Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
These can be picked up in a number of ways. Most people get them by eating food or drinking water which has been contaminated with infected faeces as a result of poor hygiene or inadequate cooking. Less commonly, they can be transmitted through cuts in the skin or mucous membranes – sharing razor blades, toothbrushes, or needles if injecting drugs are common risk factors. Hepatitis A can be also passed on by having unprotected sex with a person who already has the virus, usually between men who have sex with men. The hepatitis caused by HAV and HEV is usually mild, and doesnt require treatment, although hepatitis E can occasionally be serious in those with a weakened immune system. A vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis A – people with cirrhosis and those visiting developing countries should be vaccinated. There is not yet a commercially available vaccine for HEV. Find out more about hepatitis E here.
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis B
A hepatitis B infection can result in either an acute infection or a chronic infection. When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an “acute infection” . Most healthy adults that are infected do not have any symptoms and are able to get rid of the virus without any problems. Some adults are unable to get rid of the virus after six months and they are diagnosed as having a “chronic infection.” A simple blood test can diagnose an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus. The younger a person is when they are first infected, the greater the risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection:
- More than 90% of infants that are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of young children between 1 and 5 years who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of healthy adults 19 years and older who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
The recommendation for hepatitis B vaccination of babies and children is so important because they are at the greatest risk of developing a chronic infection if they are not protected against the hepatitis B virus as soon as possible.
What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis B
About 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments almost always work if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Via Saliva
How Can I Protect Myself Against Viral Hepatitis
There are many ways you can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis:
- Get the vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- Use a condom during sex.
- Don’t share needles to take drugs.
- Practice good personal hygiene such as thorough hand-washing with soap and water.
- Don’t use an infected person’s personal items.
