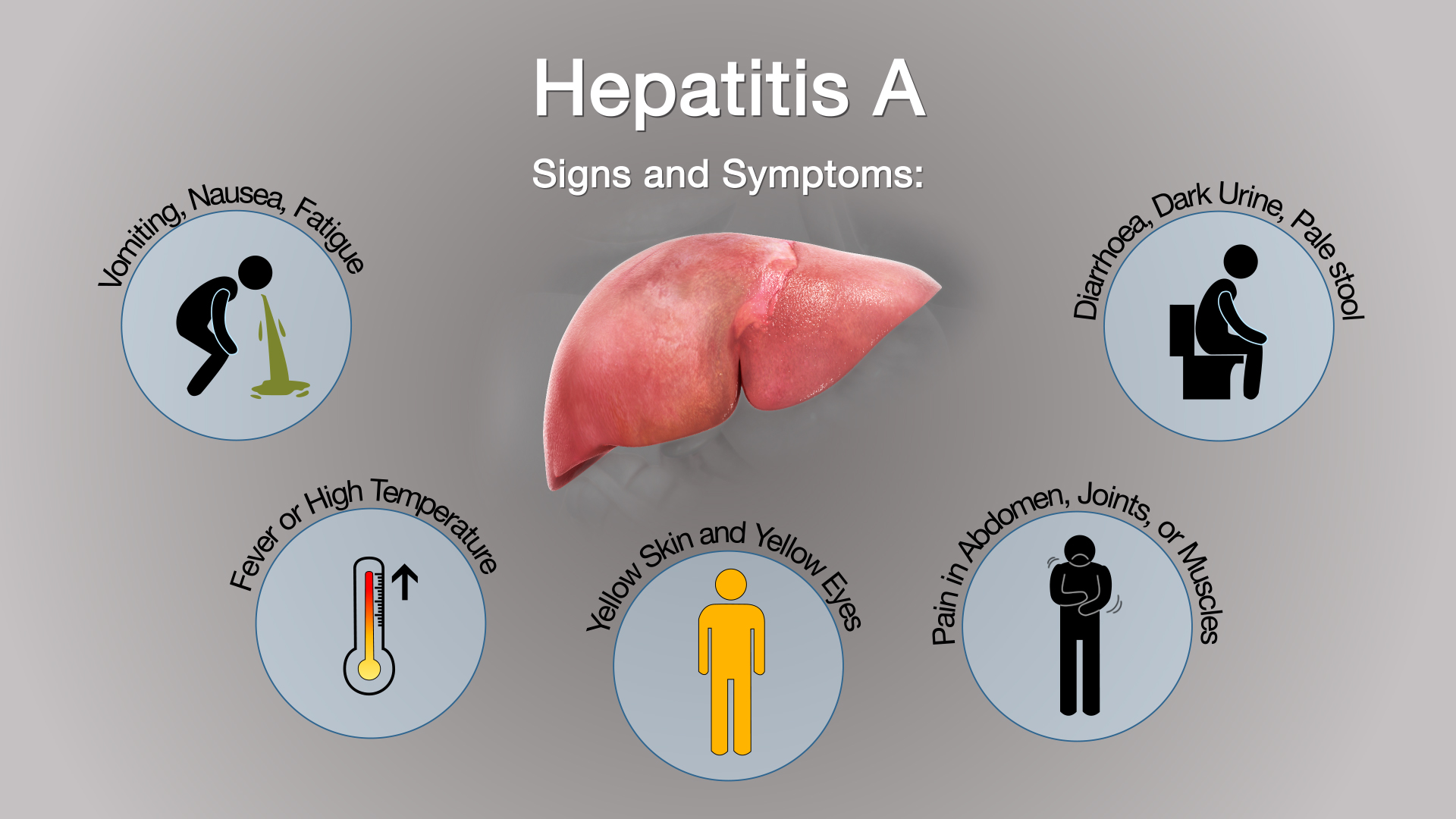
What Are The Seven Signs Of Hepatitis
The different forms of hepatitis have different signs and symptoms, making regular screenings important for health. While hepatitis B and C dont always cause symptoms, hepatitis A can trigger symptoms similar to the flu as well as these seven common signs:
While these symptoms can resolve in a few weeks, hepatitis A can lead to serious illness that lasts for months. If you suspect you may have hepatitis, schedule an appointment with Dr. Rivas right away to get a diagnosis and start treatment if applicable.
Willowbrook State School Experiments
A New York University researcher named Saul Krugman continued this research into the 1950s and 1960s, most infamously with his experiments on mentally disabled children at the Willowbrook State School in New York, a crowded urban facility where hepatitis infections were highly endemic to the student body. Krugman injected students with gamma globulin, a type of antibody. After observing the temporary protection against infection this antibody provided, he then tried injected live hepatitis virus into students. Krugman also controversially took feces from infected students, blended it into milkshakes, and fed it to newly admitted children.
