Adults Living With Hepatitis B
If you test positive for the hepatitis B virus for longer than 6 months, this indicates that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection.
All patients with chronic hepatitis B infections, including children and adults, should be monitored regularly since they are at increased risk for developing cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
You should make an appointment with a hepatologist or gastroenterologist familiar with hepatitis B. This specialist will order blood tests and possibly a liver ultrasound to evaluate your hepatitis B status and the health of your liver. Your doctor will probably want to see you at least once or twice a year to monitor your hepatitis B and determine if you would benefit from treatment.
Not everyone who tests positive for hepatitis B will require medication. Depending on your test results, you and your doctor might decide to wait and monitor your condition. If your test results indicate that you would be a good candidate for treatment, then your doctor will discuss the current treatment options with you. Whether you start treatment or not, your doctor will want to see you every six months, or at minimum once every year.
Before you start any treatment, make sure you research each treatment option, and ask your doctor to thoroughly explain each option, so that you are well informed. It also might be a good idea to get a second opinion from another doctor before starting any treatment, because more information is always better!
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hbv Infection
HBV can cause a wide range of symptoms, from a mild illness and general feeling of being unwell to more serious chronic liver disease that can lead to liver cancer. Someone with hepatitis B may have symptoms similar to those caused by other viral infections, like the flu. The person might:
- be extra tired
- feel like throwing up or actually throw up
- not feel like eating
- have a mild fever
HBV also can cause darker than usual pee, jaundice , and belly pain.
People exposed to hepatitis B may start to have symptoms from 1 to 6 months later. Symptoms can last for weeks to months.
In some people, hepatitis B causes few or no symptoms. But even someone who doesn’t have any symptoms can still spread the disease to others.
What Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
Hepatitis B is a serious infection. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer, which can cause severe illness and even death.
If a pregnant woman has the hepatitis B virus, her baby has a very high chance of having it unless the baby gets a special immune injection and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
Sometimes, HBV doesn’t cause symptoms until a person has had the infection for a while. At that stage, the person already might have more serious problems, such as liver damage.
Don’t Miss: How Bad Is Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
Considerable progress has been made by past clinical trials in the medical treatment of hepatitis C. The rate of cure has increased with the development of direct-acting, all-oral antiviral regimens, and the length of therapy is much shorter. Treatment recommendations continue to change as new medicines become available. Treatment helps to reduce progression of liver damage to cirrhosis, may prevent liver cancer, and may prevent spread of the infection to other people.
What Is The Medical Treatment For Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B infection
Acute hepatitis B infection is not treated with antiviral medications.
- If the infected person is dehydrated from vomiting or diarrhea, a doctor may prescribe IV fluids to help them feel better. Medications may also be used to control these symptoms.
- People with mild symptoms can be cared for at home.
Chronic hepatitis B infection
The degree of liver damage is related to the amount of active, replicating virus in the blood and liver. Regularly measuring the amount of HBV DNA in the blood gives your physician a good idea of how fast the virus is multiplying. The treatments now in use are classified as antiviral drugs because they work by stopping the virus from multiplying.
Treatment is usually started when blood tests indicate that liver functions are deteriorating and the amount of replicating HBV is rising. Many people never reach this point. For those who do, the interval between diagnosis and starting treatment is quite variable.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
You May Like: How Do I Get Hepatitis C
Vaccination And Other Prevention Measures
Vaccination is a safe and effective way of preventing the spread of hepatitis B. Since 1985, the hepatitis B vaccine has been part of the national immunisation schedule. In 1988, New Zealand was one of the first countries to introduce universal infant hepatitis B immunisation.The vaccine is given to babies at age six weeks, three months, and five months. Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B receive an extra dose of the vaccine at birth as well as a dose of hepatitis B-specific immune globulin.In children and adolescents who did not receive the hepatitis B vaccine in the first year of life, the full three-dose course is recommended.Hepatitis B immunisation is recommended and publicly funded for all infants and children up to their 18th birthday, household and sexual contacts of people with acute or chronic hepatitis B, and certain other high-risk populations. Measures that can help prevent the spread of the hepatitis B virus include:
- Teaching children not to touch the blood or wounds of others
- Covering cuts, scratches, and grazes
- Not sharing personal items such as razors and toothbrushes
- Never sharing needles or syringes if you use intravenous drugs
- Practising safe sex, including the use of condoms
- Seek assurance that body piercing and tattooing needles and equipment are sterile.
If I Have No Symptoms How Would I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
To confirm whether or not you have hepatitis B, you will need blood tests.