- Take precautions when getting any tattoos or body piercings.
- Take precaution when traveling to areas of the world with poor sanitation.
- Drink bottled water when traveling.
It is very important that you take these preventive measures if you participate in risky behaviors. Take preventive steps, too, if you work in places like a nursing homes, dormitories, daycare centers, or restaurants where there you have extended contact with other people and a risk of coming into contact with the disease.
How Is Viral Hepatitis Spread
Hepatitis A and hepatitis E usually spread through contact with food or water that was contaminated with an infected person’s stool. You can also get hepatitis E by eating undercooked pork, deer, or shellfish.
Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and hepatitis D spread through contact with the blood of someone who has the disease. Hepatitis B and D may also spread through contact with other body fluids. This can happen in many ways, such as sharing drug needles or having unprotected sex.
Recommended Reading: What Is Acute Hepatitis C
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
Overview Of Acute Viral Hepatitis
, MD, MPH, Weill Cornell Medical College
-
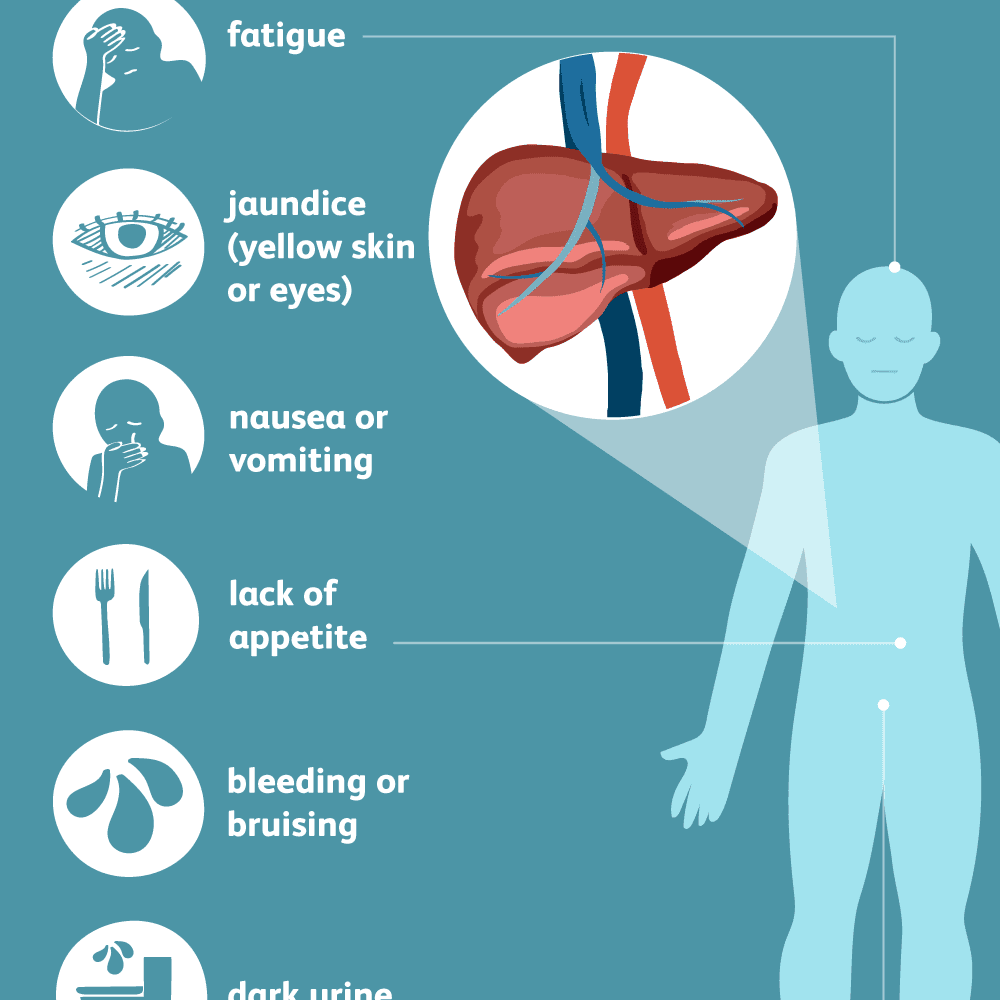
Symptoms range from none to very severe.
-
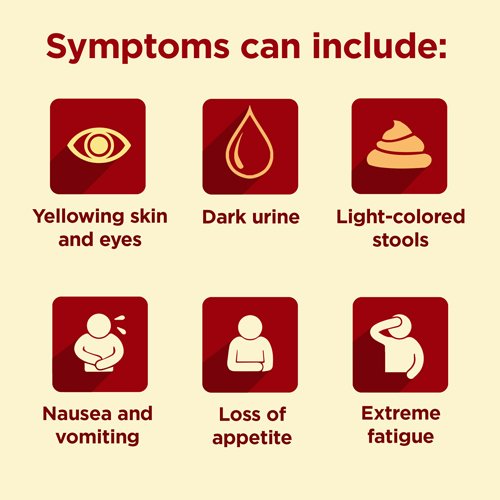
Affected people may have a poor appetite, nausea, vomiting, fever, pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, and jaundice.
-
Doctors do blood tests to diagnose hepatitis and identify its cause.
-
Vaccines can prevent hepatitis A, B, and E .
-
Usually, specific treatment is not needed.
Acute viral hepatitis is common throughout the world. Most cases of acute viral hepatitis resolve on their own, but some persist and progress to chronic hepatitis Overview of Chronic Hepatitis Chronic hepatitis is inflammation of the liver that lasts at least 6 months. Common causes include hepatitis B and C viruses and certain drugs. Most people have no symptoms, but some have vague… read more .
Don’t Miss: Is There A Home Test For Hepatitis C
What Is Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
What Is Acute Severe Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Depending on the cause, the disease can be very sudden and progress to liver failure over a few days to weeks . Some types of hepatitis can be treated and most cases recover. Acute severe hepatitis in children is a rare condition in Canada, and in many cases, an underlying or contributing cause is not known. Most children recover with supportive medical care.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Hepatic Steatosis
When To See Your Doctor
Always check with your doctor if you have any of the signs of hepatitis. If you don’t get treatment it can lead to cirrhosis, a serious scarring of your liver.