How Can You Prevent Alcoholic Hepatitis
The best way to prevent alcoholic hepatitis is to avoid alcohol or drink only in moderation. Moderate drinking is defined as less than two drinks per day for men and less than one drink per day for women.
You can also reduce your risk by taking steps to protect yourself from hepatitis B and hepatitis C. The bloodborne viruses that cause these conditions can be transmitted in several ways, including shared needles or razors and through body fluids during sex. Currently, vaccines are available for hepatitis B, but not for hepatitis C.
Your healthcare team may also recommend certain lifestyle changes based on your specific symptoms and health needs.
For example:
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
Hepatitis C: What Happens
About 25% of people who get hepatitis C defeat the virus after a short-term infection. The rest will carry the virus in their body for the long term. Chronic hepatitis C can cause very serious complications, including liver failure and liver cancer. There are effective treatments for the virus, though.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis A: What Happens
Hepatitis A is highly contagious and can spread from person to person in many different settings. It typically causes only a mild illness, and many people who are infected may never realize they’re sick at all. The virus almost always goes away on its own and does not cause long-term liver damage.
Also Check: What’s In The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Symptoms Of A Chronic Infection
If the hepatitis C infection progresses to a chronic infection , it can take years before symptoms develop. Symptoms of advanced liver disease caused by long-term chronic infection can include: jaundice fluid build-up and blood in stool or vomit. Sleep disturbances, depression, weight loss, dry or itchy skin, and brain fog also occur in people with chronic hepatitis C but the cause of these symptoms remains uncertain.
Cytopathic Effects On The Host Cell
The range of structural and biochemical effects that viruses have on the host cell is extensive. These are called ”. Most virus infections eventually result in the death of the host cell. The causes of death include cell lysis, alterations to the cell’s surface membrane and . Often cell death is caused by cessation of its normal activities because of suppression by virus-specific proteins, not all of which are components of the virus particle. The distinction between cytopathic and harmless is gradual. Some viruses, such as , can cause cells to proliferate without causing malignancy, while others, such as , are established causes of cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Manage Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
Symptoms alone generally dont offer enough information for a doctor to diagnose hepatitis C. Whats more, you might not have symptoms or notice any signs of the condition.
Thats why its so important to connect with a doctor or other healthcare professional and ask about getting tested if youve been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
The also recommend hepatitis C testing for people who have abnormal liver tests, along with those who are:
- pregnant
- on hemodialysis
A healthcare professional can order a few different tests to help diagnose hepatitis C. These include:
- Blood tests. They may order a series of blood tests to check for the virus, starting with a hepatitis C antibody test. A PCR test can tell your healthcare professional whether the virus is currently active, and viral load testing can measure the amount of virus in your blood.
- Genotype test. This test can reveal which hepatitis C genotype you have. This information will help your healthcare professional find an effective treatment approach.
- Liver function test. If blood test results suggest chronic hepatitis C or your healthcare professional believes you could have liver damage, theyll order a liver function test. This test checks your blood for signs of heightened enzymes from your liver.
- Liver biopsy.This procedure can also help check for liver damage. A biopsy involves taking a small piece of tissue from your liver and testing it for cell abnormalities.
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis happens when scar tissue permanently replaces the healthy tissue of your liver. Scar tissue affects the normal function of your liver and can eventually cause it to fail.
