrhosis or liver fibrosis is determined by liver biopsy, noninvasive fibrosis scans, or formulas that estimate liver fibrosis based on blood tests, such as AST-to-platelet Ratio Index or Fibrosis-4 Index.3
A very important aspect of treatment is the elimination of all alcohol consumption. Alcohol adds fuel to the fire when it comes to chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol greatly worsens liver fibrosis and speeds progression to cirrhosis, and there is no safe amount to drink for someone with chronic hepatitis. Drinking alcohol also makes it harder for the medications to be effective and may interfere with proper dosing.
Hepatitis C: Who Is At Risk
Hepatitis C is a serious liver disease caused by a viral infection. It can cause serious, lifelong health problems including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer and even death. Hepatitis C is a leading cause of liver cancer and the leading cause of liver transplants.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine How Many Doses
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C has an incubation period of 2 weeks to 6 months.
During this time, symptoms may appear with varying intensity and more subtle than in hepatitis B.
Some people who are infected show no symptoms at all, in other cases fatigue, jaundice , fatigue, loss of appetite, headache and sometimes abdominal pain and fever may appear.
When the infection lasts longer than six months it becomes chronic and is referred to as chronic Hepatitis C infection.
A percentage of people with chronic Hepatitis C see the disease progress and report subsequent liver damage and cancer .
Recommended Reading: Which Hepatitis Is Not Sexually Transmitted
Nat: Detection Of Hcv Rna
Molecular virological techniques play a key role in diagnosis and monitoring of treatment for HCV. Because it is difficult to cultivate the virus in cell culture, molecular techniques were instrumental in first identifying HCV, making it one of the first pathogens to be identified by purely molecular methods. NAT is considered the gold standard for detecting active HCV replication. HCV NAT is extremely useful in establishing the diagnosis of acute HCV infection, since RNA is detectable as early as 1 week after exposure via needle-stick or blood transfusion, and at least 4-6 weeks prior to seroconversion as demonstrated in a number of transmission settings. The diagnosis of HCV infection is established with antibody screening followed by NAT for HCV RNA for confirmation as well as for follow-up of patients on treatment. Viral load assessment at baseline is also critical for determining response kinetics during therapy. enumerates the role of NAT in HCV diagnosis.
Read Also: Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
What Are Signs Of Hepatitis B
When you first get hepatitis B, it is called acutehepatitis B. Most adults who have hepatitis B willrecover on their own. However, children and someadults can develop chronic hepatitis B.
Acute hepatitis B: Signs of acute hepatitis B canappear within 3 months after you get the virus.These signs may last from several weeks to 6 months.Up to 50% of adults have signs of acute hepatitis Bvirus infection. Many young children do not show anysigns. Signs include:
- Yellow skin or eyes
Read Also: What Is The Best Treatment For Hepatitis C