Also make an appointment if a friend or member of your family comes down with the disease. There’s a risk you could get infected, too.
Be on the lookout for symptoms of hepatitis if you travel to a country where the disease is common. Call your doctor if you think you’re showing any signs.
Show Sources
How Long Does It Last
Hepatitis A can last from a few weeks to several months.
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long condition. More than 90% of unimmunized infants who get infected develop a chronic infection, but 6%10% of older children and adults who get infected develop chronic hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious, life-long infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Diagnosis Of Acute Viral Hepatitis
Doctors suspect acute viral hepatitis based on symptoms. During the physical examination, a doctor presses on the abdomen above the liver, which is tender and somewhat enlarged in about half of the people with acute viral hepatitis.
Doctors suspect fulminant hepatitis if
-
People are very ill and develop jaundice very quickly.
-
Mental function quickly deteriorates.
-
Blood tests to determine how quickly blood clotsâprothrombin time or international normalized ratio âare abnormal.
-
People who have liver disease start worsening rapidly.
Treatment Of Acute Hepatitis In Children
Also read: Hepatitis: Be Safe From Viral Hepatitis With These Expert Tips
There are the standard precautions of clean water, good food, and healthy habits to prevent any type of liver infection. Helping to prevent the spread of viral hepatitis can be done by having good personal health habits, such as hand washing. The parents can immunize the child against the two most common viral infections of the liver that cause hepatitis A and B. Other types of viral hepatitis can be contracted from anywhere. There isn’t much you can do to protect yourself from that. However, as previously stated, close correlation and follow-up of any child with any type of liver dysfunction goes a long way toward preventing morbidity and mortality. To stop your childs liver from damage, your childs treatment may include:
- Medicines can be used to relieve itching, treat a virus, or manage an autoimmune disease
- Supportive care includes eating a nutritious diet and getting adequate rest
- Reducing the risk is important and can be made sure by abstaining from alcohol and illegal drugs
- Blood testing can indicate whether or not the disease is progressing
- Hospital stay, but it is only done in extreme cases
- Liver transplant is also done in cases of advanced liver failure
All image credits: Freepik
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B
What Is The Outlook For Hepatitis
Hepatitis A and E usually only cause short-term infections that your body can overcome. The others can also cause acute infections, but might also cause chronic infections. The chronic forms are more dangerous. Hepatitis non-E is usually acute, but can become chronic.
Most people recover fully from hepatitis even though it might take several months for the liver to heal. To help improve your health and to help speed up your recovery:
- Practice good nutrition.
- If you feel sick, rest.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about your medicines, even over-the-counter drugs or vitamins and supplements, to know which ones you should take and which to avoid until you are recovered.
With hepatitis, your healthcare provider will also be looking for long-term damage to the liver in the forms of cirrhosis or liver failure. You may be asked to take other types of tests, such as liver function tests, imaging tests or possibly a liver biopsy.
If you have questions, new symptoms, or worsening of any existing symptoms, you should call the office of your healthcare provider.
In the U.S., A, B and C are the most common viral forms of hepatitis. It doesnt matter how you were infectedwhat matters is taking care of yourself once you have been diagnosed and taking care not to spread the infection to anyone else.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 01/06/2020.
References
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
Read Also: How To Spread Hepatitis B
How Is Acute Hepatitis C Treated
Acute hepatitis C is typically monitored and not treated. Treatment during the acute stage doesnt change the risk that the disease will progress to the chronic form. An acute infection may resolve on its own without treatment. The following treatment may be all thats necessary:
- adequate fluids
Some people may need treatment with prescription medication. Your doctor will be able to work with you about what treatment options may be best for you.