If you develop cirrhosis as a result of heavy alcohol use, alcoholic hepatitis can get worse. Cirrhosis can also raise your risk of liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Ab With Reflex To Hcv Pcr
Hepatitis A And B Vaccines
There are vaccines to protect against hepatitis A and B. The CDC recommends hepatitis A vaccination for all children ages 12 to 23 months and for adults who plan to travel or work in areas with hepatitis A outbreaks or who have other risk factors. People with chronic hepatitis B or C should also get the hepatitis A vaccine if they don’t already have immunity to the disease. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants at birth and for adults who have any of the risk factors we discussed earlier. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
When To See Your Doctor
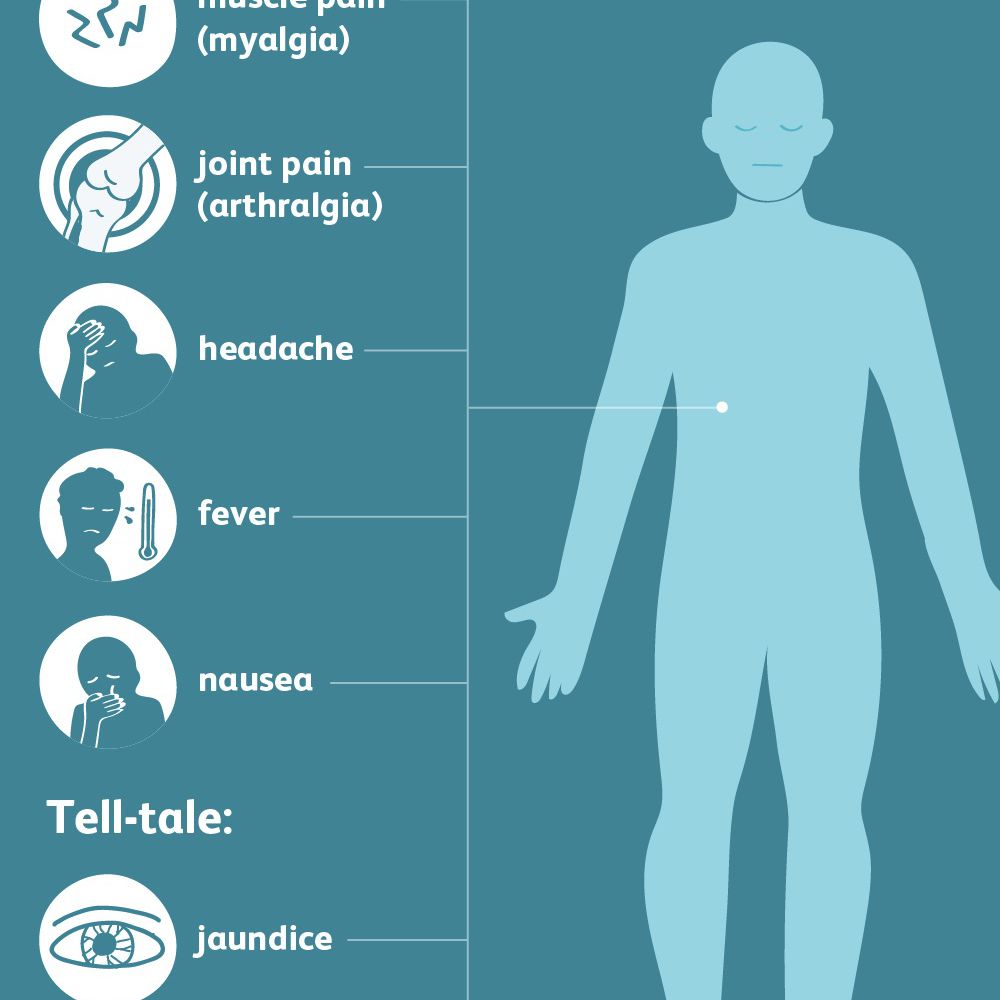
Always check with your doctor if you have any of the signs of hepatitis. If you don’t get treatment it can lead to cirrhosis, a serious scarring of your liver.
Also make an appointment if a friend or member of your family comes down with the disease. There’s a risk you could get infected, too.
Be on the lookout for symptoms of hepatitis if you travel to a country where the disease is common. Call your doctor if you think you’re showing any signs.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose For Adults
How Can I Protect Myself Against Viral Hepatitis
There are many ways you can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis:
- Get the vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- Use a condom during sex.
- Don’t share needles to take drugs.
- Practice good personal hygiene such as thorough hand-washing with soap and water.
- Don’t use an infected person’s personal items.
- Take precautions when getting any tattoos or body piercings.
- Take precaution when traveling to areas of the world with poor sanitation.
- Drink bottled water when traveling.
It is very important that you take these preventive measures if you participate in risky behaviors. Take preventive steps, too, if you work in places like a nursing homes, dormitories, daycare centers, or restaurants where there you have extended contact with other people and a risk of coming into contact with the disease.
Symptoms Of An Acute Infection
Few people show symptoms during acute infection . These symptoms can include: fatigue tenderness or an aching feeling on the right side of the abdomen decreased appetite perhaps with weight loss flu-like symptoms nausea tendency to bruise or bleed easily jaundice rash dark-coloured urine and light or clay-coloured stools. These symptoms often go away after a short time.
Don’t Miss: Can I Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Initial symptoms of hepatitis are vague and could be attributed to other things.
They include nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, and vomiting. As hepatitis progresses, other symptoms include dark urine and light-colored stool. The more serious symptoms include jaundice, which is the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
As this inflammation of the liver becomes more prominent, then you get the most distinctive symptoms, like the whites of the eyes turn yellow and a yellowish cast on the skin, Schaffner said. It can be accompanied by light stools and dark urine. The symptoms of hepatitis are vague until it gets more serious.