If you have at least one risk factor , you should ask your health care provider to be tested for hepatitis B. Also, you should be tested for hepatitis B if:
- you were born in a region where hepatitis B is more common, including Asia, Africa, southern and eastern Europe, the Pacific Islands, the Middle East, and the Arctic
- one or both of your parents immigrated from a region where hepatitis B is more common
- you live or travel to regions where hepatitis B is more common
- you have a family history of liver disease or liver cancer
- you have been in prison
- you are pregnant
- you have ever used injection drugs, even just once
- you have unexplained abnormal liver enzymes or if
- you receive medicines that suppress the immune system.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hiv And Hepatitis
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Don’t Miss: Signs N Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Treating Hepatitis B With Tenofovir
Violetta Shamilova, PharmD, is a board-licensed pharmacist. She is an assistant professor at the Touro College School of Health Sciences, and has worked at CVS pharmacy for five years. She completed the certified APhA Delivering Medication Therapy Management Services course.
Tenofovir, also called tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is an antiviral drug for treating chronic hepatitis B in adults and children who are 12 years and older. It is also used, in combination with other drugs, to treat the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV. It’s sold under the brand name Viread by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work

If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
You May Like: How Do People Get Hepatitis
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with an infected partner
- injection-drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to an infected mother
- contact with blood from or open sores on an infected person
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with an infected person that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts of water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected people
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health-care and public-safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Hemodialysis patients
Who should be screened for HBV?
CDC recommends that the following people be screened for HBV :
- fever,
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
You May Like: Is Fasting Required For Hepatitis C Test
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Hepatitis B Symptoms & Treatment
FAST FACTS
- Hepatitis B is a virus found in infected blood, semen and vaginal fluids.
- Its a sexually transmitted infection that can be passed on through unprotected sex. You can also get it from contaminated needles and syringes. Its also commonly passed on from a mother to her baby during birth.
- There is a vaccine to prevent hepatitis B, which is routinely offered to infants as well as at-risk groups.
- You can prevent hepatitis B by practising safer sex, never sharing needles and syringes, and avoiding unlicensed tattoo parlours and acupuncturists.
- Most people dont need treatment for acute hepatitis B. If the infection becomes chronic, there is no cure, but it can be managed with treatment.
You May Like: Hepatitis A And B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B
If you’re diagnosed with hepatitis B, your GP will usually refer you to a specialist, such as a hepatologist .
Many people do not have any troublesome symptoms, but if you do feel unwell, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, for tummy pain
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing, and avoid hot baths or showers if itching is a problem
- take medication, such as metoclopramide, to stop you feeling sick, and chlorphenamine to reduce itching your doctor can give you a prescription for these if necessary
Most people recover completely in a couple of months, but you’ll be advised to have regular blood tests to check that you’re free of the virus and have not developed chronic hepatitis B.
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
Also Check: Cure For Hepatitis A And B
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
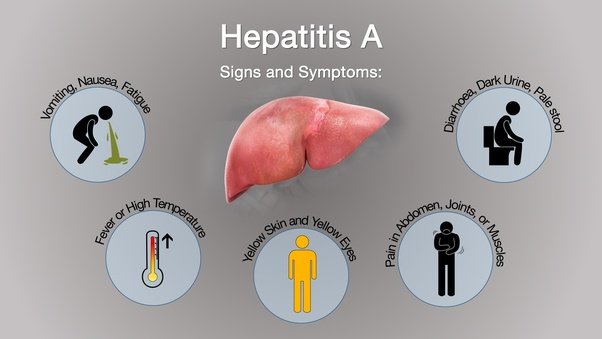
If you develop chronic hepatitis B, youll be given treatment to reduce the risk of permanent liver damage and liver cancer. Treatment does not cure chronic hepatitis B and most people who start treatment need to continue for life.
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis B can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly.
A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer, and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, there is no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Screening 1945 To 1965
What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Doctors refer to hepatitis B infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HBV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HBV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis B infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and causes lifelong illness. An estimated 850,000 to more than 2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HBV.
The younger someone is when infected, the greater the chances for chronic hepatitis B. About 90% of babies with HBV will develop a chronic infection. That risk drops to 6%10% when someone over 5 years old is infected. Because of this, the World Health Organization and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that all babies get the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 1224 hours of birth. They’ll get two more doses later, at 12 months of age and at 618 months of age.
Approved Drugs For Adults
There are currently 7 approved drugs in the United States for adults living with chronic hepatitis B infection. These include 5 types of antiviral drugs that are taken as a pill once a day for 1 year or longer. And there are 2 types of immune modulator drugs called interferon that are given as an injection for 6 months to 1 year.
It is important to know that not everyone needs to be treated. A liver specialist should evaluate your health through a physical exam, blood tests, and an imaging study of your liver . Then you can discuss together whether you are a good candidate for treatment since the approved drugs are most effective when there are signs of active liver disease. In addition, talk to your provider about HBV Clinical Trials since there are several new drugs being tested that are available for infected adults.
All adults, however, should be seen regularly by a liver specialist whether they are on treatment or not.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Hepatitis A