Those most at risk for acute and chronic hepatitis C are people who use or share contaminated needles. Mothers can transmit HCV to their babies during childbirth, but not through breastfeeding. Other risk factors for transmission of HCV include:
- healthcare work, especially work around needles
- getting a tattoo or body piercing with unsterile equipment
- undergoing hemodialysis
- living in a household with someone with HCV
- sharing personal hygiene products, such as razors or toothbrushes
- engaging in sexual activity with multiple partners without condoms or dental dams
- having a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992 or receiving clotting factors before 1987
The most serious long-term risk of acute hepatitis C is developing chronic hepatitis C, which can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. In 75 to 85 percent of those with acute hepatitis C, the disease will progress to the more serious chronic hepatitis C.
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, do individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . Up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
You May Like: What Kind Of Virus Is Hepatitis C
Deterrence And Patient Education
Vaccinations for both hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus have been available since the 1990s and have significantly decreased the incidence of these infections. Hepatitis A virus gets transferred by fecal-oral contamination, and improved food handling, water purification, and improved hygiene will reduce the risk of spreading infection. The risk of contracting hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection can be decreased by avoiding IV drug use and safe sex practices.
Accidently toxic ingestion of acetaminophen by children can be reduced with safe storage practices out of reach from children and utilizing packaging that utilize childproof safety precautions. Also, in adults, unintentional toxic ingestion can be reduced with education about the many non-prescription products which contain acetaminophen.
For stable minimally symptomatic patients, if an etiology for acute hepatitis is not determined initially, then they need follow-up to monitor for the normalization of the liver tests or further evaluation if the abnormal test results continue.
What Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Patients infected with HBV and HCV can develop chronic hepatitis. Doctors define chronic hepatitis as hepatitis that lasts longer than 6 months. In chronic hepatitis, the viruses live and multiply in the liver for years or decades. For unknown reasons, these patients’ immune systems are unable to eradicate the viruses, and the viruses cause chronic inflammation of the liver.
Chronic hepatitis can lead to the development over time of extensive liver scarring , liver failure, and liver cancer. Liver failure from chronic hepatitis C infection is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the U.S. Patients with chronic viral hepatitis can transmit the infection to others with blood or body fluids as well as infrequently by transmission from mother to newborn.
Don’t Miss: How Can Someone Get Hepatitis C
How Do Doctors Treat Acute Hepatitis
If you have mild acute viral hepatitis:
-
You’ll probably recover in 4 to 8 weeks with no special treatment
-
Your doctor will ask you not to drink alcohol or take certain drugs until you’re healthy
If you have severe acute viral hepatitis, you may need:
-
To be cared for in the hospital
-
Medicines that help kill the virus
-
Rarely, a liver transplant Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation is the surgical removal of a healthy liver or sometimes a part of a liver from a living person and then its transfer into a person whose liver no longer functions. (See… read more
Treatment Of Acute Viral Hepatitis

-
Supportive care
-
Antiviral drugs for acute hepatitis C
For most people with acute viral hepatitis, special treatment is not necessary. However, people with severe acute hepatitis may require hospitalization so that symptoms can be treated. If doctors suspect that fulminant hepatitis is developing, the person is hospitalized so that mental status can be monitored, liver tests can be done, and doctors can determine whether liver transplantation is needed.
After the first several days, appetite usually returns and people do not need to stay in bed. Severe restrictions of diet or activity are unnecessary, and vitamin supplements are not required. Most people can safely return to work after the jaundice clears, even if their liver test results are not quite normal.
People with hepatitis should not drink alcohol until they have fully recovered.
The infected liver may not process drugs normally. So a doctor may need to stop a drug or reduce the dosage of a drug that could accumulate to harmful levels in the body . Thus, people with hepatitis should tell their doctor all the drugs they are taking , so that the dosage of the drug can be adjusted if necessary.
If itching occurs, cholestyramine, taken by mouth, is often effective.
Read Also: What Is Stage 3 Hepatitis C