How Long Does Hepatitis A Last
How long it lasts can vary from person to person. Symptoms can range from mild to severe. Some things to keep in mind:
- Mild hepatitis A may last 1 to 2 weeks.
- Most people are much better within 3 weeks.
- Young children who get symptoms usually get better within 2 months.
If you have a severe infection, it can cause problems for several months. You may need to stay in the hospital.
Some people have symptoms that can last more than 3 months or have problems that come and go for 3 to 9 months.
Show Sources
CDC: “Traveler’s Health: Hepatitis A,” “Viral Hepatitis,” Hepatitis A Questions and Answers for the Public,” “Hepatitis A Vaccine.”
National Health Service: “Hepatitis A — Complications.”
Mandell, G.L., Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., editors, Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 7th edition, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2009.
Long, S.S., editor, Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 3rd edition, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2008.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases: “Hepatitis A Vaccine Recommendations.”
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis A.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis A virus infection in adults: Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis.â
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B that are available in the U.S. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. Since you can only get hepatitis D if you have hepatitis B, getting the vaccine against B should protect you against hepatitis D. There is no FDA approved vaccine against hepatitis E, but vaccines against hepatitis E exist overseas .
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- alcohol
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Genotype 1b Treatment
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Hepatitis A: How Does It Spread

It usually spreads through food or water. Food can be tainted when it’s touched by a person with hepatitis who did not wash their hands after using the bathroom. This transfers tiny amounts of infected stool to the food. Raw shellfish, fruits, vegetables, and undercooked foods are common culprits in hepatitis A outbreaks. The virus can also spread in daycare centers if employees aren’t careful about washing hands after changing diapers.
Also Check: Which Hepatitis Is Not Sexually Transmitted
What Do Hepatitis Symptoms Look Like In Children
The C.D.C. issued an alert after clusters of severe hepatitis cases popped up among children around the globe. What signs should parents watch out for?
-
Send any friend a story
As a subscriber, you have 10 gift articles to give each month. Anyone can read what you share.
Give this article
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued an alert on Thursday to physicians nationwide notifying them of a cluster of severe and unexplained hepatitis cases in otherwise healthy young children.
Between October 2021 and February 2022, nine children between the ages of 1 and 6 in Alabama were admitted to the hospital with acute hepatitis two required liver transplants.
Similar cases have also popped up in North Carolina, as well as in Europe. The U.K. Health Security Agency has reported more than 100 cases of sudden-onset hepatitis in children under 10 since January 2022, 10 of whom required liver transplants.
Heres what we know about these hepatitis cases, and what symptoms parents should watch for.
Does Hepatitis A Always Cause Symptoms
There’s a lot of variety in how people feel when they have the disease. It’s possible you might not have any symptoms. But people often feel and look sick. You might even need to go to the hospital.
Symptoms and complications are more common as you get older. Most children under age 6 with hep A don’t have any.
Also Check: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: What Happens
Many adults who get hepatitis B have mild symptoms for a short time and then get better on their own. But some people are not able to clear the virus from the body, which causes a long-term infection. Nearly 90% of infants who get the virus will carry it for life. Over time, hepatitis B can lead to serious problems, such as liver damage, liver failure, and liver cancer.
When Should You See A Doctor Or Other Healthcare Professional
Since so many people dont experience any symptoms, healthcare professionals recommend getting screened for hepatitis C at least once in your adult life. They may recommend more frequent screenings if you have a higher risk of contracting the virus.
Hepatitis C doesnt always become severe, but the chronic form can increase your risk for liver damage, liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have any symptoms that suggest hepatitis C, especially if theres a chance youve been exposed, connect with a doctor or another healthcare professional as soon as possible to discuss your options for testing and treatment.
With a prompt diagnosis, you can get treatment earlier, which may help prevent damage to your liver.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A And C Symptoms
What Causes Hepatitis A And How Is It Contracted
People develop a hepatitis A infection after contracting HAV. This virus is typically transmitted by ingesting food or liquid contaminated with fecal matter that contains the virus. Once transmitted, the virus spreads through the bloodstream to the liver, where it causes inflammation and swelling.
In addition to transmission from eating food or drinking water containing HAV, the virus can also be spread by close personal contact with someone who already has it. HAV is contagious, and a person who has hepatitis A can easily pass the disease to others living in the same household.
You can contract hepatitis A by:
- eating food prepared by someone with the hepatitis A virus
- eating food handled by preparers who dont follow strict hand-washing routines before touching food that you eat
- eating sewage-contaminated raw shellfish
- having sex with someone who has the hepatitis A virus
- drinking polluted water
- coming in contact with hepatitis A-infected fecal matter
If you contract the virus, youll be contagious 2 weeks before symptoms even appear. The contagious period ends about 1 week after symptoms appear.